What is the ICD 9 code for hyperglyceridemia?
Pure hyperglyceridemia ICD-9-CM 272.1 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 272.1 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What is the ICD 10 Index for hypertriglyceridemia?
Hypertriglyceridemia ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index. The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index is designed to allow medical coders to look up various medical terms and connect them with the appropriate ICD codes. There are 0 terms under the parent term 'Hypertriglyceridemia' in the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index .
What is the ICD-9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 272.1 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 272.1 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for pure hypercholesterolemia?
Hyperlipidemia ICD 10 Code Description; E78.0: Pure hypercholesterolemia group A · E78.00: Pure hypercholesterolemia Fredrickson's hyperlipoproteinemia, type Iia Hyperbetalipoproteinemia (Pure) hypercholesterolemia NOS · E78.01: Familial hypercholesterolemia: E78.1: Hyperlipidemia, group B Pure hyperglyceredemia
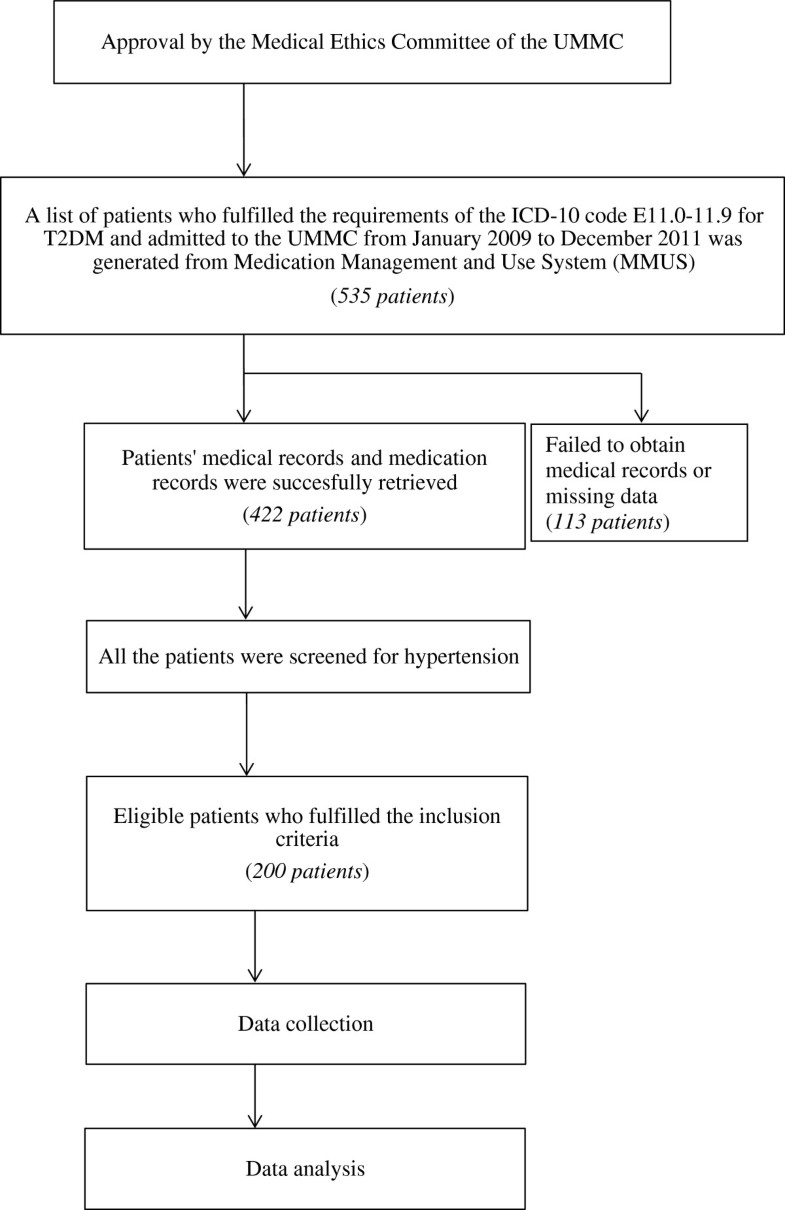
How do you code hypertriglyceridemia?
ICD-10 Code for Pure hyperglyceridemia- E78. 1- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypertriglyceridemia?
E78. 1 - Pure hyperglyceridemia. ICD-10-CM.
What ICD-10 code covers hyperlipidemia?
E78.5ICD-Code E78. 5 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Hyperlipidemia, Unspecified. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 272.4.
What does diagnosis E78 2 mean?
ICD-10 code E78. 2 for Mixed hyperlipidemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is mild hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia means your blood has too many lipids (or fats), such as cholesterol and triglycerides. One type of hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, means you have too much non-HDL cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol in your blood. This condition increases fatty deposits in arteries and the risk of blockages.
What is the meaning of hypertriglyceridemia?
Hypertriglyceridemia refers to a fasting plasma triglyceride measurement that is increased, typically above the 95th percentile for age and sex — although additional quantitative or qualitative lipoprotein abnormalities can also be present.
Is hyperlipidemia the same as high cholesterol?
Is hyperlipidemia the same as high cholesterol? Yes, hyperlipidemia is another name for high cholesterol, and so is hypercholesterolemia.
