What is the prognosis for renal cell carcinoma?
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) has the highest mortality rate of the genitourinary cancers and the incidence of RCC has risen steadily. If detected early, RCC is curable by surgery although a minority are at risk of recurrence. Increasing incidental detection ...
What is the treatment for renal cell cancer?
… Non-clear renal cell carcinomas (nccRCCs) are less frequent in kidney cancer with histopathological heterogeneity. A better understanding of the tumor biology of nccRCC can provide more effective treatment paradigms for different subtypes.
What is the life expectancy of someone with kidney cancer?
Understanding the numbers
- People now being diagnosed with kidney cancer may have a better outlook than these numbers show. ...
- These numbers apply only to the stage of the cancer when it is first diagnosed. ...
- These numbers don’t take everything into account. ...
What are the stages of renal cell carcinoma?
Treatment of Kidney Cancer by Stage
- Stages I, II, or III. Stage I and II cancers are still contained in the kidney. ...
- Stage IV. Stage IV kidney cancer means the cancer has grown outside of the kidney or has spread to other parts of the body such as distant lymph nodes or ...
- Recurrent cancer. Cancer is called recurrent when it come backs after treatment. ...
What is the ICD-10 code for renal cell carcinoma?
Kidney Cancer - Renal Cell Carcinoma (ICD-10: C64) - Indigomedconnect.
How do you code renal cell carcinoma?
Renal cell carcinoma (8312) is a group term for glandular (adeno) carcinomas of the kidney.
What is the ICD-10 code for renal cell carcinoma left kidney?
ICD-10 Code for Malignant neoplasm of left kidney, except renal pelvis- C64. 2- Codify by AAPC.
What is the diagnosis code for history of renal cell carcinoma?
Z85. 528 - Personal history of other malignant neoplasm of kidney. ICD-10-CM.
Is renal cell carcinoma considered a solid tumor?
Solid tumors of the kidney are rare - approximately three-fourths of these tumors are cancerous with the potential to spread. The most common types of kidney cancer include: Renal cell carcinoma (adenocarcinoma)
What is clear cell renal cell carcinoma?
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, or ccRCC, is a type of kidney cancer. The kidneys are located on either side of the spine towards the lower back. The kidneys work by cleaning out waste products in the blood. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is also called conventional renal cell carcinoma.
What is the ICD-10 code C64 1?
C64. 1 - Malignant neoplasm of right kidney, except renal pelvis | ICD-10-CM.
What is transitional cell carcinoma?
Transitional cell (urothelial) carcinoma is by far the most common type of bladder cancer. It is also referred to as “transitional cell carcinoma” or just “urothelial carcinoma.” This cancer originates in the urothelial cells that line the inside of the bladder.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
10 for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
Where does renal cell carcinoma originate from?
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases.
What is the ICD 10 code for squamous cell carcinoma?
ICD-10-CM Code for Squamous cell carcinoma of skin, unspecified C44. 92.
What is a Nephroureterectomy?
Listen to pronunciation. (NEH-froh-YER-eh-ter-EK-toh-mee) Surgery to remove a kidney and its ureter. Also called ureteronephrectomy.
What is the ICd 10 code for malignant neoplasm of kidney?
189.0 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of malignant neoplasm of kidney, except pelvis. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
How to tell if a tumor is in the kidney?
Symptoms include a lump in the abdomen, blood in the urine, and a fever for no reason. Tests that examine the kidney and blood are used to find the tumor.
What does NEC mean in code?
NEC "Not elsewhere classifiable" - This abbreviation in the Alphabetic Index represents "other specified". When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Alphabetic Index directs the coder to the "other specified” code in the Tabular List.
What is a code also note?
Code also note - A "code also" note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction.
How many kidneys are there?
You have two kidneys. They are fist-sized organs on either side of your backbone above your waist. The tubes inside filter and clean your blood, taking out waste products and making urine. Kidney cancer forms in the lining of tiny tubes inside your kidneys.
Why is kidney cancer more likely to occur as you age?
Kidney cancer becomes more likely as you age. Risk factors include smoking, having certain genetic conditions, and misusing pain medicines for a long time.
What is the treatment for cancer?
It might include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation, biologic, or targeted therapies. Biologic therapy boosts your body's own ability to fight cancer. Targeted therapy uses substances that attack cancer cells without harming normal cells.
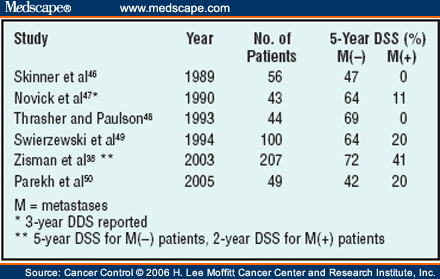
How many people died from renal cell carcinoma in 2006?
In the USA ( from where stats are more accurate) there were 38,890 new cases of Renal Cell carcinoma (RCC) diagnosed and 12,840 people died from the cancer in 2006.
Where does renal cell carcinoma originate?
