What is the ICD 9 code for benign prostatic hypertrophy?
Billable Medical Code for Hypertrophy (benign) of Prostate with Urinary Obstruction and other Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 600.01. Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 600.01. The Short Description Is: BPH w urinary obs/LUTS. Known As
What is the ICD 10 code for prostate neoplasms?
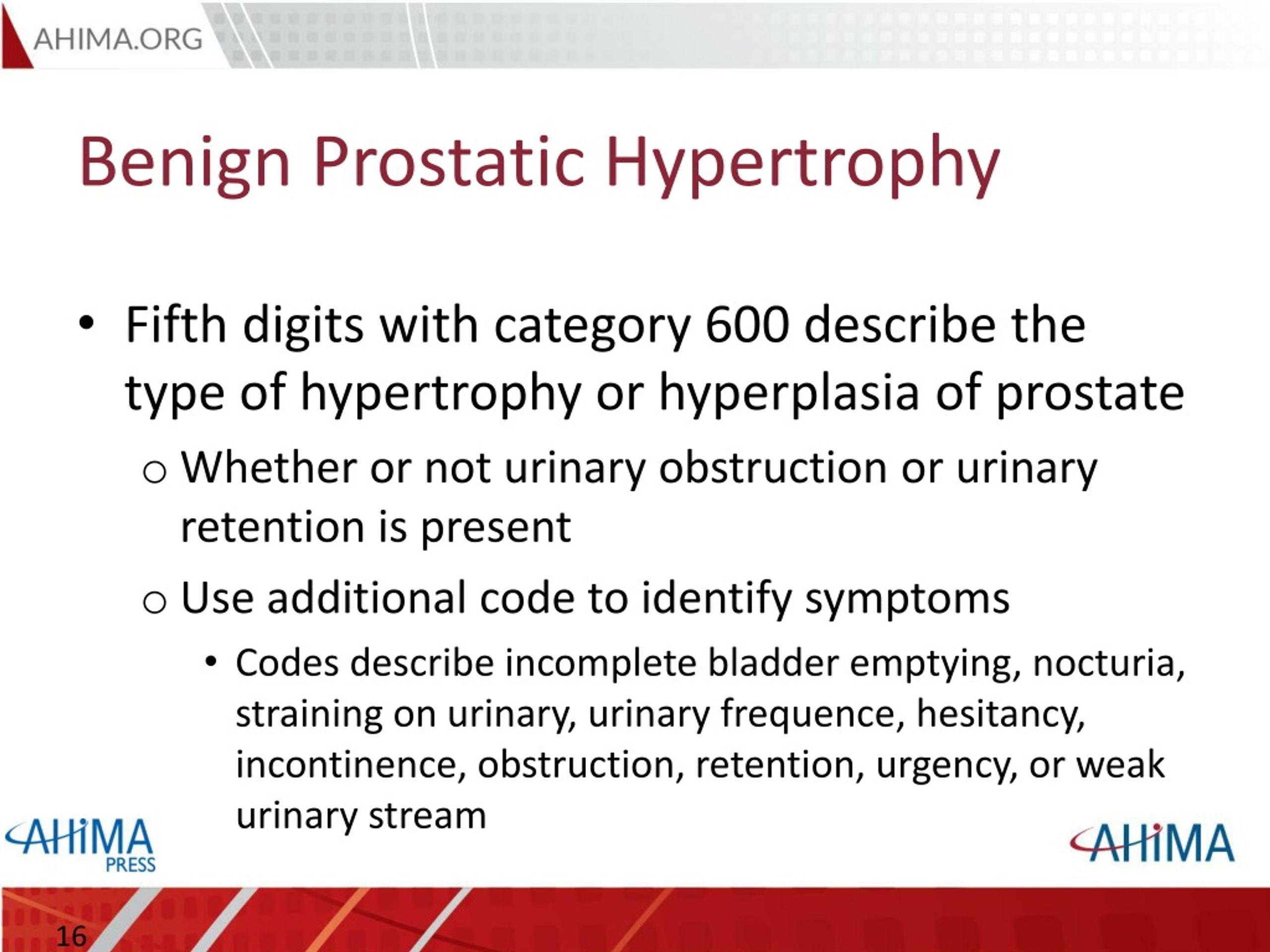
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 600 : Hyperplasia of prostate Hyperplasia of prostate 2015 Non-Billable Code There are 5 ICD-9-CM codes below 600 that define this diagnosis in greater detail. Do not use this code on a reimbursement claim. Clinical Information
What are the causes of hypertrophy in the prostate?
ICD-9 Code 600.01 Hypertrophy (benign) of prostate with urinary obstruction and other lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) ICD-9 Index; Chapter: 580–629; Section: 600-608; Block: 600 Hyperplasia of prostate; 600.01 - BPH w urinary obs/LUTS
What is benign prostatic hypertrophy (benign) of prostate with urinary retention?
