What is the etiology of prerenal azotemia?
For each classification of azotemia, there are unique etiologies. Prerenal azotemia manifests from some insult/injury source before the kidney.
What is intrinsic azotemia in kidney disease?
[1] Intrinsic azotemia results from damage to the structure of the kidney; the structures affected include glomeruli, renal tubules and interstitium, and renal vasculature. This can result from inflammatory conditions, such as vasculitis, toxins, drugs, infections, and damage from hypoperfusion.
What is pre-renal and postrenal uremia?
A disorder characterized by the acute loss of renal function and is traditionally classified as pre-renal (low blood flow into kidney), renal (kidney damage) and post-renal causes (ureteral or bladder outflow obstruction).
Which lab tests are performed in the evaluation of azotemia?
Laboratory evaluation for azotemia includes a basic metabolic panel (BMP), BUN/Cr, urinary sodium (Na), protein, Cr, urea, urine osmolality (Ur Osmo), urinalysis (UA). Radiographic evaluation can be with a renal US (ultrasound), CT of the abdomen and pelvis with or without contrast, or renal Doppler examination.
How do you code Prerenal azotemia?
Prerenal azotemia is assigned to code 788.9, Other symptoms involving urinary system.
What is the ICD-9 code for renal failure?
Chronic renal failure (ICD-9-CM: 585; ICD-10: N18), or. Renal failure unspecified (ICD-9-CM: 586; ICD-10: N19)
What is ICD 10 code N179?
Acute kidney failure, unspecifiedICD 10 N179 - Acute kidney failure, unspecified - Dexur Data & Statistics Reference Kindle Edition.
What is the code for acute renal failure?
Acute kidney failure, unspecified N17. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N17. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-9 code for dialysis?
39.95 Hemodialysis - ICD-9-CM Vol.
What is the ICD-10 code for dialysis?
ICD-10 code Z99. 2 for Dependence on renal dialysis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is Prerenal azotemia?
Prerenal azotemia is the most common form of kidney failure in hospitalized people. Any condition that reduces blood flow to the kidney may cause it, including: Burns. Conditions that allow fluid to escape from the bloodstream. Long-term vomiting, diarrhea, or bleeding.
What is the ICD-10 code for N17 9?
ICD-10 code: N17. 9 Acute renal failure, unspecified.
What does acute kidney injury N17 9 mean?
ICD-10 code N17. 9 for Acute kidney failure, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is R79 89?
ICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What N18 31?
N18. 31- Chronic Kidney Disease- stage 3a.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute on chronic kidney failure?
N17-N19 Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney ...
Can you code acute renal failure and ESRD together?
When both acute renal failure and ESRD are clearly documented in the record, both conditions are to be coded.
What is the ICD-10 code for AKI on CKD 3?
Chronic kidney disease, stage 3 unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N18. 30 became effective on October 1, 2021.
When will ICD-10 N17.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N17.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a clinical syndrome characterized by a sudden decrease in glomerular filtration rate?
Clinical syndrome characterized by a sudden decrease in glomerular filtration rate, usually associated with oliguria and always associated with biochemical consequences of the reduction in glomerular filtration rate such as a rise in blood urea nitrogen (bun) and serum creatinine concentrations.
What is a pre renal disease?
A disorder characterized by the acute loss of renal function and is traditionally classified as pre-renal (low blood flow into kidney), renal (kidney damage) and post-renal causes (ureteral or bladder outflow obstruction).
What is prerenal azotemia?
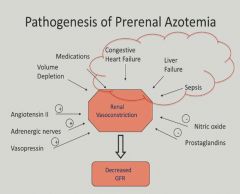
Prerenal azotemia manifests from some insult/injury source before the kidney. Most commonly, we see this in the form of hypoperfusion, or decreased blood flow, to the kidneys from various etiologies of volume depletion, such as the physiologic state shock, dehydration, hemorrhage, over-diuresis, burns, and even intravascular depletion from low-oncotic pressure states, such as congestive heart failure and liver failure. [1]
What is the lab evaluation for azotemia?
Laboratory evaluation for azotemia includes a basic metabolic panel (BMP), BUN/Cr, urinary sodium (Na), protein, Cr, urea, urine osmolality (Ur Osmo), urinalysis (UA). Radiographic evaluation can be with a renal US (ultrasound), CT of the abdomen and pelvis with or without contrast, or renal Doppler examination.
What is azotemia 2021?
