Atrial Fibrillation
A disease of the heart characterized by irregular and often faster heartbeat.
What is the ICD 10 code for atrial fibrillation?
I48.0 ICD-10-CM Code for Atrial fibrillation and flutter I48 ICD-10 code I48 for Atrial fibrillation and flutter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system. Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is atrial fibrillation (AFIB)?
• Atrial fibrillation (427.31) is a fast and chaotic heartbeat that becomes uncoordinated. Instead of the atria and ventricles producing a single contraction, the atria beats so rapidly that it fibrillates.
What are the ICD-9 codes for heart failure?
Heart Failure (ICD-9-CM 428.0, 428.1, 428.20 to 428.23 Range, 428.30 TO 428.33 Range, 428.40 TO 428.43 Range, 428.9) *Codes with a greater degree of specificity should be considered first. I10 Essential (primary) hypertension Hypertension (ICD-9-CM 401.9) 6 Aortic Valve Disorders (ICD-9-CM 424.1)
Can a PCP code AFIB if you have a pacemaker?
Some say because the PCP has to prescribe medications, they should still be able to code afib. Some say once the pacemaker is placed, they should only code the pacemaker.” She then asked my opinion. I have a greater appreciation for this after my father had a recent admission for a heart rate of 27.
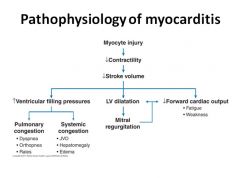
What is the diagnosis code for persistent atrial fibrillation?
ICD-10-CM Code for Persistent atrial fibrillation I48. 1.
What is the ICD 10 code for heart block?
I45. 5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I45.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for atrial fibrillation with RVR?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48 I48.
What is the CPT code for I48 91?
91: Unspecified atrial fibrillation.
How do you code a complete heart block?
2.
What is complete heart block?
Complete heart block is the most serious type of AV heart block. It happens when the electrical impulses that tell your heart when to beat don't pass between the top (atria) and bottom chambers (ventricles) of your heart. This can affect the flow of blood to your body and brain.
Can an ICD be used for atrial fibrillation?
Implantable cardioverter‐defibrillator ( ICD ) improves survival when used for primary or secondary prevention of sudden cardiac death. Whether the benefits of ICD in patients with atrial fibrillation ( AF) are similar to those with normal sinus rhythm ( NSR ) is not well established.
Can you code atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter together?
Chronic AF is reported using code I48. 20 (a CC) when the specific type of AF is not documented. When the diagnosis is atrial flutter/fibrillation, assign both the code for atrial flutter (I48. 92) and atrial fibrillation based on the specific type of atrial fibrillation.
What is diagnosis code Z51 81?
ICD-10 code Z51. 81 for Encounter for therapeutic drug level monitoring is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the CPT code 33208?
Group 1CodeDescription33207INSERTION OF NEW OR REPLACEMENT OF PERMANENT PACEMAKER WITH TRANSVENOUS ELECTRODE(S); VENTRICULAR33208INSERTION OF NEW OR REPLACEMENT OF PERMANENT PACEMAKER WITH TRANSVENOUS ELECTRODE(S); ATRIAL AND VENTRICULAR1 more row
What is the ICD 10 code for I45 5?
Other specified heart blockI45. 5 - Other specified heart block | ICD-10-CM.
What is an AV node block?
Atrioventricular (AV) block is an interruption or delay of electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles due to conduction system abnormalities in the AV node or the His-Purkinje system. Conduction delay or block can be physiologic if the atrial rate is abnormally fast or pathologic at normal atrial rates.
What is a 1st degree AV block?
First-degree atrioventricular (AV) block is a condition of abnormally slow conduction through the AV node. It is defined by ECG changes that include a PR interval of greater than 0.20 without disruption of atrial to ventricular conduction. This condition is generally asymptomatic and discovered only on routine ECG.
What is high grade AV block?
High-grade AV block, also known as advanced heart block, is a form of third-degree heart block. This occurs when AV dissociation is present; however, intermittently some sinus node action potentials (P waves) are randomly conducted to the ventricles.
What is the code for SVT?
If the SVT is documented as paroxysmal, then code 427.0 is assigned. However, if only SVT is documented, then code 427.89 is assigned. Paroxysmal means the arrhythmia begins and ends suddenly. If the documentation is unclear, the physician may need to be queried for clarification.
What happens if you don't treat ventricular tachycardia?
If not treated promptly, sustained ventricular tachycardia may progress into ventricular fibrillation. • Ventricular fibrillation (427.41) is rapid, chaotic electrical impulses causing the ventricles to fibrillate ineffectively so they fail to pump blood.
