What is the ICD 9 code for unspecified disorders of nervous system?
Unspecified disorders of nervous system Short description: Cns disorder NOS. ICD-9-CM 349.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however,... You are viewing the 2012 version of ICD-9-CM 349.9. More recent version (s) of ICD-9-CM 349.9: 2013 ...
What is the ICD 9 code for mental health?
MENTAL, BEHAVIORAL AND NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS ICD-9 Code range (290-319) The ICD-9 code range for MENTAL, BEHAVIORAL AND NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS …
What is unspecified neurodevelopmental disorder?
This is a shortened version of the fifth chapter of the ICD-9: Mental Disorders. It covers ICD codes 290 to 319. The full chapter can be found on pages 177 to 213 of Volume 1, which contains all …
What versions of the DSM are in the ICD-9?
Oct 01, 2014 · Use additional code to identify any associated neurological disorder . Excludes: infantile autism (299.0) schizophrenic syndrome of childhood (299.9) 8 2015 ICD-9 Diagnosis …

What is the ICD-10 code for neurological disorders?
G96. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G96. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are 3 neurological diseases?
- Headaches. Headaches are one of the most common neurological disorders and can affect anyone at any age. ...
- Epilepsy and Seizures. ...
- Stroke. ...
- ALS: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. ...
- Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia. ...
- Parkinson's Disease.
What is the ICD-9 code for peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy that is not further specified as being caused by an underlying condition is assigned to code 356.9.Dec 17, 2012
What is the disorder for the code V60 89?
| V60.0 (Z59.0) | Homelessness |
|---|---|
| V60.1 (Z59.1) | Inadequate Housing |
| V60.89 (Z59.2) | Discord With Neighbor, Lodger, or Landlord |
| V60.6 (Z59.3) | Problem Related to Living in a Residential Institution |
| V60.2 (Z59.4) | Lack of Adequate Food or Safe Drinking Water |
What are the neurological disorders?
What are the top 5 neurological disorders?
- Stroke. ...
- Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia. ...
- Migraines. ...
- Spinal Cord Disorders. ...
- Epilepsy. ...
- Your Neurological Experts in Lone Tree, Colorado Springs, and Aurora.
What is neuralgia and neuritis?
What is the difference between neuropathy and polyneuropathy?
What is ICD-10 code for diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E10. 42 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E10. 42 - other international versions of ICD-10 E10.
What is diagnosis code Z03 89?
What is V code diagnosis?
What are Z codes used for?
What is the ICD-9 code for a hospital?
is based on the World Health Organization’s Ninth Revision, International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9). ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. The ICD-9 is used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates.
What is the V code?
The V codes are provided to deal with occasions when circumstances other than a disease or injury classifiable to categories 001-999 (the main part of ICD), or to the E codes (supplementary classification of external causes of injury and poisoning), are recorded as “diagnoses” or “problems.” This can arise mainly in three ways:
What is 779.3?
779.3 Disorder of stomach function and feeding problems in newborn 779.31 Feeding problems in newborn Slow feeding in newborn Excludes: feeding problem in child over 28 days old (783.3) 779.34 Failure to thrive in newborn Excludes: failure to thrive in child over 28 days old (783.41)
Common ICD-10 Codes for Neurology
Below is a list of common ICD-10 codes for Neurology. This list of codes offers a great way to become more familiar with your most-used codes, but it's not meant to be comprehensive. If you'd like to build and manage your own custom lists, check out the Code Search!
Play training games with Neurology codes!
You can play training games using common ICD-9/10 codes for Neurology! When you do, you can compete against other players for the high score for each game. As you progress, you'll unlock more difficult levels! Play games like...
What is an unspecified neurodevelopmental disorder?
Unspecified Neurodevelopmental Disorder (UNDD) is a DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition), diagnosis assigned to individuals who are experiencing symptoms of a neurodevelopmental disorder, but do not meet the full diagnostic criteria for one of the Neurodevelopmental disorders.
Which brain structure is most frequently implicated in NDD?
The amygdala is the brain structure most frequently implicated in NDD, which would include UNDD. A sub-cortical structure regulates our response to potentially dangerous environmental stimuli. Sensory input goes to the orbito-frontal cortex, and to the amygdala for processing on an ongoing basis.
What happens if your amygdala is underactive?
An underactive amygdala can result in high-risk behavior, and inappropriate social behavior. An overactive amygdala can produce excessive anxiety and risk aversion, as well as avoidance of social interaction (Schumann, Bauman, and Amaral, 2011).
How are psychological disorders diagnosed?
Most psychological disorders are diagnosed based on the presence of symptoms, which are self-reported by the patient or their family or associates, or observed by the clinician. The symptoms of disorders indicative of UNDD are not always clearly defined, and could include:
What are the symptoms of NDD?
There is commonality in that symptoms are manifested as disruption in physical, intellectual, emotional, behavioral, and cognitive functioning, typically first apparent in early childhood ( (American Psychiatric Association, 2013; Elsevier Ltd., 2013). The debatable exceptions are Schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. Schizophrenia does not typically manifest until the late teens-early twenties. The increasingly prominent view of Bi-polar disorder it cannot be reliably diagnosed until adulthood. However, the apparent age of emergence of these two disorders may be a result of failure to recognize early predictors. Infants can present what are termed soft neurological signs that are predictive of schizophrenia later in life. The signs include:
When do boys develop OCD?
There are also gender differences in the onset of symptoms, e.g., boys tend to present with OCD symptoms about age five, while girls may not have symptoms until the mid-teens.
