What are the signs of Parkinsons dementia?
Understanding Parkinson’s Disease Dementia
- Behaviors seen in Parkinson’s disease dementia. As dementia progresses, managing disorientation, confusion, agitation, and impulsivity can be a key component of care.
- Lewy body dementia vs. Parkinson’s disease dementia. ...
- End-stage Parkinson’s disease dementia. ...
- Life expectancy with Parkinson’s disease dementia. ...
- Takeaway. ...
Does Parkinson disease cause dementia?
The Parkinson’s Foundation estimates that 930,000 Americans will be living with the disease by 2020. Parkinson’s can cause a condition called Parkinson’s disease dementia. This condition is marked by a decline in thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving.
What is the ICD 10 code for early onset dementia?
What is the ICD 10 code for early onset dementia? ICD-10 code G30. 0 for Alzheimer's disease with early onset is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system . How do you code Alzheimer's dementia? Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's dementia requires two ICD-9-CM codes.
Is chronic kidney disease stage 5 ICD 10 curable?
N18.5 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Chronic kidney disease, stage 5 . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 . ICD-10 code N18.5 is based on the following Tabular structure:
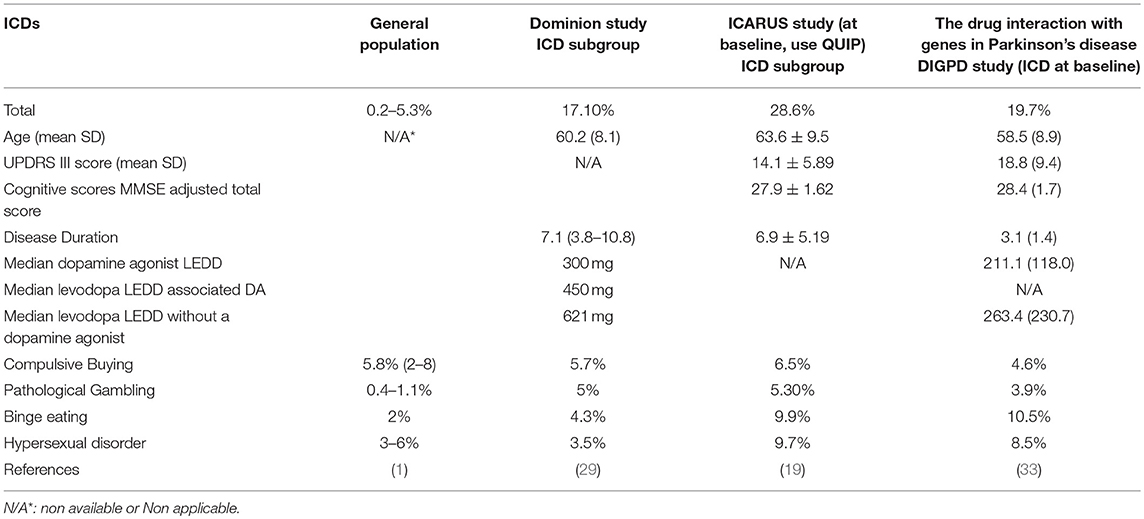
How do you code Parkinson's with dementia?
Disease, Parkinson: You will see Parkinsonism dementia listed with the codes G31. 83 and F02. 80.
Do you have to code dementia with Parkinson's?
ICD-10-CM Coding: You will see Parkinsonism dementia listed and an additional code F02. 80 which appears in brackets and indicates this code would be assigned also but as a secondary.
What is the ICD-9 code for Parkinson's disease?
The ICD-9 CM code, 332.0, which is generally considered the code to identify Parkinson's disease, did not distinguish between parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease.
What is the ICD-9 code for dementia?
For hospital discharge abstracts data, use the ICD-9-CM codes: 291.1x, 291.2x and 292.82 to define dementia.
Can you have Parkinson's and dementia?
Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD) can occur as Parkinson's advances, after several years of motor symptoms. Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) is diagnosed when cognitive decline happens first, or when Parkinson's motor symptoms and cognitive decline occur and progress closely together.
Is Parkinson's disease a type of dementia?
Parkinson's can cause a condition called Parkinson's disease dementia. This condition is marked by a decline in thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving. An estimated 50 to 80 percent of people with Parkinson's will eventually experience Parkinson's disease dementia.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for Parkinson's disease?
ICD-10 code G20 for Parkinson's disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is the ICD-10 code for Parkinsonian features?
Secondary parkinsonism, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G21. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G21. 9 - other international versions of ICD-10 G21.
What is secondary Parkinson's disease?
Definition. Secondary parkinsonism is when symptoms similar to Parkinson disease are caused by certain medicines, a different nervous system disorder, or another illness. Parkinsonism refers to any condition that involves the types of movement problems seen in Parkinson disease.
