What is the ICD 10 code for Escherichia coli infection?
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code A04.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM A04.0 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the NIH guidelines category for E coli (E coli)?
Below is a list of some commonly used strains of E. coli, and the NIH Guidelines category applicable to those strains. The following E. coli laboratory strains are K12 or derived from K-12 and therefore most research utilizing these strains is exempt from the NIH Guidelines. (RG1, Exempt, NIH Guideline III-F, F-8, Appendix C-II)
What is the exempt status for E coli?
This exempt status allows for faster review and approval of the Biohazard Use Authorization. Below is a list of some commonly used strains of E. coli, and the NIH Guidelines category applicable to those strains.
What is the ICD 10 code for Bacillus colibacillosis?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to B96.20: Bacillus - see also Infection, bacillus coli infection B96.20 - see also Escherichia coli Colibacillosis A49.8 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code A49.8 Escherichia coli (E. coli) B96.20 Infection, infected, infective (opportunistic) B99.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B99.9
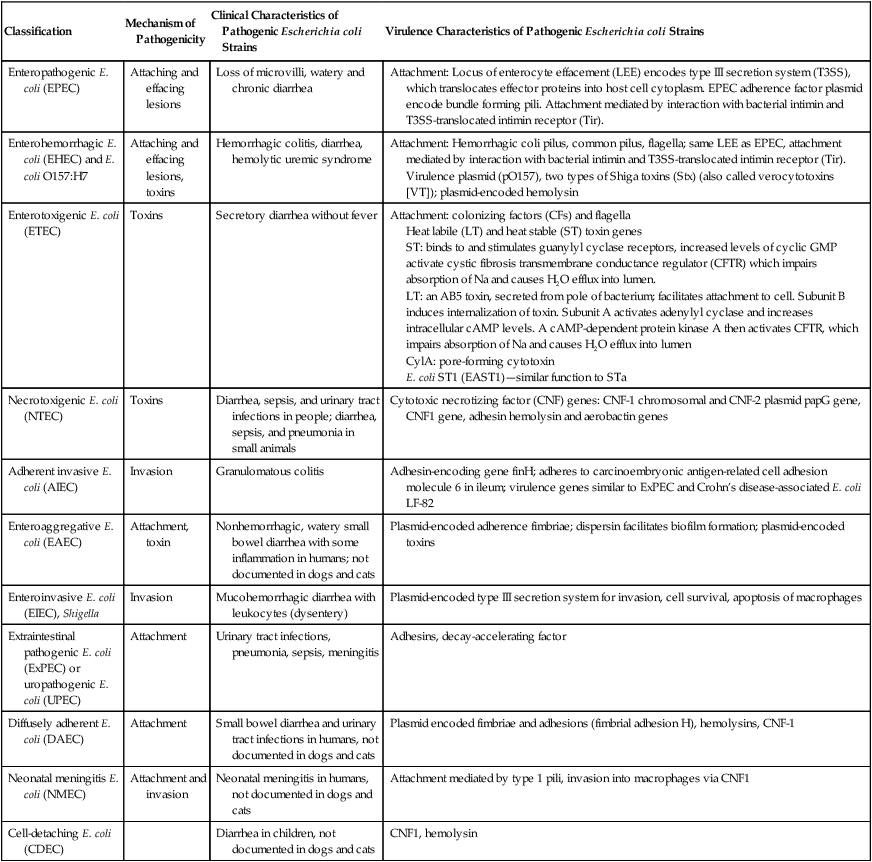
What are the different strains of E. coli?
coli (EHEC) and verocytotoxin-producing E. coli (VTEC). Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC): This strain is commonly known as a cause of travelers' diarrhea.
What is the most common strain of E. coli?
A particular strain of E. coli known as E. coli O157:H7 causes a severe intestinal infection in humans. It is the most common strain to cause illness in people.
What is ICD-10 code for E. coli?
2 for Escherichia coli [E. coli ] as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
Is generic E. coli pathogenic?
Most E. coli are harmless and actually are an important part of a healthy human intestinal tract. However, some E. coli are pathogenic, meaning they can cause illness, either diarrhea or illness outside of the intestinal tract.
Which E. coli strain is pathogenic?
Most E. coli strains are harmless, but pathogenic varieties cause serious food poisoning, septic shock, meningitis, or urinary tract infections in humans. Unlike normal flora E....Pathogenic Escherichia coliOrder:EnterobacterialesFamily:EnterobacteriaceaeGenus:EscherichiaSpecies:E. coli9 more rows
How are pathogenic E. coli serotypes typically classified and named?
E. coli is classified into 150 to 200 serotypes or serogroups based on somatic (O), capsular (K), fimbrial (F) and flagellar (H) antigens.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for ESBL E. coli?
ICD-10 code Z16. 12 for Extended spectrum beta lactamase (ESBL) resistance is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the CPT code for Escherichia coli?
If culture is isolated, identification will be performed at an additional charge (CPT code(s): 87077, 87147).
How do you code E. coli bacteremia?
coli] A41. 51.
Is E. coli k12 pathogenic?
coli K-12 is innately defective as a pathogen, and a very low likelihood of acting as a pathogen of humans or animals. The ability of certain E. coli serotypes to cause disease appears to be associated with certain specific capsular antigens.
Is E. coli an opportunistic pathogen?
E. coli is a bacterium that can not be seen without a microscope and is often considered an opportunistic pathogen because it infects whenever it has the opportunity.
What do you mean by pathogenicity?
