How do you code peripheral neuropathy?
To help you manage peripheral neuropathy:
- Take care of your feet, especially if you have diabetes. Check daily for blisters, cuts or calluses. ...
- Exercise. Regular exercise, such as walking three times a week, can reduce neuropathy pain, improve muscle strength and help control blood sugar levels. ...
- Quit smoking. ...
- Eat healthy meals. ...
- Avoid excessive alcohol. ...
- Monitor your blood glucose levels. ...
Is peripheral neuropathy a serious condition?
There are two situations in which peripheral neuropathy is the most serious. The first is if you are unable to feel in your hands and feet. This means that you can unknowingly sustain cuts, burns, and other damage, which, if infected, can be dangerous.
What is the diagnosis code for neuropathy?
Polyneuropathy, unspecified
- G62.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G62.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 G62.9 may differ.
What does peripheral neuropathy look like?
What Does Neuropathy Look Like If you have lost feeling in your extremities, you may be suffering from peripheral neuropathy. Numbness. Prickling. Tingling. Burning. Debilitating pain in the feet, toes, and lower legs. Or in the hands, fingers and lower arms. Perhaps even in both locations.
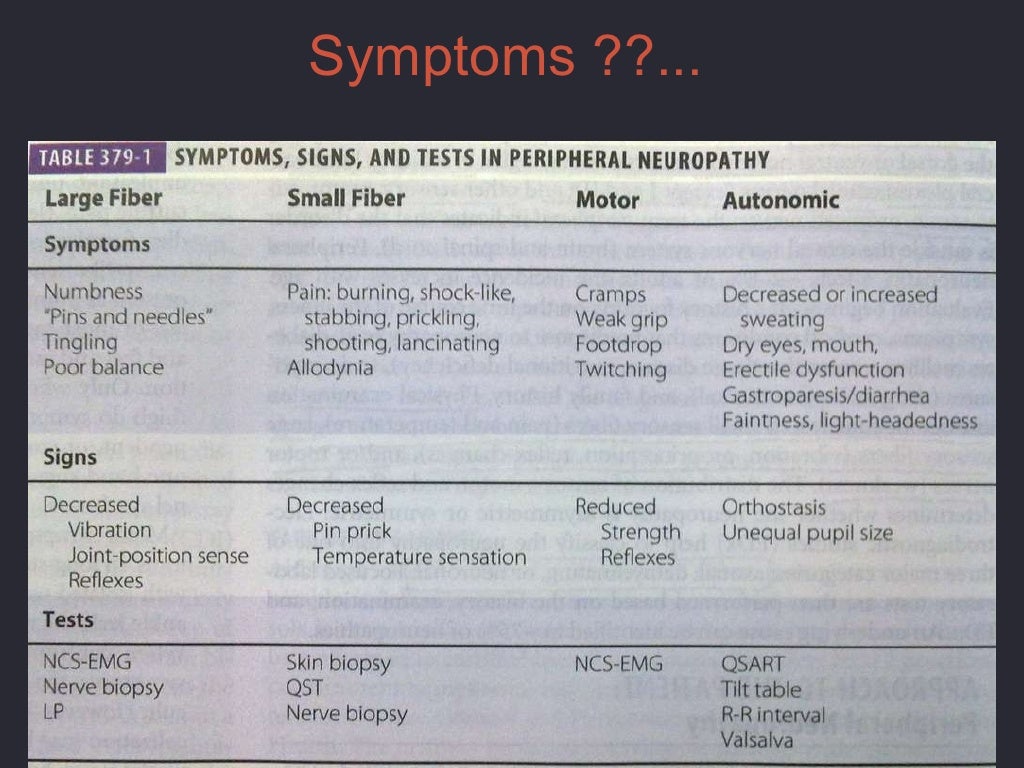
Is peripheral neuropathy motor or sensory?
Peripheral Neuropathy Types To help doctors classify them, they are often broken down into the following categories: Motor neuropathy. This is damage to the nerves that control muscles and movement in the body, such as moving your hands and arms or talking. Sensory neuropathy.
What is peripheral motor neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy, a result of damage to the nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord (peripheral nerves), often causes weakness, numbness and pain, usually in the hands and feet. It can also affect other areas and body functions including digestion, urination and circulation.
What is the ICD 9 code for peripheral neuropathy?
356.9ICD-9-CM Coding Peripheral neuropathy that is not further specified as being caused by an underlying condition is assigned to code 356.9.
Does peripheral neuropathy affect motor nerves?
Neuropathy can affect nerves that control muscle movement (motor nerves) and those that detect sensations such as coldness or pain (sensory nerves). In some cases, it can affect internal organs, such as the heart, blood vessels, bladder, or intestines.
What is the difference between peripheral neuropathy and neuropathy?
Neuropathies frequently start in your hands and feet, but other parts of your body can be affected too. Neuropathy, often called peripheral neuropathy, indicates a problem within the peripheral nervous system. Your peripheral nervous system is the network of nerves outside your brain and spinal cord.
What causes motor neuropathy?
The exact, underlying cause of multifocal motor neuropathy is not fully understood. The disorder is believed to be caused by or related to an abnormal response of the immune system. The immune system is the body's natural defense system against foreign or invading organisms or substances.
What is ICD 10 code for peripheral neuropathy unspecified?
Other idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy G90. 09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G90. 09 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for neuropathy pain?
2.
What is the ICD 10 code for neuromuscular?
Myoneural disorder, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G70. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the four types of neuropathy?
There are four types of diabetic neuropathy:Peripheral neuropathy (also called diabetic nerve pain and distal polyneuropathy)Proximal neuropathy (also called diabetic amyotrophy)Autonomic neuropathy.Focal neuropathy (also called mononeuropathy)
What is sensory motor axonal neuropathy?
Abstract. Acute motor and sensory axonal neuropathy (AMSAN) is a recently described subtype of Guillain-Barré syndrome characterized by acute onset of distal weakness, loss of deep tendon reflexes and sensory symptoms.
What is secondary peripheral neuropathy?
Neuropathy is injury to the peripheral nerves. These are nerves that are not in the brain or spinal cord. Neuropathy secondary to drugs is a loss of sensation or movement in a part of the body due to nerve damage from taking a certain medicine or combination of medicines.
What is graphesthesia in medical terms?
Graphesthesia is the ability of the patient to identify numbers or letters drawn in the palm of the hand.
What is the difference between involvement of one side and involvement of the other side?
Involvement of both sides of the body is consistent with a polyneuropathy or spinal cord disease, while involvement of one side is consistent with contralateral disease of the brainstem, thalamus, or cerebral cortex.
What are the primary sensory modalities?
The primary sensory modalities usually are examined first. These include touch, proprioception, vibration, temperature, and pain. Abnormalities in these sensations may occur with any sensory syndrome (eg, peripheral nerve injury, radiculopathy, spinal cord syndromes, thalamic and cerebral hemispheric syndromes). A disproportionate loss of vibration sense and proprioception, compared with pain and temperature sensation, tends to occur with diseases of the dorsal columns of the spinal cord (eg, tabes dorsalis, vitamin B12 deficiency, multiple sclerosis) and also with demyelinating neuropathies and sensory neuronopathies. (See "Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and treatment of late syphilis" and "Etiology and clinical manifestations of vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency".)
What does sensory loss mean?
Sensory loss that is confined to a part of a limb suggests injury to a peripheral nerve, nerve plexus, or spinal root (eg, mononeuropathy or radiculopathy). In contrast, sensory loss involving most of an extremity or the trunk suggests the presence of other disorders, that may be distinguished as follows (figure 3):
What is sensory examination?
SENSORY EXAMINATION — The goal of the sensory examination is to "localize the lesion." This portion of the examination tends to be subjective because it relies on the patient's responses to various stimuli; thus, it is usually done following the motor examination. With the more objective data obtained from the motor examination, the examiner is often able to narrow down a differential and proceed with a more focused sensory examination, resulting in less frustration for both the patient and examiner. (See "The detailed neurologic examination in adults", section on 'Sensory examination'.)
What is the diminished ability to perceive pain, temperature, touch, or vibration?
Hypesthesia is the diminished ability to perceive pain, temperature, touch, or vibration.
What nerves are involved in touch?
These fibers terminate in the dorsal horns, fanning out over several segments [2]. They synapse with the second order neurons in the dorsal horns. These neurons then cross the midline of the cord in the anterior commissure in front of the central canal, and these second order neurons ascend (now on the opposite side of the spinal cord to the peripheral nerve ) in either the anterior spinothalamic tract (touch) or the lateral spinothalamic tract (pain and temperature) to the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. Here, they synapse with neurons which ascend to the primary sensory cortex in the parietal lobe (figure 1).
Stories of Peripheral Neuropathy
My daughter Imi (rhymes with Jimmy) has a genetic disorder called Ectodermal Dysplasia. It affects the skin, teeth and nails. For her it has resulted in neuroapthy. She has burning in her feet and at her last visit with the neurologist she showed a l...
Peripheral Neuropathy forum
i take Lyrica but the pain persist. It hurts to excercise and massag only helps in as so long as it being done. Stop and the pain starts. Is th re anything else I can do
What is a disease of multiple peripheral nerves?
Diseases of multiple peripheral nerves simultaneously. Polyneuropathies usually are characterized by symmetrical, bilateral distal motor and sensory impairment with a graded increase in severity distally. The pathological processes affecting peripheral nerves include degeneration of the axon, myelin or both. The various forms of polyneuropathy are categorized by the type of nerve affected (e.g., sensory, motor, or autonomic), by the distribution of nerve injury (e.g., distal vs. Proximal), by nerve component primarily affected (e.g., demyelinating vs. Axonal), by etiology, or by pattern of inheritance.
What is a cranial nerve disorder?
Clinical Information. A disorder affecting the cranial nerves or the peripheral nervous system. It is manifested with pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness. It may be the result of physical injury, toxic substances, viral diseases, diabetes, renal failure, cancer, and drugs.
When will the ICD-10 G62.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for abd pain
- 2. icd 10 code for bilateral foot swelling
- 3. icd 10 code for abnormal weight gain
- 4. icd 10 code for complication of a heart vad
- 5. icd 10 code for prominent central pulmonary vasculature
- 6. icd 9 code for severe mvp
- 7. icd 10 code for nodular liver contour
- 8. icd 9 cm code for l4 compression fracture
- 9. 2017 icd 10 code for metastatic prostate cancer
- 10. icd 10 code for extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy bladder stone