What are the symptoms of a tachycardia?
If symptoms are present, they may include tachycardia (fast heartbeat), bradycardia (slow heartbeat), palpitations or skipped beats, fluttering in chest, chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, dizziness, weakness or fatigue, syncope or near syncope, paleness, or sweating.
Is atrial fibrillation paroxysmal?
Atrial fibrillation may be considered paroxysmal (lasting for a short time) or an ongoing, chronic condition. • Atrial flutter (427.32) is caused by one or more rapid circuits in the atrium. It is more organized and regular than atrial fibrillation and often becomes atrial fibrillation or may be present with such.
What is the diagnosis of Z86.74?
If a patient has an episode of sudden cardiac arrest from which they are resuscitated, and has an AICD implanted, they would carry a diagnosis of Z86.74, Personal history of sudden cardiac arrest and Z95.810, Presence of automatic cardiac defibrillator. They are not in a persistent state of cardiac arrest; it is historical.
Why do you need a pacemaker for atrial fibrillation?
Anticoagulation is often prescribed, because clots can form in the heart and be embolized to the brain, causing strokes. Pacemakers in atrial fibrillation are most commonly placed for symptomatic bradycardia, either medication-induced or due to aging, diseased heart muscle. It is less common to insert a pacemaker for overdrive atrial pacing.
What is the most common cardiac dysrhythmia?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac dysrhythmia, afflicting between 2 and 6 million people in the United States. Changes in the anatomy and electrophysiology of the smaller upper chambers of the heart, or atria, cause chaotic electrical impulses, which are unpredictably propagated to the lower chambers, or ventricles, ...
What is pacemaker addressing?
If a patient has AF with a slow ventricular response, a pacemaker is addressing the pauses or bradycardia, the resultant symptoms or the risk of a nine-second asystole – like my father had. It is not resolving or eradicating the atrial fibrillation. The AF is still present, underlying the paced rhythm. The bradycardia and pacemaker firing could also be only intermittent, like in my father’s situation. In his case, his post-discharge pacemaker check showed it was only operating 4 percent of the time. If the pacemaker were to malfunction or to be turned off, the observed rhythm would be AF in such a patient. They may even remain on anticoagulation or medication for rate control. AF is a valid diagnosis.
What if a patient undergoes a successful maze procedure for AF, reverts to?
What if a patient undergoes a successful maze procedure for AF, reverts to normal sinus rhythm, and stays in sinus? That would be curative. You could capture personal history codes, but the patient no longer has a current cardiac condition.
Can a PCP code AFIB?
Some say because the PCP has to prescribe medications, they should still be able to code afib. Some say once the pacemaker is placed, they should only code the pacemaker.”. She then asked my opinion. I have a greater appreciation for this after my father had a recent admission for a heart rate of 27.
Can a pacemaker be used for overdrive atrial pacing?
It is less common to insert a pacemaker for overdrive atrial pacing. The pacemaker does not directly treat atrial fibrillation, and it certainly does not cure or resolve it. There are reasons why we code. We translate the acute patient encounter into codes to determine reimbursement.
What is cardiac arrest?
The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of circulation. Cardiac arrest may be reversed by cpr, and/or defibrillation, cardioversion or cardiac pacing.
What does "cardiac standstill" mean?
Cardiac standstill or arrest; absence of a heartbeat.
When will ICD-10-CM I46.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I46.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is HCC code?
For hierarchical condition categories (HCC) used in Medicare Advantage Risk Adjustment plans, certain diagnosis codes are used as to determine severity of illness, risk, and resource utilization. HCC impacts are often overlooked in the ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM conversion. The physician should examine the patient each year and compliantly document the status of all chronic and acute conditions. HCC codes are payment multipliers.
Is there an error in the prescription for Coumadin?
Note: There is nothing in the documentation that says that there was an error in the prescription for Coumadin or that the patient took it incorrectly. If the prescription was correctly prescribed and correctly administered/taken then it would be an adverse effect.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for acute chest syndrome
- 2. icd 10 code for soliosisr
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for acute appendectomy
- 4. icd 10 code for gj tube replacement
- 5. icd 10 code for candida esophagitis
- 6. icd 10 code for parechymal lung biopsy
- 7. icd 10 code for acute gastrointestinal bleeding
- 8. 2017 icd 10 diagnosis code for gastric ulcer
- 9. icd 10 code for removal of interstim device
- 10. icd 10 code for burning sensation