Specifically, pathogenicity is the quality or state of being pathogenic, the potential ability to produce disease, whereas virulence is the disease producing power of an organism, the degree of pathogenicity within a group or species.
What is E. coli k12 strain?
Escherichia coli (/ˌɛʃɪˈrɪkiə ˈkoʊlaɪ/; commonly abbreviated E. coli) is a Gram-negative gammaproteobacterium commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms (endotherms). The descendants of two isolates, K-12 and B strain, are used routinely in molecular biology as both a tool and a model organism.
What is E. coli B?
Escherichia coli B serves as a research model for studying phage sensitivity, restriction-modification systems, and bacterial evolution, and also as a workhorse for protein expression in life science laboratories and in the biotech industry.
Are there different types of E. coli bacteria?
There are around 200 different E. coli O serotypes producing Shiga toxin, of which over 100 have been associated with human disease. Two major Shiga toxin types (Stx1 and Stx2) have been associated with strains causing human disease.
What is a strain of bacteria?
A strain is a genetic variant or subtype of a microorganism (e.g., a virus, bacterium or fungus). For example, a "flu strain" is a certain biological form of the influenza or "flu" virus. These flu strains are characterized by their differing isoforms of surface proteins.
Agent Characteristics
Risk Group : RG-2 associated with human disease, rarely serious; preventive or therapeutic interventions often available.
Laboratory Handling Guidelines
Attenuated Strain Alternatives: Due to the extremely low infectious dose of this pathogen, attenuated strains should be worked with where possible. Recommended alternative strains include: E. coli K12, E. coli 25922, E. coli Nissle, E. coli Castellani and Chalmers ATCC 700728, and other E.
Exposure and Spill Procedures
Mucous Membranes : Flush eyes, mouth, or nose for 15 minutes at an eyewash station. See: responding to exposures.
How to get e. coli infection?
Cook meat well, wash fruits and vegetables before eating or cooking them, and avoid unpasteurized milk and juices. You can also get the infection by swallowing water in a swimming pool contaminated with human waste .most cases of e. Coli infection get better without treatment in 5 to 10 days.
When will the ICd 10 B96.20 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B96.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the name of the bacteria that lives in your intestines?
Approximate Synonyms. E coli infection. Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Infection due to escherichia coli. Clinical Information. e. Coli is the name of a type of bacteria that lives in your intestines. Most types of e.
Can you get e. coli from eating?
Coli causes bloody diarrhea, and can sometimes cause kidney failure and even death. These problems are most likely to occur in children and in adults with weak immune systems. You can get e. Coli infections by eating foods containing the bacteria. To help avoid food poisoning and prevent infection, handle food safely.
Is E. coli exempt from the NIH guidelines?
National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant or Synthetic Nucleic Acid Molecules (NIH Guidelines) states that with some exceptions, experimental use of Escherichia coli (E. coli) K-12 strain and its derivatives are exempt from the requirements of the NIH Guidelines. This exempt status allows for faster review ...
Is E. coli derived from K-12?
The following E. coli laboratory strains are not derived from K-12 and therefore any research utilizing these strains is not exempt from the NIH Guidelines. Non-K12 E. coli strains (RG1, not exempt, NIH Guideline III-E)

Overview
This is a shortened version of the first chapter of the ICD-9: Infectious and Parasitic Diseases. It covers ICD codes 001 to 139. The full chapter can be found on pages 49 to 99 of Volume 1, which contains all (sub)categories of the ICD-9. Volume 2 is an alphabetical index of Volume 1. Both volumes can be downloaded for free from the website of the World Health Organization.
Intestinal infectious diseases (001–009)
• 001 Cholera disease
• 002 Typhoid and paratyphoid fevers
• 003 Other Salmonella infections
• 004 Shigellosis
Tuberculosis (010–018)
• 010 Primary tuberculous infection
• 011 Pulmonary tuberculosis
• 012 Other respiratory tuberculosis
• 013 Tuberculosis of meninges and central nervous system
Zoonotic bacterial diseases (020–027)
• 020 Plague
• 021 Tularemia
• 022 Anthrax
• 023 Brucellosis
• 024 Glanders
Other bacterial diseases (030–041)
• 030 Leprosy
• 031 Diseases due to other mycobacteria
• 032 Diphtheria
• 033 Whooping cough
• 034 Streptococcal sore throat and scarlatina
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection (042–044)
• 042 Human immunodeficiency virus infection with specified conditions
• 043 Human immunodeficiency virus infection causing other specified
• 044 Other human immunodeficiency virus infection
Poliomyelitis and other non-arthropod-borne viral diseases of central nervous system (045–049)
• 045 Acute poliomyelitis
• 046 Slow virus infection of central nervous system
• 047 Meningitis due to enterovirus
• 048 Other enterovirus diseases of central nervous system
Viral diseases accompanied by exanthem (050–059)
• 050 Smallpox
• 051 Cowpox and paravaccinia
• 052 Chickenpox
• 053 Herpes zoster
• 054 Herpes simplex
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for chronic dvt right lower leg
- 2. icd 10 code for vern prolapse
- 3. icd-10-cm code for rf positive ra
- 4. icd 10 cm code for transient alteration of awareness
- 5. icd 10 code for deformed merit
- 6. icd 10 code for fall from atv
- 7. icd 10 code for diastasis recti abdominis
- 8. icd code for migraine with aura
- 9. icd 10 code for neck pain
- 10. what is the icd 10 cm code for screening colonoscopy