What is the ICD-10 code for dementia unspecified?
Unspecified dementia without behavioral disturbance F03. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F03. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for senile dementia?
290.0 - Senile dementia, uncomplicated. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for dementia with behaviors?
ICD-10 Code for Unspecified dementia with behavioral disturbance- F03. 91- Codify by AAPC.
Do you have to code dementia with Alzheimer's?
Alzheimer's disease and dementia coding: Dementia is an inherent part of the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. The physician does not have to give both a diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and dementia in order to report both codes. Per the ICD-10-CM Alphabetic Index, G30. 9 would be reported first, followed by F02.
Can dementia be used as primary diagnosis?
Unspecified dementia is determined to be a contributory condition to her terminal status, but cannot be listed as a principal diagnosis because it is listed on the 2014 List of Hospice Invalid Principal diagnosis Codes.
How is dementia coded?
Because the etiology of the dementia is not known, the ICD-10-CM code F03. 91 is the most appropriate to use for this patient.
What is the difference between Alzheimer's dementia and Parkinson's?
Alzheimer's mainly affects language and memory at the outset, whereas Parkinson's affects problem-solving, speed of thinking, memory, and mood. Unlike in Alzheimer's disease, people with Parkinson's-related dementia often experience hallucinations, delusions, and paranoid thoughts.
What are the symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
Symptoms of parkinson's disease may include. trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face. stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk. slowness of movement. poor balance and coordination. as symptoms get worse, people with the disease may have trouble walking, talking or doing simple tasks.
What is progressive degenerative disorder?
Progressive, degenerative disorder of the nervous system characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, and gait abnormalities; caused by a loss of neurons and a decrease of dopamine in the basal ganglia.
What is Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease is a disorder that affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. In parkinson's, neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements.
How old do you have to be to get Parkinson's?
They may also have problems such as depression, sleep problems or trouble chewing, swallowing or speaking. Parkinson's usually begins around age 60, but it can start earlier.
What is progressive degenerative disorder?
Progressive, degenerative disorder of the nervous system characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, and gait abnormalities; caused by a loss of neurons and a decrease of dopamine in the basal ganglia.
What is neurocognitive disorder?
Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior.
What is dementia in other diseases?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease is a disorder that affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. In parkinson's, neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements.
How old do you have to be to get Parkinson's?
They may also have problems such as depression, sleep problems or trouble chewing, swallowing or speaking. Parkinson's usually begins around age 60, but it can start earlier.
What is progressive degenerative disorder?
Progressive, degenerative disorder of the nervous system characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, and gait abnormalities; caused by a loss of neurons and a decrease of dopamine in the basal ganglia.
What is neurocognitive disorder?
Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior.
What is dementia in other diseases?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior.
When will the ICD-10 G20 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What are the symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
The early stages of PD include the following signs and symptoms: Slight shaking of a finger, hand, leg, chin, or lip. Stiffness or difficulty walking. Difficulty getting out of a chair.
What is the PD G20 code?
With PD G20 code, you will be coding associated signs and symptoms or those complications not necessarily inherent to the disease. Most of these complications will be found in Chapter 18, as signs and/or symptoms.
What are the most common drugs for PD?
The first category includes drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain. The most common drugs for PD are dopamine pre cursors—substances such as levodopa that cross the blood-brain barrier and are then changed into dopamine.
What are the symptoms of PD?
PD is associated with the physical symptoms of tremor and/or rigidity. These symptoms may be shown as head bobbing or other sudden involuntary jerking movements and shaking hand (s).
What is the third category of medication for PD?
The third category of drugs prescribed for PD includes medications that help control the non-motor symptoms of the disease ; that is, the symptoms that don't affect movement. For example, people with PD-related depression may be prescribed antidepressants.
What is the second category of PD drugs?
The second category of PD drugs affects other neurotransmitters in the body in order to ease some of the symptoms of the disease. For example, anticholinergic drugs interfere with production or uptake of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. These can be effective in reducing tremors.
How many people have PD?
Worldwide up to 14 million people have a diagnosis of PD. Most individuals with PD are diagnosed when they are 60 years old or older, but early-onset PD also occurs, like that of actor Michael J. Fox and deceased professional boxer Muhammad Ali.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for postobstructive pneumonia
- 2. icd 10 code for swelling both legs
- 3. icd 10 code for right eye infection
- 4. icd 10 code for plantar fascia left
- 5. icd 10 code for jaw numbness
- 6. icd 9 code for peripheral vascular disease with claudication
- 7. icd 10 cm code for acute and chronic sinusitis
- 8. icd 10 cm code for swelling ankle and feet
- 9. icd 10 code for foreign body in esophagus
- 10. icd 10 code for leucorrhea due to trichomoniasis