How do you cure kidney failure?
So, how we can reverse the kidney disease symptoms?
- