Full Answer
What is proximal junctional kyphosis?
Proximal junctional kyphosis (PJK) has become the greatest challenge in surgery for spinal deformity. PJK is detected by radiologic findings indicating that a pathologic problem has developed internally around the adjacent segment after a spinal fusion.
What is the ICD 10 code for kyphosis?
Other kyphosis, thoracic region 1 M40.294 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M40.294 became effective on October 1, 2018. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M40.294 - other international versions of ICD-10 M40.294 may differ.
Does type of anchor affect proximal junctional kyphosis after long posterior spinal fusion?
Type of anchor at the proximal fusion level has a significant effect on the incidence of proximal junctional kyphosis and outcome in adults after long posterior spinal fusion. Spine Deformity. 2013; 1(4):299–305.
When is surgery indicated for the treatment of proximal junction syndrome?
Once a patient has a problem around the proximal junction, evaluating the existence of clinical symptoms should be prioritized. If there are no symptoms prompt treatment is not required in most cases, but if severe symptoms exist or a deformity of the proximal junction progresses rapidly surgical treatment will be required.
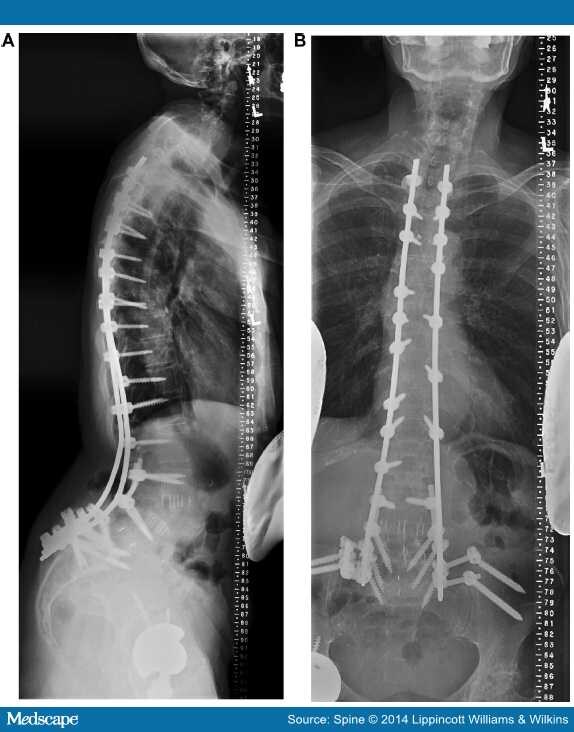
What is proximal junctional kyphosis?
Proximal junctional kyphosis (PJK) is a common complication following adult spinal deformity surgery or a long spinal fusion. It is characterized by an abnormal bend of the vertebral column or spine, resulting in pain and reduced function.
What is the proximal Junction?
Abstract. Proximal junctional kyphosis (PJK) is a common complication following adult spinal deformity surgery. It is defined by two criteria: a proximal junctional sagittal Cobb angle (1) ≥10° and (2) at least 10° greater than the preoperative measurement.
What is the ICD-10 code for kyphosis?
Unspecified kyphosis, site unspecified M40. 209 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M40. 209 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is proximal junctional failure?
DEFINITION OF PROXIMAL JUNCTIONAL FAILURE PJF is a progressive form of the PJK spectrum including vertebral fracture of UIV or UIV+1, subluxation between UIV and UIV+1, failure of fixation, neurological deficit, which may require revision surgery for proximal extension of fusion16,40,44,49).
What is distal junctional kyphosis?
Distal junctional kyphosis (DJK) is a radiographic finding in patients that undergo spinal instrumentation and fusion, since there is an abrupt transition between fixed and mobile spinal segments. The true incidence of DJK is variable in literature and seems that has a multifactorial etiology.
Is kyphosis a disease?
Kyphosis is a spinal disorder in which an excessive curve of the spine results in an abnormal rounding of the upper back. The condition is sometimes known as roundback or — in the case of a severe curve — as hunchback. Kyphosis can occur at any age but is common during adolescence.
What is the ICD 10 code for thoracic kyphosis?
Unspecified kyphosis, thoracic region M40. 204 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M40. 204 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is unspecified kyphosis?
Kyphosis refers to a condition in which the spine in the upper back has an excessive curvature. Also known as round back or hunchback, this spinal disorder can occur in any age, but is most common in adolescence or young adulthood. Having a small curve in the upper back area is normal.
What is the difference between lordosis and kyphosis?
Lordosis (also known as swayback) is when the lower back, above the buttocks, curves inward too much, causing the child's abdomen to protrude and buttocks to stick out. Kyphosis is when the upper spine curves too far outward, forming a hump on the upper back.
What is PJK after surgery?
PJK is a common problem after the surgery for adult spinal deformity. We have found several risk factors for the development of this problem. Some solutions have been suggested. The solutions focus on pre-operative planning, alignment, and steps to augment the upper level fixation.
What is the effect of transition rods on the PJK?
Use of transition rods may create a less rigid construct. The material of the rod can also have an effect on the rigidity of the construct. The use of titanium alloy, which is less stiff, has a lower rate of PJK compared to cobalt chrome. Ligaments and Muscular Tissues.
How long does it take for PJK to occur?
The rate varies between 17% - 46%. Most cases occur within 2 years of surgery. Two-third of cases occur within the first 3 months of surgery.
Does extending the construct higher increase the risk of failure and weakness in limbs?
However, extending the construct higher also increases the risk of failure and weakness in limbs. Combined approach was also found to be a risk factor. Preservation of ligaments and muscle may have an effect in patients undergoing posterior surgery.
Risk Factors
The etiologies of PJK and PJF are likely multifactorial as no study has elucidated a single variable that strongly and consistently predicts their development. However, several major risk factors for PJK and PJF have been described.
Modes of Failure and Classification
Given that the prevalence of elevated thoracic kyphosis ranges between 20 and 40 % and is more common in geriatric patients, some authors posit that PJK represents a recurrence of deformity and/or natural history of aging rather than a postoperative complication.
Evaluation and Preoperative Planning
Failure to recognize and differentiate PJF from PJK and initiate the proper workup and treatment can put patients at risk of neurologic compromise. Unlike patients with PJK, patients with PJF can experience loss of neurologic function. Although pain can be substantial, some patients may have limited new complaints [ 18, 22, 24, 27, 29 ].
Treatment Concepts
Currently, there is no standard consensus to guide the surgeon in determining which patients with PJK would benefit most from revision surgery. In general, patients who are asymptomatic are managed with reassurance, education, and close monitoring (Figs. 17.1 and 17.2 ).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for acute non intractable headache
- 2. icd 10 code for suspicious lesion lower lip
- 3. icd 10 code for poor focus
- 4. icd 10 pcs code for small post voiding residual with indentation on dome of urinary bladder
- 5. icd 10 code for tired
- 6. icd 10 code for factor v clotting disorder
- 7. 2017 icd 10 code for aneurysm of the left cavernous internal carotid
- 8. icd 9 code for ct scan of hip no apwxidiws
- 9. icd 10 code for diet and exercise counseling
- 10. icd 10 code for hypertrophic actinic keratosis