Lung (ICD-9 code 162) Lung cancer includes tumours of the trachea, bronchi and lung. Virtually all lung cancers arise in epithelial tissue, and most originate from the lining of the bronchi.
What is the diagnosis code for lung cancer?
2012 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 162.9 Malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung, unspecified Short description: Mal neo bronch/lung NOS. ICD-9-CM 162.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 162.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is ICD 9 diagnosis?
162.9 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent. ICD-9:
What is the ICD 9 code for chronic lung disease?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 162.3 : Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe, bronchus or lung. Home > 2015 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes > Neoplasms 140-239 > Malignant Neoplasm Of Respiratory And Intrathoracic Organs 160-165 > Malignant neoplasm of trachea bronchus and lung 162-.
What is the survival rate for squamous lung cancer?
Metastatic Lung Cancer ICD 9 Code Billable Medical Code for Malignant Neoplasm of Bronchus and Lung, Unspecified Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 162.9

What is the ICD 10 code for lung cancer?
Malignant neoplasm of unspecified part of right bronchus or lung. C34. 91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the code for metastatic carcinoma to lung?
Basic DifferencesLung NeoplasmTopography CodeBehavior CodeMetastatic neoplasm of the lung (such as metastatic seminoma from the testis)C34.9M-9061/6In situ neoplasm of the lung (such as squamous carcinoma in situ)C34.9M-8070/2Benign neoplasm of lung (such as adenoma)C34.9M-8140/02 more rows
What is the ICD 10 code for right lung cancer?
ICD-10-CM Code for Malignant neoplasm of unspecified part of right bronchus or lung C34. 91.
What is the code for carcinoma?
k. Code C80. 1, Malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified, equates to Cancer, unspecified. This code should only be used when no determination can be made as to the primary site of a malignancy.Dec 3, 2018
What is the ICD 10 code for small cell lung carcinoma?
C34. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C34. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for lung mass?
For example, lung mass and multiple lung nodules are specifically indexed to code R91. 8, Other nonspecific abnormal finding of lung field.Feb 28, 2017
What is diagnosis code r91 8?
Other nonspecific abnormal finding of lung field8: Other nonspecific abnormal finding of lung field.
What is malignant neoplasm of unspecified part of unspecified bronchus or lung?
Bronchogenic carcinoma is a malignant neoplasm of the lung arising from the epithelium of the bronchus or bronchiole.
How do you code non small cell lung cancer?
Non-small cell carcinoma (80463) A general term used sloppily to separate small cell from the "non-small cell" types (such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, large cell, etc.) of carcinomas. Only use 8046/3 when there is no other type of non-small cell carcinoma contained in the source documents.
What is c79 51 ICD-10?
51: Secondary malignant neoplasm of bone.
What is carcinoma in situ?
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells that are found only in the place where they first formed in the body (see left panel). These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread to nearby normal tissue (see right panel).
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
9.
What is the ICd 10 code for bronchus?
162.9 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
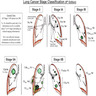
What is the stage of squamous cell carcinoma of lung?
Squamous cell carcinoma of lung, TNM stage 1. Squamous cell carcinoma of lung, TNM stage 2. Squamous cell carcinoma of lung, TNM stage 3. Squamous cell carcinoma of lung, TNM stage 4. T3: Lung tumor of any size in the main bronchus < 2 cm distal to the carina but without involvement of the carina.
How do doctors diagnose lung cancer?
Doctors diagnose lung cancer using a physical exam, imaging, and lab tests. Treatment depends on the type, stage, and how advanced it is. Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. Targeted therapy uses substances that attack cancer cells without harming normal cells.
Known As
Metastatic lung cancer is also known as adenocarcinoma lung stage 1, adenocarcinoma lung stage 2, adenocarcinoma lung stage 3, adenocarcinoma lung stage 4, clear cell carcinoma of lung, giant cell carcinoma of lung, small cell carcinoma of lung, small cell carcinoma lung, squamous cell carcinoma lung stage 3, squamous cell carcinoma lung stage 4, and squamous cell carcinoma right lung..
Metastatic Lung Cancer Definition and Symptoms
Metastatic lung cancer is cancer that begins somewhere else in the body and spreads to the lungs. Symptoms include intense coughing, shortness of breath, changes in the voice, pain in the chest, wheezing, snoring, drop in weight, headache, and bone pain.
