Malignant neoplasm of colon, unspecified site Short description: Malignant neo colon NOS. ICD-9-CM 153.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 153.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for metastatic colon cancer?
Dec 08, 2013 · Need more info: The code for colon cancers is 153._. 153.9 is for colon cancer of unspecified site. There is a separate group of codes for metastasis and the site. The number after 153 is for the site of the primary tumor.
What is the ICD 10 code for screening colonoscopy?
Colorectal Cancer Screening ICD-9-CM diagnosis code for an average risk patient presenting for colonoscopy is: V76.51 Special Screening for Malignant Neoplasm, Colon Code V76.51 should be the first listed diagnosis code if the reason for the visit is specifically for the screening exam.
What is the life expectancy of someone with colon cancer?
Malignant neoplasm of colon, unspecified site 2015 Billable Thru Sept 30/2015 Non-Billable On/After Oct 1/2015 ICD-9-CM 153.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 153.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
When to code metastatic cancer?
Billable Medical Code for Malignant Neoplasm of Colon, Unspecified Site Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 153.9. Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 153.9. The Short Description Is: Malignant neo colon NOS. Known As
What is the ICD 10 code for metastatic colon cancer?
The following 2021 ICD-10 codes are effective from October 1, 2021 through September 30, 2022....Diagnosis codes for LONSURF use in metastatic colorectal cancer. 1.ICD-10-CMDescriptionC78.5Secondary malignant neoplasm of large intestine and rectum15 more rows
What is metastatic colon cancer?
Metastasis means that the cancer cells have spread beyond the colon to other organs. This is also referred to as advanced colon cancer or stage IV colon cancer. Your treatment options will depend on several factors, including the extent of the cancer and what other organs it has spread to.
What is the CPT code for metastatic cancer?
If the site of the primary cancer is not documented, the coder will assign a code for the metastasis first, followed by C80. 1 malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified. For example, if the patient was being treated for metastatic bone cancer, but the primary malignancy site is not documented, assign C79. 51, C80.Oct 5, 2017
What is the ICD 10 code for colon cancer?
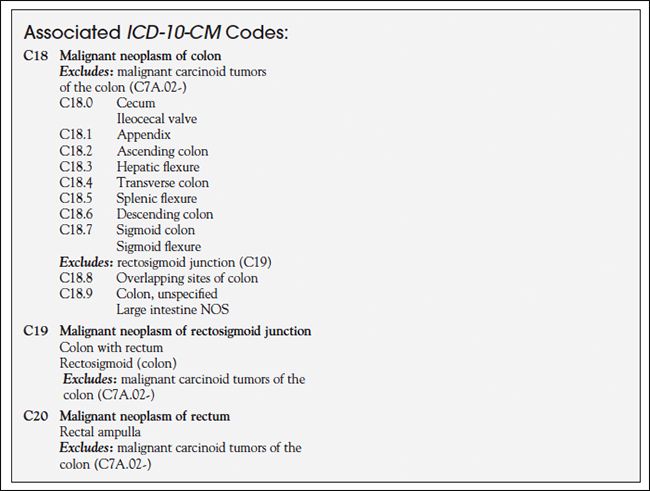
C18. 9 - Malignant neoplasm of colon, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
Where does colorectal cancer metastasize?
The most common site of metastases for colorectal cancer, which includes colon cancer or rectal cancer is the liver. Colorectal cancer cells may also spread to the lungs, bones, brain or spinal cord.
Where does colorectal cancer usually metastasize to?
Colorectal cancer usually spreads to the liver. It can also spread to the lungs, the lining of the abdomen, the ovaries, the brain, and other organs. Recent advances in treatment have improved the outlook for people with metastatic rectal cancer, including stage IV cancer.
What is the ICD-10 code for metastatic unknown primary?
ICD-10-CM Code for Malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified C80. 1.
Is metastatic cancer primary or secondary?
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the primary cancer. For example, breast cancer that spreads to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated as stage IV breast cancer, not as lung cancer.Nov 10, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code for C79 9?
9 Secondary malignant neoplasm, unspecified site.
What is diagnosis code C18 9?
Table 5DiagnosisICD-9 codeICD-10 codeColon unspecified153.9C18.9Malignant neoplasm of appendix vermiformis153.5N/AMalignant neoplasm of appendixN/AC18.1Malignant neoplasm of other specified sites of large intestine153.8N/A19 more rows•Aug 19, 2019
What does malignant neoplasm of colon unspecified mean?
The term "malignant neoplasm" means that a tumor is cancerous. A doctor may suspect this diagnosis based on observation — such as during a colonoscopy — but usually a biopsy of the lesion or mass is needed to tell for sure whether it is malignant or benign (not cancerous).Sep 21, 2017
What diagnosis code is reported for secondary neoplasm of the descending colon?
ICD-10-CM Code for Secondary malignant neoplasm of large intestine and rectum C78. 5.
Colorectal Cancer Screening ICD 9 for Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a widely used endoscopic technique used to screen individuals for colorectal cancer. It is very sensitive in detecting colorectal cancers. Colonoscopy is an endoscopic procedure in which a thin tube with a camera at the tip is introduced through the anus till the start of the colon.
