What is the ICD 9 code for venous thrombosis?
Short description: VENOUS THROMBOSIS NOS. ICD-9-CM 453.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 453.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
How do you find the ICD-9 index of thrombosis?
So, basically, start in your ICD-9 index under Thrombosis, and then look at the indents under brain or under heart, depending on the specifics of your case. it's heart...i used 429.89?
What is the ICD 10 code for thrombosis of the atrium?
Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I23.6 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Thrombosis of atrium, auricular appendage, and ventricle as current complications following acute myocardial infarction. Thombos of atrium/auric append/ventr as current comp fol AMI; Left ventricular mural thrombus post acute heart attack; Mural thrombus of heart, ...
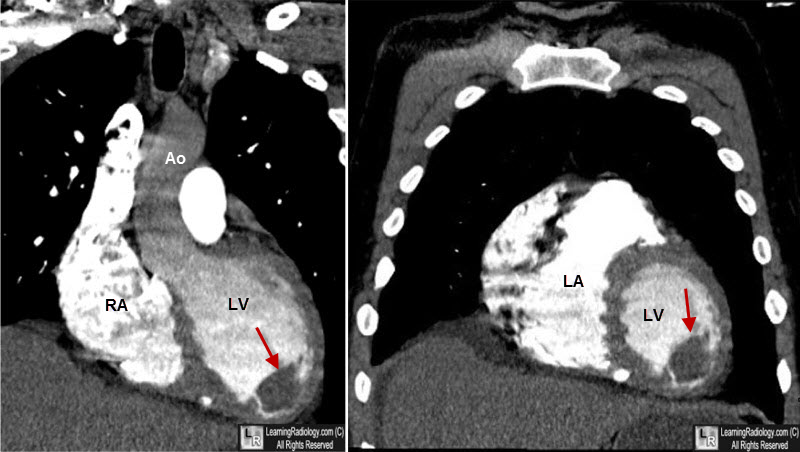
What is the ICD-10 code for LV thrombus?
I51. 3 - Intracardiac thrombosis, not elsewhere classified | ICD-10-CM.
What is left ventricular mural thrombus?
Left ventricular mural thrombus Is a well-known complication of acute anterior MI and frequently develops after left anterior wall infarction.
What is the ICD-10 code for apical thrombus?
Thrombosis of atrium, auricular appendage, and ventricle as current complications following acute myocardial infarction. I23. 6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I23.
How is LV thrombus treated?
Results: The authors identified 159 patients with confirmed LV thrombus. These patients were treated with vitamin K antagonists (48.4%), parenteral heparin (27.7%), or direct oral anticoagulants (22.6%). Antiplatelet therapy was used in 67.9% of cases.
What is LV apical thrombus?
Left ventricular thrombus is a blood clot (thrombus) in the left ventricle of the heart. LVT is a common complication of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Typically the clot is a mural thrombus, meaning it is on the wall of the ventricle.
What is right ventricular thrombus?
RHT typically represent mobilised deep vein thromboses that have become lodged temporarily in the right atrium or RV [8, 9]. Though the increased use of two-dimensional echocardiography for risk stratification of PE patients has led to increased detection of RHT, the incidence of RHT remains unknown.
How common is left atrial appendage?
The left atrial appendage (LAA) is a finger-like extension originating from the main body of the left atrium. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common clinically important cardiac arrhythmia, occurring in approximately 0.4% to 1% of the general population and increasing with age to >8% in those >80 years of age.
What is heart thrombosis?
What is thrombosis? Thrombosis is a serious condition where a clot forms inside a blood vessel (an artery or vein) in your body or sometimes inside of your heart. This is dangerous because clots that form inside blood vessels can block blood flow.
What is aortic mural thrombus?
Mural thrombi are thrombi that attach to the wall of a blood vessel and cardiac chamber. Mural thrombus occurrence in a normal or minimally atherosclerotic vessel is a rare entity in the absence of a hypercoagulative state or inflammatory, infectious, or familial aortic ailments.
How is LV thrombus diagnosed?
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is the gold standard technique for detecting thrombus of the left atrium or left atrial appendage although TTE is also widely used for excluding LV thrombus in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
How common is LV thrombus?
The incidence of LV thrombus was 12.3% (26/210) by CMR and 6.2% (13/210) by two-dimensional echocardiography. Echocardiography had 50% sensitivity and 100% specificity for LV thrombus detection compared to CMR. LV thrombus was found in 23.6% of patients with anterior STEMI (22/93).
What is the difference between blood clot and thrombosis?
Thrombosis occurs when a thrombus, or blood clot, develops in a blood vessel and reduces the flow of blood through the vessel. Embolism occurs when a piece of a blood clot, foreign object, or other bodily substance becomes stuck in a blood vessel and largely obstructs the flow of blood.
What is a left ventricular thrombus?
Left ventricular thrombus is a blood clot ( thrombus) in the left ventricle of the heart. LVT is a common complication of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Typically the clot is a mural thrombus, meaning it is on the wall of the ventricle. The primary risk of LVT is the occurrence of cardiac embolism, in which the thrombus detaches from ...
What is the primary risk of LVT?
The primary risk of LVT is the occurrence of cardiac embolism, in which the thrombus detaches from the ventricular wall and travels through the circulation and blocks blood vessels. Blockage can be especially damaging in the heart or brain ( stroke ).
What is the best treatment for LVT after AMI?
Anticoagulants are also shown to reduce the risk of embolisms when a thrombus is already formed. Heparin, an injectable, fast-acting anticoagulant, is effective in high doses for preventing LVT formation after AMI.
What is the best diagnostic tool for LVT?
Echocardiography is the main diagnostic tool for LVT. A distinct mass is visible in the left ventricle. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging are effective, but less common ways to detect LVT, due to their costs and risks.
When does LVT occur?
LVT occurs most often during the first 2 weeks following AMI. AMI patients most at risk display the 3 characteristics of Virchow's triad:
Can a thrombus become an embolus?
It is possible to assess whether a thrombus will become an embolus through echocardiography. Mobility and protrusion of the thrombus are two characteristics associated with increased embolic potential. Play media. Thrombus of the left ventricle resulting in embolism of the spleen. Play media.
Is LVT good for heart?
For several days after AMI, the levels of tissue factor and D-dimer, which are involved in coagulation, are high, which increases the risk of LVT formation. LVT may be good for the heart when tissues are severely damaged because it acts to thicken the wall, thu s protecting it against rupture.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for paranoia
- 2. icd 10 code for af on anticoagulation therapy
- 3. icd-10 code for below knee amputation unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for secondary malignant neoplasm of upper limb
- 5. what is the icd 9 code for open wound of ear drum uncomplicated
- 6. icd 10 code for recurrent depression
- 7. icd-10 code for low white blood count
- 8. icd 10 code for cellulitis gums
- 9. icd 10 diagnosis code for nstemi
- 10. icd-9-cm code for hepatocellular adenoma