Which type of hernia repair is best?
You may not avoid a hiatal hernia entirely, but you can avoid making a hernia worse by:
- losing excess weight
- not straining during bowel movements
- getting help when lifting heavy objects
- avoiding tight belts and certain abdominal exercises
How do you repair abdominal hernia?
Here’s what that means:
- Open — An incision of 3" to 6" is made in the abdomen to give the surgeon access to the hernia.
- Tension — The edges of healthy tissue around the hernia are pulled together and sewn with sutures.
- The incision is then closed with dissolving sutures or abdominal adhesive.
What are the complications of hernia repair?
Hernia Mesh Rejection
- Extreme swelling at the surgical site
- Tenderness or pain
- Redness
- Flu-like symptoms
What are the complications of mesh hernia repair?
Some of the most common complications associated with any type of hernia mesh surgery include:
- Infections
- Adhesions
- Recurrent hernia
- Seroma
- Hematoma
- Testicular complications
- Chronic pain
- Risks of anesthesia, including heart attack and stroke

What is the ICD-10 code for Parastomal hernia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Parastomal hernia without obstruction or gangrene K43. 5.
What is the CPT code for open Parastomal hernia repair?
(Also note that the correct code for open repair of parastomal colostomy hernia is 44346, Revision of colostomy; with repair of paracolostomy hernia [separate procedure]) The surgeon uses some kind of mesh for the repair, such as an AlloMax graft.
What is the code for a Parastomal hernia with gangrene?
4: Parastomal hernia with gangrene.
What is the ICD-10 code for ostomy?
Z93.3Z93. 3 - Colostomy status | ICD-10-CM.
What is a Parastomal hernia repair?
In all cases of parastomal hernia repair, the basic tenets involve reduction of the hernia, excision of the hernia sac, reapproximation of the hernia defect around the bowel, and placement of mesh to support the repair. The onlay repair involves the placement of mesh over a primary fascial repair.
What is a Parastomal hernia?
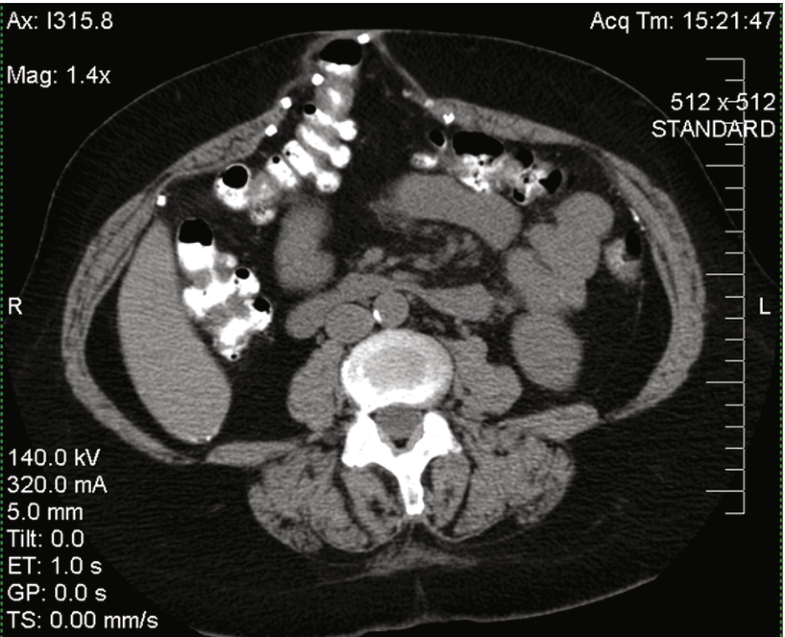
A parastomal hernia is a type of incisional hernia that allows protrusion of abdominal contents through the abdominal wall defect created during ostomy formation (image 1).
Where is a Parastomal hernia?
A parastomal hernia occurs when the intestines press outward near a stoma, the hole created for a colostomy or ileostomy appliance. This causes a bulge under the skin. It can also cause pain and bothersome leakage. Parastomal hernias are the most common complication of ostomy surgery.
What does Parastomal hernia look like?
A stoma hernia resembles a bulge or a lump. Many people describe it a looking like a “golf ball” or a “grapefruit” behind their stoma. Having a hernia can cause your stoma to look more pronounced and potentially change shape, it may also appear larger or flatter than it did before the hernia.
What is ileostomy surgery called?
Permanent Ileostomy In the standard or Brooke ileostomy (also known as an end ileostomy), surgeons pull the ileum up and through an incision in the abdomen. Then they turn the ileum inside out and suture it to the abdomen to create a stoma. Waste coming through the stoma is deposited into an external pouch.
What is the difference between colostomy and ostomy?
A colostomy is an operation that connects the colon to the abdominal wall, while an ileostomy connects the last part of the small intestine (ileum) to the abdominal wall.
What is the ICD-10 code for Encounter for ostomy care education?
Z43. 3 - Encounter for attention to colostomy | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 PCS code for colostomy?
2022 ICD-10-PCS Procedure Code 0D1L0Z4: Bypass Transverse Colon to Cutaneous, Open Approach.
What is a parastomal hernia?
Parastomal hernias happen when part of your intestines stick out through a stoma. A stoma is a surgically made opening in your stomach, small bowel, or colon that allows you to pass waste into a bag.
What are the risk factors for parastomal hernia?
Common risk factors include: older age. obesity, especially if you carry weight around your waist, stomach, or hip area. cancer. diabetes. high blood pressure. respiratory diseases.
Where is mesh placed in a hernia?
Then, mesh is placed either over the repaired stoma or below the abdominal wall. Eventually, the mesh incorporates into the tissue around it.
What is the most successful surgery for a hernia?
This surgery is most successful when the hernia is small. Relocating the stoma.
Can a new parastomal hernia form around a new stoma?
However, a new parastomal hernia can form around the new stoma. Mesh. Mesh inserts are currently the most common type of surgical parastomal hernia repair. Either synthetic or biological mesh can be used. Biological mesh is often considered more comfortable, but is much more expensive.
Can a parastomal hernia be repaired?
of parastomal hernias are severe enough to need surgical repair. There are several surgical repair options for a parastomal hernia, including: Closing the stoma. This is the best option for repairing a parastomal hernia. It’s only an option for a small group of people who have enough healthy bowel left to reattach the end that forms the stoma.
Can you wear a support belt for a parastomal hernia?
Wearing an abdominal support belt, like this one, can also help ease symptoms. However, about 20 percent. Trusted Source. of parastomal hernias are severe enough to need surgical repair.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for ptt
- 2. icd 10 code for squa,ous cell ca
- 3. icd 10 pcs code for hysteroscopy with dilation and curettage
- 4. icd 10 code for genetic testing in pregnancy
- 5. icd 9 diagnosis code for foreign body in cervix
- 6. 5. what is the icd-10-cm external cause code for the external cause status?
- 7. icd 10 code for vasomotor symptoms of menopause
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for fragile x syndrome
- 9. icd code 10 for radical prostatectomy
- 10. icd 10 code for open abdominal wound unspecified