Last Update: May 12, 2021. Continuing Education Activity. Azotemia is a biochemical abnormality, defined as elevation, or buildup of, nitrogenous products (BUN-usually ranging 7 to 21 mg/dL), creatinine in the blood, and other secondary waste products within the body. Raising the level of nitrogenous waste is attributed to the inability ...
What is a biochemical abnormality?
Azotemia is a biochemical abnormality, defined as elevation, or buildup of, nitrogenous products (BUN-usually ranging 7 to 21 mg/dL), creatinine in the blood, and other secondary waste products within the body.
How common is azotemia?
With that said, azotemia is quite common, responsible for 8% to 16% of hospital admissions and more so associated with a significantly higher risk of mortality.[3] . There is a need for studies to help understand new knowledge about the incidence of AKI and its epidemiology.
What are the most common findings of AKI?
Some of the most common findings in AKI include ischemia, apoptosis, tubular necrosis, the detachment of renal epithelial cells from the basement membranes, effacement of the brush border in proximal tubules, tubular casts from sloughing of cells, interstitial edema, and even peritubular capillary congestion. [5]
What is the BP range for a nephrotoxic drug?
Along with that line, blood pressure goals are just important as well, not only in keeping the BP range less than 140/90 mmHg but also in ensuring the appropriate choice of medications to reduce nephrotoxic side effects of the drugs.
What is the urine SG of a cat with azotaemia?
If an azotaemic animal has a urine SG less than these values then the patient must have impaired urine concentrating ability, because if the azotaemia was due to pre-renal factors only and the patient had normal renal concentrating ability, the urine SG would be >1.030 (dogs) or 1.035 (cats). Note that most dehydrated cats with normally functioning kidneys will have a urine SG > 1.045.
What is the first step in determining azotaemia?
If a patient has been confirmed as being polyuric and polydipsic and/or azotaemia has been identified, the initial and most important diagnostic step is to determine the urine specific gravity (SG) --without this information, appropriate interpretation of other pathology results can be difficult.
What are the prerenal processes?
Prerenal processes include hypovolaemia and severe dehydration. Mild azotaemia may also occur after a large meat meal and when there is GI bleeding.
Why is my dog azotaemic?
However, if an animal with a polyuric disorder such as pyometra, hyperadrenocorticism or liver disease becomes dehydrated it may become azotaemic entirely due to the prerenal factor of dehydration but it may still have inappropriately dilute urine (because of the factors that interfere with urine concentration).
What causes azotaemia in the glomerulus?
Hypercalcaemia-- calcium causes constriction of the afferent arteriole in the glomerulus thus decreasing GFR and hence causing azotaemia.
Can low SG cause azotaemia?
Too often a patient with low urine SG and azotaemia is diagnosed as having renal failure--this is of course a very possible diagnosis especially in cats, but there are other disorders that impair both urine concentration and cause azotaemia that the practitioner must always consider.
Does sodium cause azotaemia?
Hyponatraemia-- due to hypovolaemia--sodium is the osmotic backbone of the plasma, thus loss of sodium reduces total body water and blood volume which in turn reduces GFR and therefore results in azotaemia. Low sodium also impairs the natural osmotic stimuli for ADH secretion (low serum osmolality) and so promotes dilute urine despite the dehydration which exacerbates fluid loss and therefore pre-renal azotaemia.
What are the symptoms of AKI?
Symptoms of AKI. Signs and symptoms of acute kidney failure may include decreased urine output (although occasionally urine output remains normal), fluid retention, swelling in your legs or feet, shortness of breath, fatigue, confusion, nausea, weakness, irregular heartbeat, chest pain, pressure, seizures, or a coma in severe cases.
Can kidney failure be caused by AKI?
If you were healthy before your kidneys suddenly failed and you were treated for AKI right away, your kidneys may work normally or almost normally after your AKI is treated. Some people have lasting kidney damage after AKI. This is called chronic kidney disease, and it could lead to kidney failure if steps are not taken to prevent the kidney damage from getting worse.
What is the ICd 10 code for end stage renal disease?
N18.6 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for End stage renal disease . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Disease, diseased see also Syndrome.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for foraminal stenosis of lumbosacral region
- 2. icd 10 code for mdd recurrent severe
- 3. icd 10 code for breast burning
- 4. icd 10 code for juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- 5. icd 10 code for cervical pain
- 6. icd 10 code for open toe wound with nail damage
- 7. icd-10 code for iv hydration
- 8. icd 10 code for cognitive delay
- 9. icd 9 code for necrotizing fasciitis
- 10. icd 10 code for valvular heart disease unspecified