What is the ICD-10 code for Primary aldosteronism?
Primary aldosteronism ICD-10-CM E26.09 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 643 Endocrine disorders with mcc 644 Endocrine disorders with cc
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperaldosteronism?
Other primary hyperaldosteronism. E26.09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E26.09 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E26.09 - other international versions of ICD-10 E26.09 may differ.
What is primary aldosteronism?
Not what you're looking for? Primary aldosteronism (hyperaldosteronism) is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands produce too much aldosterone, the hormone responsible for balancing potassium and sodium in the body.
What is primary hyperaldosteronism (PA)?
Primary hyperaldosteronism (PA) is an under-diagnosed cause of hypertension. The presentation is classically known to occur as a patient with hypertension and hypokalemia. However, in reality, most patients will present without hyperkalemia.

What is the ICD 10 code for primary hyperaldosteronism?
E26.09E26. 09 - Other primary hyperaldosteronism | ICD-10-CM.
What is primary aldosteronism?
Primary aldosteronism (hyperaldosteronism) is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands produce too much aldosterone, the hormone responsible for balancing potassium and sodium in the body.
Is Conn's syndrome primary hyperaldosteronism?
Conn's syndrome is a rare health problem that occurs when the adrenal glands make too much aldosterone. This problem is also known as primary hyperaldosteronism. Aldosterone is a hormone that controls salt and potassium levels in the blood. Too much leads to high blood pressure.
What causes primary hyperaldosteronism?
Primary hyperaldosteronism is due to a problem of the adrenal glands themselves. Most cases are caused by a noncancerous (benign) tumor of the adrenal gland. Secondary hyperaldosteronism is due to a problem elsewhere in the body that causes the adrenal glands to release too much aldosterone.
How is primary aldosteronism diagnosis?
Diagnosis and Tests Doctors diagnose primary aldosteronism by measuring the levels of hormones like aldosterone and renin along with electrolytes, including sodium and potassium in patients with high blood pressure. Electrolytes are minerals that help balance the amount of water in your body.
How do you test for primary aldosteronism?
Lab Testing for the Diagnosis of Primary Hyperaldosteronism (Conn's Syndrome) The ARR Screening Test. The aldosterone to renin ratio (ARR) is the most reliable screening test for primary hyperaldosteronism. This is very easy to do and only requires one tube of blood to be drawn from your arm.
What is the most common cause of Conn syndrome?
Conn syndrome is most often caused by an adrenal tumor, such as aldosterone-producing adenomas. Commonly, these tumors are benign but in rare cases, they can be malignant.
Which finding is consistent with a diagnosis of hyperaldosteronism?
24-hour Urinary Excretion of Aldosterone Test If the level of aldosterone in the urine is high, such results can confirm that a patient has primary hyperaldosteronism.
How common is primary hyperaldosteronism?
The prevalence of hyperaldosteronism is debated. Initial studies reported that it probably affects 0.1–1% (1 in 1,000 to 1 in 100) of all patients with high blood pressure. However, with the wider use of screening tests in patients with high blood pressure, estimates of the prevalence have risen.
What is the treatment for hyperaldosteronism?
The treatment of hyperaldosteronism depends on the cause. If the cause is hyperplasia in both adrenal glands, your doctor may prescribe a drug that blocks the effects of aldosterone. These drugs include spironolactone (Aldactone®), eplerenone (Inspra®), or amiloride (Midamor®).
How is primary aldosteronism treated naturally?
Start by choosing fresh, unprocessed foods to reduce your salt intake. Try incorporating elements of the DASH diet, which is designed for people with high blood pressure. In addition, many blood pressure medications work better when combined with a healthy diet. A diet lower in salt is often key in hyperaldosteronism.
Can hyperaldosteronism cause kidney stones?
Typical manifestations of hyperaldosteronism include salt retention, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis. However, a consequence infrequently recognized and described is hypocitraturia. In combination with hypercalciuria, aldosterone-induced hypocitraturia can trigger calcium nephrolithiasis.
What are the symptoms of too much aldosterone?
Hyperaldosteronism is a condition in which one or both adrenal glands produce too much of the hormone aldosterone....Symptoms and CausesWeakness.Tingling feelings.Muscle spasms.Temporary paralysis.Extreme thirst.Frequent urination (having to urinate often)
What happens when aldosterone levels are high?
Too much aldosterone is called hyperaldosteronism. This extra aldosterone causes high blood pressure and low potassium levels. Sometimes it can look like moderate to severe high blood pressure and go undiagnosed for a long time.
How serious is hyperaldosteronism?
Without proper treatment, patients with hyperaldosteronism often suffer from poorly controlled high blood pressure and are at increased risk for heart attacks, heart failure, strokes, kidney failure, and early death. However, with appropriate treatment, this disease is treatable and has an excellent prognosis.
How is primary aldosteronism treated naturally?
Start by choosing fresh, unprocessed foods to reduce your salt intake. Try incorporating elements of the DASH diet, which is designed for people with high blood pressure. In addition, many blood pressure medications work better when combined with a healthy diet. A diet lower in salt is often key in hyperaldosteronism.