When can a diagnosis be assigned?
The diagnosis can be assigned when the clinician decides not to specify the reason the diagnostic criteria are unmet, or if there is insufficient information available at the time of the evaluation to make a more specific diagnosis (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
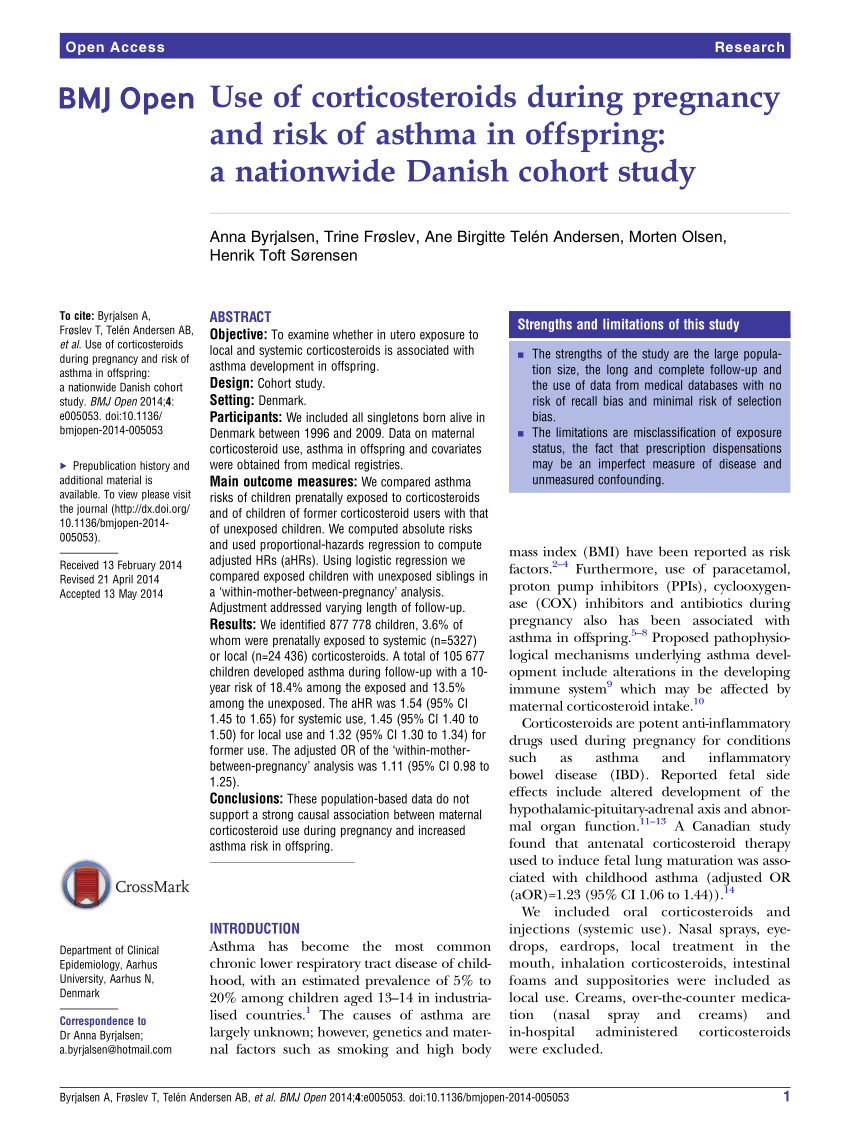
Overview
Hereditary and Degenerative diseases of the central nervous system (330–337)
• 330 Cerebral degenerations usually manifest in childhood
• 331 Other cerebral degenerations
• 332 Parkinson's disease
• 333 Other extrapyramidal disease and abnormal movement disorders
Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system (320–326)
• 320 Bacterial meningitis
• 321* Meningitis due to other organisms
• 322 Meningitis of unspecified cause
• 323 Encephalitis, myelitis and encephalomyelitis
• 320 Bacterial meningitis
• 321* Meningitis due to other organisms
• 322 Meningitis of unspecified cause
• 323 Encephalitis, myelitis and encephalomyelitis
Other disorders of the central nervous system (340–349)
• 340 Multiple sclerosis
• 341 Other demyelinating diseases of central nervous system
• 342 Hemiplegia
• 343 Infantile cerebral palsy
Disorders of the peripheral nervous system (350–359)
• 350 Trigeminal nerve disorders
• 351 Facial nerve disorders
• 352 Disorders of other cranial nerves
• 353 Nerve root and plexus disorders
Disorders of the eye and adnexa (360–379)
• 360 Disorders of the globe
• 361 Retinal detachments and defects
• 362 Other retinal disorders
• 363 Chorioretinal inflammations and scars and other disorders of choroid
• 360 Disorders of the globe
• 361 Retinal detachments and defects
• 362 Other retinal disorders
• 363 Chorioretinal inflammations and scars and other disorders of choroid
Diseases of the ear and mastoid process (380–389)
• 380 Disorders of external ear
• 381 Nonsuppurative otitis media and Eustachian tube disorders
• 382 Suppurative and unspecified otitis media
• 383 Mastoiditis and related conditions
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lumbar mass
- 2. icd 10 code for diff
- 3. icd 10 code for osteoarthritis, bilateral
- 4. icd code for creatinine
- 5. icd 10 code for bursitis left shoulder
- 6. icd 10 cm code for lower back contusion
- 7. icd code for external cause - wilderness
- 8. icd 10 code for chronic pain of right knee
- 9. icd-10 code for left arm swelling
- 10. icd 10 cm code for sinus tachycardia.