What is DX code e11 9?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus Without complications9: Type 2 diabetes mellitus Without complications.
Is hyperlipidemia the same as dyslipidemia?
You may hear the term hyperlipidemia used interchangeably with dyslipidemia. But that's not entirely accurate. Hyperlipidemia refers to high levels of LDL or triglycerides. Dyslipidemia can refer to levels that are either higher or lower than the normal range for those blood fats.
Can you code E78 00 and E78 5 together?
Expert. You wouldn't code them together. Cholesterol is a type of lipid. If the provider diagnosed pure hypercholesterolemia, you would code that.
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
Can E78 2 and E29 1 be billed together?
For example, E78. 2 Mixed hyperlipidemia cannot be coded with 5-alpha-reductase deficiency (E29. 1 Testicular hypofunction), but the note for this is not at E78.
What are the symptoms of Mixed hyperlipidemia?
Symptoms of Mixed HyperlipidemiaChest pain.Cramping of one or both calves when walking.Sores on the toes that do not heal.Sudden stroke-like symptoms, such as trouble speaking, drooping on one side of the face, weakness of an arm or leg, and loss of balance.
What does anemia D64 9 mean?
Code D64. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Anemia, Unspecified, it falls under the category of diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. Anemia specifically, is a condition in which the number of red blood cells is below normal.
What is hypercholesterolemia cholesterol levels?
Hypercholesterolemia is defined as serum total cholesterol of 200 mg/dl or more, according to the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) III guidelines.
What does obesity unspecified mean?
Having a high amount of body fat (body mass index [bmi] of 30 or more). Having a high amount of body fat. A person is considered obese if they have a body mass index (bmi) of 30 or more.
Not Valid for Submission
272.1 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of pure hyperglyceridemia. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Convert 272.1 to ICD-10
The following crosswalk between ICD-9 to ICD-10 is based based on the General Equivalence Mappings (GEMS) information:
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 272.1 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in your blood. Too much of this type of fat may raise the risk of coronary artery disease, especially in women.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What does hypertriglyceridemia mean?
Etymology. The word hypertriglyceridemia uses combining forms of hyper- + triglyceride + -emia, thus corresponding to "high triglyceride levels in the blood" or "too many triglycerides in the blood".
How to treat hypertriglyceridemia?
Treatment. Lifestyle changes including weight loss, exercise and dietary modification may improve hypertriglyceridemia. This may include restriction of carbohydrates (specifically fructose) and fat in the diet and the consumption of omega-3 fatty acids from algae, nuts, and seeds.
What is the best medication for high triglycerides?
Medications are recommended in those with high levels of triglycerides that are not corrected with lifestyle modifications, with fibrates being recommended first. Epanova (omega-3-carboxylic acids) is another prescription drug used to treat very high levels of blood triglycerides.
What are the symptoms of elevated triglycerides?
Some forms of primary hypertriglyceridemia can lead to specific symptoms: both familial chylomicronemia and primary mixed hyperlipidemia include skin symptoms (erup tive xanthom a ), eye abnormalities (lip emia retin alis), hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the liver and spleen ), and neurological symptoms. Some experience attacks of abdominal pain that may be mild episodes of pancreatitis. Eruptive xanthomas are 2–5 mm papules, often with a red ring around them, that occur in clusters on the skin of the trunk, buttocks and extremities. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia causes larger, tuberous xanthomas; these are red or orange and occur on the elbows and knees. Palmar crease xanthomas may also occur.
What are the components of metabolic syndrome?
Obesity. Diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance - it is one of the defined components of metabolic syndrome (along with central obesity, hypertension, and hyperglycemia) Excess alcohol consumption. Kidney failure, nephrotic syndrome.
Is hypertriglyceridemia a hereditary condition?
There is a hereditary predisposition to both primary and secondary hypertriglyceridemia. Acute pancreatitis may occur in people whose triglyceride levels are above 1000 mg/dL (11.3 mmol/L). Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with 1–4% of all cases of pancreatitis.
Is hypertriglyceridemia a secondary cause of pancreatitis?
Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with 1–4% of all cases of pancreatitis. The symptoms are similar to pancreatitis secondary to other causes, although the presence of xanthomas or risk factors for hypertriglyceridemia may offer clues.
Triglycerides
Have you ever thought what our body does with extra calories it gets from food.These are converted to triglycerides and stored in fat cells. When needed, mostly in between meals, it is utilized as energy. So, it is very clear when the amount of extra calorie increases in turn the level of triglycerides also increases.
Cholesterol
Body cells require cholesterol for its growth. A part of this is made by liver and another part comes from foods we eat. Altogether when body gets extra cholesterol, it gets stored in blood vessels.
Hyperlipidemia ICD 10 Codes guidelines
It is located in ICD-10 CM manual chapter 4, Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases (E00-E89)

Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for adjacent skin graft
- 2. icd 10 cm code for late onset alzheimer's disease with dementia
- 3. icd 10 code for shoulder grooving
- 4. icd 10 code for vulvectomy
- 5. icd 10 code for inferior mi
- 6. icd 10 code for reaction to bee sting
- 7. icd 10 code for c8r
- 8. icd 10 code for indisclosed pain in right hip
- 9. icd 10 cm code for occipital neuralgia
- 10. icd 10 code for cavitary lung lesion