What is the best medicine to stop post nasal drip?
Postnasal drip ICD-9-CM 784.91 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 784.91 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What foods are good for post nasal drip?
Postnasal drip 784.91 784.9 ICD9Data.com 784.92 ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 784.91 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare.
How do you post nasal drip?
Postnasal drip 784.91 784.9 ICD9Data.com 784.92 ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 784.91 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare.
How to stop sinus drainage and post nasal drip naturally?
Apr 05, 2022 · 784.91 Postnasal drip ICD-9-CM Vol. 1 Diagnostic Codes 784.91 - Postnasal drip The above description is abbreviated. This code description may also have Includes, Excludes, Notes, Guidelines, Examples and other information. Access to this feature is available in the following products: Find-A-Code Essentials HCC Plus Find-A-Code Professional

The ICD code R098 is used to code Post-nasal drip
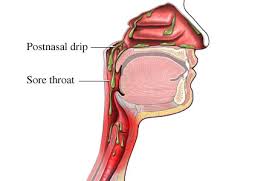
Post-nasal drip (PND, or post nasal drip syndrome, PNDS, also known as Upper Airways Cough Syndrome, UACS) occurs when excessive mucus is produced by the nasal mucosa. The excess mucus accumulates in the throat or back of the nose.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #154-156 - Other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'R09.82 - Postnasal drip'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code R09.82. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 784.91 was previously used, R09.82 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is the R09.82 code?
R09.82 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of postnasal drip. The code R09.82 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What does it mean when your nose is swollen?
Sinusitis means your sinuses are inflamed. The cause can be an infection or another problem. Your sinuses are hollow air spaces within the bones surrounding the nose. They produce mucus, which drains into the nose. If your nose is swollen, this can block the sinuses and cause pain.
How to treat sinusitis?
You may also need imaging tests. Treatments include antibiotics, decongestants, and pain relievers. Using heat pads on the inflamed area, saline nasal sprays, and vaporizers can also help.
How long does sinusitis last?
There are several types of sinusitis, including. Acute, which lasts up to 4 weeks. Subacute, which lasts 4 to 12 weeks. Chronic, which lasts more than 12 weeks and can continue for months or even years. Recurrent, with several attacks within a year.
What causes sinuses to be sore?
Allergies, nasal problems, and certain diseases can also cause acute and chronic sinusitis. Symptoms of sinusitis can include fever, weakness, fatigue, cough, and congestion. There may also be mucus drainage in the back of the throat, called postnasal drip.
What is the ICD code for nasal congestion?
R09.81 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of nasal congestion. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the cause of post nasal drip?
Post-nasal drip (PND, or post nasal drip syndrome, PNDS, also known as Upper Airways Cough Syndrome, UACS) occurs when excessive mucus is produced by the nasal mucosa. The excess mucus accumulates in the throat or back of the nose. It is caused by rhinitis, sinusitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or by a disorder of swallowing (such as an esophageal motility disorder). It is frequently caused by an allergy, which may be seasonal or persistent throughout the year.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for dehydratiio
- 2. icd 10 code for cardiac sarcoidosis
- 3. icd 10 code for strokes
- 4. icd 10 code for strain left shoulder
- 5. icd 10 code for rule out sepsis
- 6. icd code for knee strain
- 7. icd-10 code for pressure ulcer buttock stage 4
- 8. icd-10 code for personal history of drug use
- 9. icd-10 code for pt inr testing
- 10. icd 10 code for deconditioned state