Renal cell carcinomas originate from the cells of proximal tubules of the nephron. Disease Prevalence – The incidence of renal cell carcinoma is on the increase. Rare in young, it usually affects adults between 50 and 70 years old. Male to female ratio is 2:1. Key Risk factors - include – diet high in fat, being on long term dialysis, ...
What is the most common treatment for renal cell cancer?
CT allows assessment of renal vein and spread into IVC . Treatment Options - Radical Nephrectomy- The most common treatment for renal cell cancer.
What is clear cell carcinoma?
Pathology - Malignant cells contain glycogen – hence on staining appears clear under the microscope (called clear cell carcinoma). TCC in the renal pelvis due to transitional epithelium and constitute 4% of renal neoplasms.It may extend into renal vein and IVC or vena cava and blood-borne spread can result in 'cannon ball' pulmonary seconadries.
Does renal vein ligation reduce tumor propagation?
Renal vein ligated early to reduce tumor propagation and adjacent tissue - adrenal, perinephric fat removed with kidney. RCC resistant to Radiation and chemotherapy agents. More recently Sinitinab given orally seems to give better results than interferon and interleukin treatment in metastatic tumors.
Is renal cell carcinoma chemo resistant?
Renal cell carcinoma on early detection has a high cure rate after a nephrectomy, however in our country most of the tu mours present late and then the tumour cure rate is low as it is highly radio and chemo-resistant.
Does sunitinib help with RCC?
Some advanced cases may respond to immunotherapy. More recently there has been advent of targeted cancer therapies such as sunitinib that has vastly improved the outlook for treatment of RCC. Sunitinib has become the new standard of care in the first-line treatment of metastatic RCC and was approved by FDA in 2006.
What is the ICd code for renal cell carcinoma?
The ICD code C64 is used to code Renal cell carcinoma. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC, also known as hypernephroma, Grawitz tumor, renal adenocarcinoma) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport waste molecules from the blood to the urine.
What is the ICD code for malignant neoplasm of kidney?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code C64 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the three child codes of C64 that describes the diagnosis 'malignant neoplasm of kidney, except renal pelvis' in more detail.
What is the code for malignant neoplasm of renal calyces?
Malignant neoplasm of renal calyces - instead, use code C65.-
What is the ICd 10 code for neoplasms?
The ICD-10-CM Neoplasms Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code C64. Click on any term below to browse the neoplasms index.
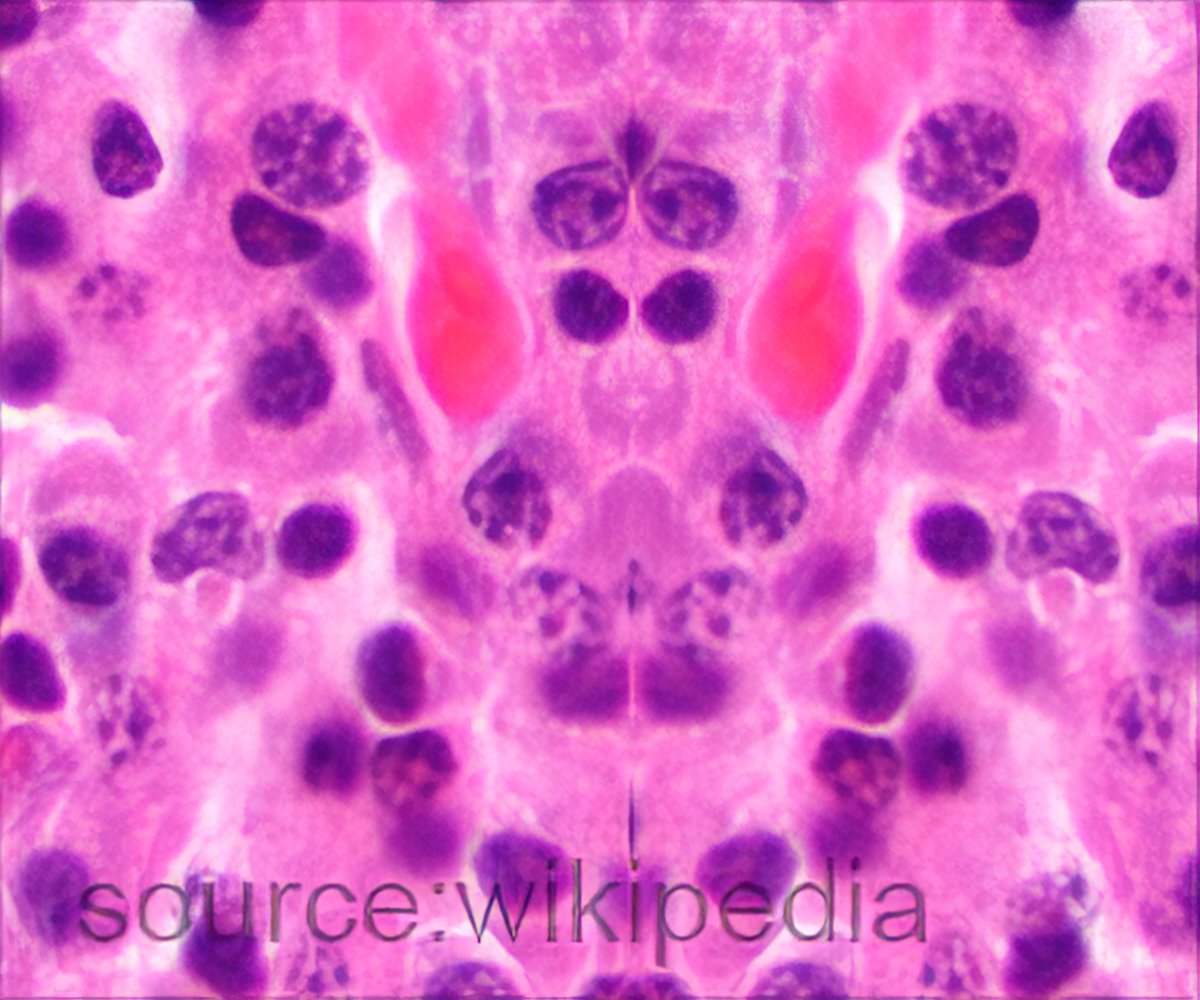
What is the most common type of kidney cancer?
RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90-95% of cases. Micrograph of the most common type of renal cell carcinoma (clear cell) - on right of the image, non-tumour kidney is on the left of the image. Nephrectomy specimen. H&E stain.
What are some synonyms for cancer of the kidney?
Approximate Synonyms. Cancer of the kidney. Cancer of the kidney, primary, localized. Cancer of the kidney, renal cell. Cancer of the kidney, sarcoma. Cancer of the kidney, transitional cell carcinoma. Cancer of the kidney, wilms tumor. Clear cell carcinoma of kidney. Localized primary malignant neoplasm of kidney.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
When will the ICD-10 C64.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C64.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can multiple neoplasms be coded?
For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, ...
What is the synonym for in situ carcinoma?
Synonyms for in situ carcinoma: CIS, Stage 0, CIN grade III, confined to epithelium, intraepithelial, involvement up to but not including the basement membrane, noninfiltrating, noninvasive, no stromal involvement, papillary noninfiltrating, noninvasive papillary, stage "Ta"
What to do if diagnostic term is not listed in pathology report?
If the diagnostic term in the pathology report is not in the list below, be sure to consult your ICD-O manual.
Overview
This is a shortened version of the second chapter of the ICD-9: Neoplasms. It covers ICD codes 140 to 239. The full chapter can be found on pages 101 to 144 of Volume 1, which contains all (sub)categories of the ICD-9. Volume 2 is an alphabetical index of Volume 1. Both volumes can be downloaded for free from the website of the World Health Organization.
See here for a tabular overview of primary, secondary, in situ, and benign neoplasms.
Malignant neoplasm of lip, oral cavity, and pharynx (140–149)
• 140 Malignant neoplasm of lip
• 141 Malignant neoplasm of tongue
• 142 Malignant neoplasm of major salivary glands
• 143 Malignant neoplasm of gum
Malignant neoplasm of digestive organs and peritoneum (150–159)
• 150 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus
• 151 Malignant neoplasm of stomach
• 152 Malignant neoplasm of small intestine, including duodenum
• 153 Malignant neoplasm colon
Malignant neoplasm of respiratory and intrathoracic organs (160–165)
• 160 Malignant neoplasm of nasal cavities, middle ear, and accessory sinuses
• 161 Malignant neoplasm of larynx
• 162 Malignant neoplasm of trachea, bronchus, and lung
• 163 Malignant neoplasm of pleura
Malignant neoplasm of bone, connective tissue, skin, and breast (170–175)
• 170 Malignant neoplasm of bone and articular cartilage
• 171 Malignant neoplasm of connective and other soft tissue
• 172 Malignant melanoma of skin
• 173 Other malignant neoplasm of skin
Kaposi's sarcoma (176–176)
• 176 Kaposi's sarcoma
Malignant neoplasm of genitourinary organs (179–189)
• 179 Malignant neoplasm of uterus, part unspecified
• 180 Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri
• 181 Malignant neoplasm of placenta
• 182 Malignant neoplasm of body of uterus
Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified sites (190–199)
• 190 Malignant neoplasm of eye
• 191 Malignant neoplasm of brain
• 192 Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified parts of nervous system
• 193 Malignant neoplasm of thyroid gland
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for puppp in pregnancy
- 2. icd 10 code for barium enema
- 3. icd 10 code for increasing weight gain
- 4. what is icd 10 code for insomnia
- 5. icd 10 code for subacute right thalamic stroke
- 6. icd 10 code for hallux valgus deformity
- 7. icd 10 code for bruising on the right shoulder
- 8. 2019 icd 10 code for pancreatic screening
- 9. icd 10 code for right knee mcl tear
- 10. icd 10 code for small cell carcinoma in both lungs, dehydration due to chemotherapy