What is the cause of hyperaldosteronism?
Primary hyperaldosteronism caused by the excess production of aldosterone by an adenoma of the zona glomerulosa or conn adenoma.
What is the cause of aldosterone overproduction?
An endocrine disorder characterized by excessive production of aldosterone by the adrenal glands. Causes include adrenal gland adenoma and adrenal gland hyperplasia. The overproduction of aldosterone results in sodium and water retention and hypokalemia. Patients present with high blood pressure, muscle weakness, and headache.
What are the symptoms of aldosteronism?
Other symptoms include: Fatigue. Headaches.
What test is used to determine aldosterone levels?
When diagnosing primary aldosteronism, the physician often will first order a blood test to determine the patient’s aldosterone and renin levels. Renin is an enzyme released by the kidneys that helps regulate blood pressure.
What causes aldosteronism in the adrenal gland?
Muscle weakness. Numbness. Sporadic temporary paralysis. Causes and Risk Factors. Many cases of primary aldosteronism are caused by a benign tumor in an adrenal gland; some are caused by overactivity of both adrenal glands, a condition known as bilateral adrenal hyperplasia.
What is the condition where the adrenal glands produce too much aldosterone?
Primary aldosteronism (hyperaldosteronism) is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands produce too much aldosterone, the hormone responsible for balancing potassium and sodium in the body.
What is the purpose of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists?
Medications known as mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists block the effects of aldosterone in the patient’s body and help lower blood pressure and increase potassium levels. © 2000-2021 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care.
Can aldosterone blockers be used for surgery?
This often permanently resolves the primary aldosteronism and the physician will follow the patient’s progress closely, adjusting or eliminating the patient’s medications as needed. When surgery is not an option, aldosterone-blocking medications can be used to manage the condition.
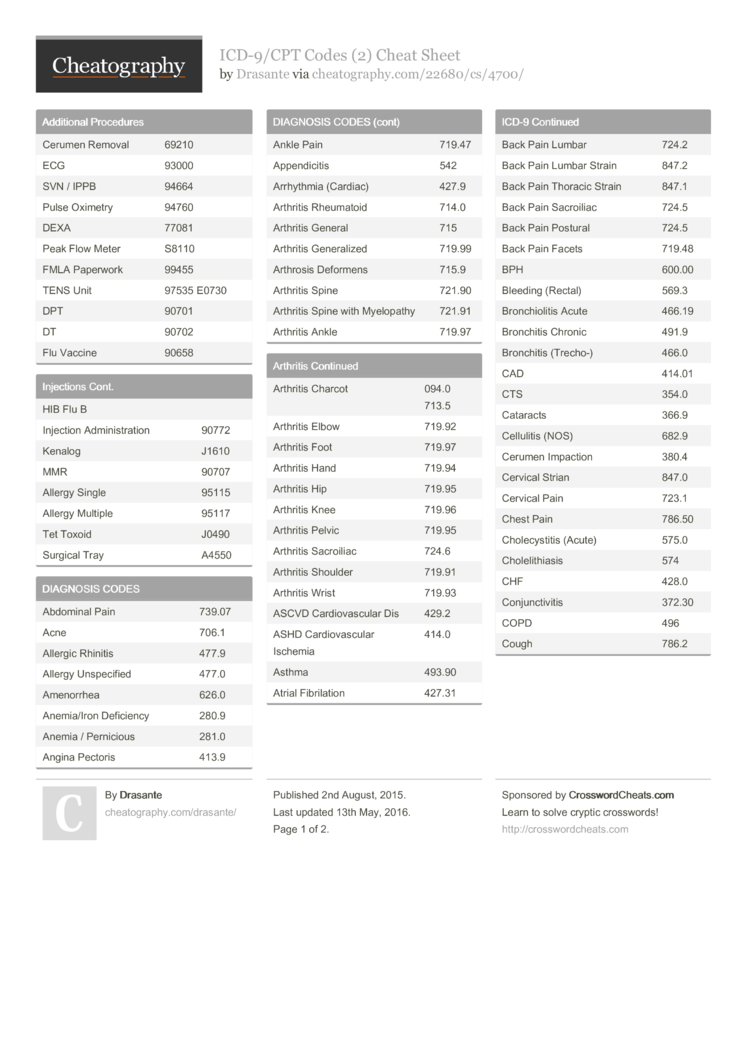
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cardiolipin
- 2. icd 10 code for rt breast subareolar dcis
- 3. icd 10 cm code for tvaginal discharge.
- 4. icd 10 cm code for hemorrhagic cyst to the kidney
- 5. icd 10 code for injury right great toenail
- 6. icd 10 code for downs syndrome
- 7. icd-10-cm code for dry skin dermatitis
- 8. icd 10 code for septic prepatellar bursitis of left knee
- 9. icd 10 code for diabetes type 2 with ketoacidosis
- 10. 2016 icd 10 code for monoclonal gammopathy