How to spot the warning signs of a pulmonary embolism?
Here is what to look out for:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
- Abnormal sweating
- Nails or lips turning blue
- Severe pain in the chest and/or back
- Loss of consciousness
What are the signs of a pulmonary embolism?
- Responses to sudden, sharp pains in the chest, especially during inhalation. This pain is called pleuritic chest pain.
- Seizures
- Blue-tinged skin is an indication that oxygen deprivation is occurring. ...
- Individuals who experience recurring (small) pulmonary emboli may also display swollen ankles or legs, and experience generalized weakness.
What is the ICD 9 code for pulmonary edema?
- I50.21, acute systolic (congestive) heart failure
- I50.23, acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure
- I50.31, acute diastolic (congestive) heart failure
- I50.33, acute on chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure
- I50.41, acute combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure
What causes pulmonary embolism?
- heart rate of 100-109 bpm: adjusted OR = 1.5; 95% CI, 1.3-1.7;
- heart rate of 110-119 bpm: aOR = 1.7; 95% CI, 1.4-1.9;
- heart rate of 120-139 bpm: aOR = 1.9; 95% CI, 1.6-2.2; and
- heart rate of 140 or higher bpm: aOR = 2.4; 95% CI, 1.9-3.1.
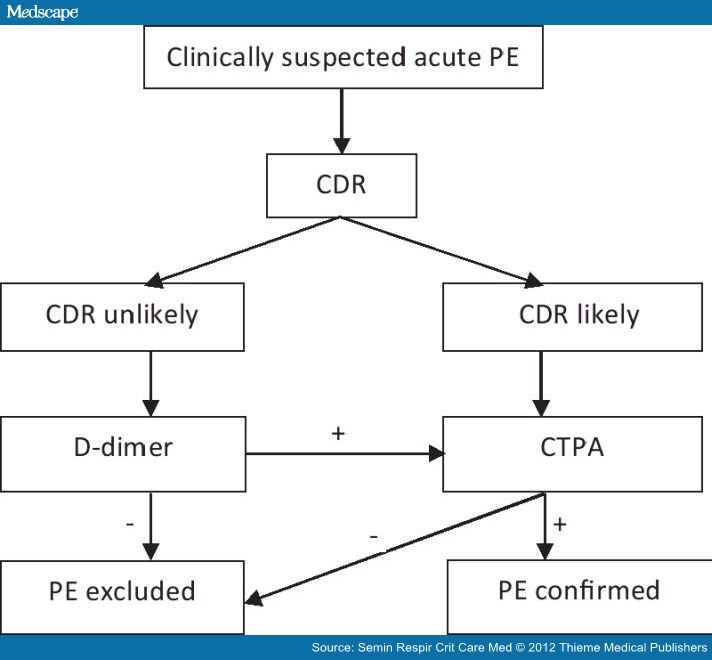
What is the ICD-10 code for PE unspecified?
Other pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale I26. 99 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I26. 99 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do you code a history of a pulmonary embolism?
711.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of pulmonary embolism?
Z86. 711 - Personal history of pulmonary embolism | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for pulmonary embolism and infarction?
415.19 - Other Pulmonary Embolism and Infarction [Internet]. In: ICD-10-CM.
What is personal HX of PE DVT?
Personal history of pulmonary embolism Z86. 711 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for long term anticoagulation?
Z79. 01 Long term (current) use of anticoagulants - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is I10 diagnosis?
ICD-Code I10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Essential (Primary) Hypertension.
What is the ICD-10 code for family history of DVT?
Family history of diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. Z83. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z83.
What is hx of DVT?
History. Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) classically produces pain and limb edema; however, in a given patient, symptoms may be present or absent, unilateral or bilateral, or mild or severe. Thrombus that does not cause a net venous outflow obstruction is often asymptomatic. Edema is the most specific symptom of DVT.
What is the ICD code for pulmonary embolism?
We used ICD-10 codes (I26. 9: pulmonary embolism without cor pulmonale, and I26. 0: pulmonary embolism with cor pulmonale) to identify patients diagnosed with PE; we refer to these identified patients as the coded PE group (Fig.
What is the ICD-10 code for blood clots?
Embolism and thrombosis of unspecified artery I74. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I74. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a Subsegmental pulmonary embolism?
Subsegmental pulmonary embolism (SSPE) affects the 4th division and more distal pulmonary arterial branches. SSPE can be isolated or affect multiple subsegments, be symptomatic or incidental (unsuspected) and may or may not be associated with deep vein thrombosis.
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral Subsegmental pulmonary embolism?
ICD-10-CM Code for Multiple subsegmental pulmonary emboli without acute cor pulmonale I26. 94.
How long is a PE considered acute?
I have asked this question myself and gotten a variety of answers, from the initial stay only being the acute phase, all the way up to and including the entire first three months of management being the acute phase.
What is a segmental PE?
Small segmental or subsegmental PE are of importance in patients with limited cardiopulmonary reserve and for diagnosis of chronic pulmonary hypertension. They may be an indicator of silent deep venous thrombosis, which may predispose patients to more severe embolic events.
How do you code recurrent DVT?
DVT on chronic anticoagulation therapy. I82. 891 – Chronic embolism and thrombosis of other unspecified vein.
What is a nodule in the lungs?
Pulmonary nodules are small oval lesions in the lungs that are detected through a CT scan. The lesion may be cancerous but are usually benign. They show no symptoms.
When will the ICd 10 code 518.89 be replaced?
Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 518.89.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is the term for the closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches?
The closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung. The obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung.
When will ICD-10-CM I26.99 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I26.99 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is a type 2 exclude note?
A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I26) and the excluded code together. chronic pulmonary embolism (.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
damage to other organs in your body from not getting enough oxygen. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
Known As
Pulmonary embolism is also known as acute massive pulmonary embolism, hemorrhagic pulmonary infarction, postoperative pulmonary embolus, pulmonary apoplexy, pulmonary artery thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary embolism (blood clot in lung), pulmonary embolism W infarction, pulmonary embolism with infarction, pulmonary fat embolism, pulmonary infarction, pulmonary microemboli, pulmonary thromboembolism, pulmonary thrombosis, pulmonary tumor embolism, pulmonary venous thrombosis, recurrent pulmonary embolism, subacute massive pulmonary embolism, thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, and tumor embolus..
Pulmonary Embolism Definition and Symptoms
Pulmonary embolism is when an artery in the lung is blocked by fat, air, blood clots, or a tumor. In majority of cases the blockage is caused by a blood clot. Symptoms include chest pain, excessive sweating, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, cough, and leg pain or swelling in the calf.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for wound dehiscence
- 2. icd 9 code for family history of coloncancer
- 3. icd 10 code for nursing diagnosis for dementia
- 4. icd 10 code for osgood–schlatter disease knee
- 5. icd 10 code for facet arthritis lumbar spine
- 6. icd 10 cm code for history of gout
- 7. icd 10 code for hx chemotherapy
- 8. icd 10 code for choleseterol
- 9. icd 10 code for decompensated diastolic heart failure
- 10. icd-10 code for bilateral femoral diaphysis