What is the ICD-9 code for lung cancer?
This type of lung cancer is more common than small cell. Regardless of the cell type, the ICD-9-CM code for primary malignant neoplasm of the lung is 162.x, with the fourth-digit subcategory identifying the specified site of the cancer such as:
What is lung cancer?
Vol. 23 No. 7 P. 27. Lung cancer is any type of malignant growth in the lungs that occurs when cells in the lung start to grow rapidly and uncontrollably. Smoking puts people at the highest risk of developing lung cancer, though exposure to secondhand smoke is also a major cause.
What is the code for a bronchoscope biopsy?
The biopsy may be performed though a bronchoscope (33.24), percutaneous needle (33.26), thoracoscopic (33.20), or open (33.28). A transthoracic needle biopsy of lung is also classified to code 33.26. Transbronchial lung biopsy (33.27) is when the bronchoscope biopsy forceps actually punctures the terminal bronchus and samples ...
What are the different types of lung cancer?
There are two major types of lung cancer, which is determined by the appearance of the cancerous cells under a microscope: • Small-cell lung cancer: Also called oat cell cancer, it is the more aggressive type and frequently metastasizes to other sites such as the liver, bone, and brain.
Does lung cancer cause hoarseness?
Lung cancer does not typically produce symptoms in the disease’s early stages. When symptoms do appear in the more advanced stages, they may include the following: • coughing (a new cough or a change in a chronic cough); • hemoptysis; • chest pain; • shortness of breath; • wheezing; • hoarseness; • weight loss;
Does lung cancer spread to other organs?
Advanced lung cancer eventually metastasizes to nearby lymph nodes or other tissues in the chest, including the other lung. In many cases, lung cancer spreads to other organs in the body such as the bone (198.5), brain (198.3), liver (197.7), and adrenal glands (198.7). Diagnosis.
Overview
Malignant neoplasm of respiratory and intrathoracic organs (160–165)
• 160 Malignant neoplasm of nasal cavities, middle ear, and accessory sinuses
• 161 Malignant neoplasm of larynx
• 162 Malignant neoplasm of trachea, bronchus, and lung
• 163 Malignant neoplasm of pleura
Malignant neoplasm of lip, oral cavity, and pharynx (140–149)
• 140 Malignant neoplasm of lip
• 141 Malignant neoplasm of tongue
• 142 Malignant neoplasm of major salivary glands
• 143 Malignant neoplasm of gum
Malignant neoplasm of digestive organs and peritoneum (150–159)
• 150 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus
• 151 Malignant neoplasm of stomach
• 152 Malignant neoplasm of small intestine, including duodenum
• 153 Malignant neoplasm colon
Malignant neoplasm of bone, connective tissue, skin, and breast (170–175)
• 170 Malignant neoplasm of bone and articular cartilage
• 171 Malignant neoplasm of connective and other soft tissue
• 172 Malignant melanoma of skin
• 173 Other malignant neoplasm of skin
Kaposi's sarcoma (176–176)
• 176 Kaposi's sarcoma
• 176 Kaposi's sarcoma
Malignant neoplasm of genitourinary organs (179–189)
• 179 Malignant neoplasm of uterus, part unspecified
• 180 Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri
• 181 Malignant neoplasm of placenta
• 182 Malignant neoplasm of body of uterus
• 179 Malignant neoplasm of uterus, part unspecified
• 180 Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri
• 181 Malignant neoplasm of placenta
• 182 Malignant neoplasm of body of uterus
Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified sites (190–199)
• 190 Malignant neoplasm of eye
• 191 Malignant neoplasm of brain
• 192 Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified parts of nervous system
• 193 Malignant neoplasm of thyroid gland
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for breathing related sleep disorder
- 2. icd 10 cm code for ref to naturepath
- 3. icd 10 code for presence of artificial left hip
- 4. icd 10 code for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
- 5. icd 10 code for a44.9
- 6. icd 10 code for chronic otitis media bilateral
- 7. icd 10 code for plummer-vinson syndrome
- 8. icd 10 code for worries
- 9. icd 9 code for edema anterior pararenal
- 10. icd 10 code for mole removal