Colonoscopy CPT Codes for Colon Cancer Screening
After the patient's bowel has been prepped, the physician inserts the colonoscope-a long, thin, flexible lighted tube-through the anus and advances the scope through the colon past the splenic flexure. The lumen of the colon and rectum is visualized. Most polyps and some cancers can be removed during this procedure.
What is a malignant tumor of the colon?
Primary adenocarcinoma of colon. Clinical Information. A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm involving the colon. A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm that affects the colon. Representative examples include carcinoma, lymphoma, and sarcoma. Malignant tumor of the colon or rectum.
What is the stage of colon cancer?
Cancer of the colon, stage 1. Cancer of the colon, stage 2. Cancer of the colon, stage 3. Cancer of the colon, stage 4. Carcinoma of colon, stage I. Carcinoma of colon, stage II. Carcinoma of colon, stage III. Carcinoma of colon, stage IV. Colon cancer.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
ICD-9-CM 153.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 153.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
Known As
Colon cancer is also known as adenocarcinoma colon, CA colon adenoca, CA of colon, cancer of the colon, cancer of the colon adenocarcinoma, cancer of the colon hereditary nonpolyposis, cancer of the colon stage 1, cancer of the colon stage 2, cancer of the colon stage 3, cancer of the colon stage 4, carcinoma of colon stage I, carcinoma of colon stage II, carcinoma of colon stage III, carcinoma of colon stage IV, colon cancer, colon cancer hereditary nonpolyposis, colon cancer stage 1, colon cancer stage 2, colon cancer stage 3, colon cancer stage 4, hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer, malignant tumor of colon, and primary adenocarcinoma of colon.
Colon Cancer Definition and Symptoms
Colon cancer refers to cancer of the large intestine, which is the lower part of the digestive system. Symptoms can include but are not limited to a change in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, persistent abdominal discomfort, cramps, weakness, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
What is the code for colon cancer?
Carcinoma of the colon is assigned to code 230.3 while carcinoma of the rectum goes to 230.4. Patients may not experience any symptoms of early-stage cancer. When signs and symptoms do appear, they may vary depending on the location of the cancer and may include changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation, ...
What are the different types of colon cancer?
Over time, the polyps become cancerous. Different types of colon polyps include adenomas; hyperplastic polyps; inflammatory polyps; familial adenomatous polyposis, a rare hereditary disorder that causes hundreds of polyps in the lining of the colon beginning in ...
What test is used to diagnose colon cancer?
To diagnose colon cancer, a physician may perform a digital rectal exam, fecal occult blood test, flexible sigmoidoscopy, barium enema, colonoscopy (45.23)—the physician may take a biopsy (45.25) or polypectomy (45.42) through the colonoscope, or virtual colonoscopy (88.01), which is a CT scan of the colon.
What is the code for anastomosis?
If the anastomosis is anything other than end to end—such as side to side, then assign an additional procedure code for the anastomosis (45.92 to 45.94) . If the surgeon can’t perform the anastomosis, then a permanent or temporary colostomy will be done.
Where does colon cancer occur?
Colon cancer occurs in the large intestine or colon, which is the lower part of the digestive system. Rectal cancer occurs in the last several inches of the colon. Collectively, they may be referred to as colorectal cancer. The majority of colon cancer cases may begin as small, benign adenomatous polyps. Over time, the polyps become cancerous.
Can radiation therapy be used for colon cancer?
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used in combination with the surgical removal of the colon cancer. Coding and sequencing for colon and rectal cancer are dependent on the physician documentation in the medical record and application of the Official Coding Guidelines for inpatient care.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified ( C25.9 ). A malignant tumor involving the rectum and sigmoid colon. The majority are carcinomas.
What are the two synonyms for malignant neoplasms?
Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs. Approximate Synonyms. Cancer of the rectosigmoid junction. Cancer of the rectosigmoid, adenocarcinoma. Carcinoma of the rectosigmoid junction. Colorectal cancer. Colorectal cancer, metastatic to brain. Colorectal malignant neoplasm metastatic to brain. Overlapping malignant neoplasm of colon and rectum.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as C19. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
What is the synonym for cancer of the colon?
Malignant neoplasm of colon. Approximate Synonyms. Cancer of the colon. Cancer of the colon, adenocarcinoma. Cancer of the colon, hereditary nonpolyposis. Cancer of the colon, stage 1. Cancer of the colon, stage 2. Cancer of the colon, stage 3. Cancer of the colon, stage 4.
What is malignant tumor?
Malignant tumor of colon. Metastasis from malignant tumor of colon. Primary adenocarcinoma of colon. Clinical Information. A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm involving the colon. A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm that affects the colon or rectum.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
Can multiple neoplasms be coded?
For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for r30.0
- 2. icd 10 code for i87.2
- 3. icd 10 cm code for chronic migraine with aura
- 4. icd 10 code for fistula in ano
- 5. icd 10 code for left chest wall ceroma
- 6. icd-10 code for acute cystitis with hematuria
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for lip lift
- 8. icd 10 code for injury due to pulling heavy objecy
- 9. icd 10 code for outisde on patio
- 10. icd 10 code for vulvovaginitis candidiasis\