Benign prostatic hypertrophy Enlargement of prostate Smooth enlarged prostate Soft enlarged prostate 600 ICD9Data.com 600.00 ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 600.0 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare.

What is the ICD 10 code for prostatic hypertrophy?
What is the meaning of prostatic hypertrophy?
Is prostatic hyperplasia the same as prostatic hypertrophy?
How do you code benign prostatic hypertrophy?
What causes benign prostatic hypertrophy?
Is prostatic hypertrophy physiologic?
Is hyperplasia and hypertrophy same?
Is hyperplasia the same as hyperplasia?
...
| Hyperplasia | |
|---|---|
| Treatment | Depends which type (see types) |
What is the medical term for a enlarged prostate?
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary frequency?
What is the ICD-10 code for pure hypercholesterolemia?
What is the ICD-10 code for hyperlipidemia?
What is the prostate gland?
The prostate is a gland in men. It helps make semen, the fluid that contains sperm. The prostate surrounds the tube that carries urine out of the body. As men age, their prostate grows bigger. If it gets too large, it can cause problems. An enlarged prostate is also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Most men will get BPH as they get older. Symptoms often start after age 50.
What is the test for BPH?
Tests for BPH include a digital rectal exam, blood and imaging tests, a urine flow study, and examination with a scope called a cystoscope. Treatments include watchful waiting, medicines, nonsurgical procedures, and surgery. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Digital rectal exam.
What tests are done to determine if you have BPH?
Tests for BPH include a digital rectal exam, blood and imaging tests, a urine flow study, and examination with a scope called a cystoscope. Treatments include watchful waiting, medicines, nonsurgical procedures, and surgery.
What is the ICd 10 code for prostate hyperplasia?
600.91 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of hyperplasia of prostate, unspecified, with urinary obstruction and other lower urinary symptoms (luts). This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the prostate gland?
The prostate is a gland in men. It helps make semen, the fluid that contains sperm. The prostate surrounds the tube that carries urine out of the body. As men age, their prostate grows bigger. If it gets too large, it can cause problems. An enlarged prostate is also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Most men will get BPH as they get older. Symptoms often start after age 50.
What is the CPT code for prostate removal?
Treatment of prostate cancer may also require surgical removal of the prostate. CPT codes for prostatectomy include: 55801. Prostatectomy, perineal, subtotal (including control of postoperative bleeding, vasectomy, meatotomy, urethral calibration, and /or dilation, and internal urethrotomy) 55812.
What is the N40 code for prostate?
Screening may detect nodules or other abnormalities of the prostate. Benign prostatic hyperplasia or hypertrophy, enlarged prostate , or nodular prostate are common conditions code in category N40. The 4 th digit is used to describe the condition and/or the presence of associated lower urinary tract symptoms as follows:
How many people die from prostate cancer each year?
It affects roughly 1.3 million people and kills more than 360,000 people each year, which represents about 4% of all cancer deaths worldwide. In its early stages, prostate cancer is highly treatable, with five-year survival rates close ...
How long does prostate cancer last?
In its early stages, prostate cancer is highly treatable, with five-year survival rates close to 100%. Once prostate cancer has metastasized, however, the 5-year survival rate falls to less than 30%, highlighting a significant need for more effective treatment of advanced stage disease. Because prostate cancer is highly curable when detected in ...
Does Medicare cover prostate cancer screening?
Because prostate cancer is highly curable when detected in the early stages, Medicare (and most commercial payers) cover the cost of annual screening for the disease in male beneficiaries over the age of 50. There are two common tests used to screen for prostate cancer, the digital rectal exam (DRE) and the Prostate specific antigen (PSA) ...
Can you ejaculate before prostate test?
This is why some doctors suggest that men abstain from ejaculation for a day or two before testing. Riding a bicycle: Some studies have suggested that cycling may raise PSA levels for a short time (possibly because the seat puts pressure on the prostate), although not all studies have found this.
Does a prostate biopsy raise PSA?
Certain urologic procedures: Some procedures done in a doctor’s office that affect the prostate, such as a prostate biopsy or cystoscopy, can raise PSA levels for a short time. Some studies have suggested that a digital rectal exam (DRE) might raise PSA levels slightly, although other studies have not found this.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for tight anastomotic stricture
- 2. icd 9 code for nonfamilial hypertriglyceridemia
- 3. icd 10 for pediatric code for disordered communications
- 4. icd 9 code for chronic hypertension
- 5. icd 10 code for acute occlusive superficial thrombosis left proximal basilic vein
- 6. icd 10 code for positive influenza a
- 7. icd 10 code for acslerosis of abdominal aorta
- 8. icd 10 dx code for toothache
- 9. icd 10 code for 2nd degree burn bilateral hands
- 10. icd 9 code for h pylori screening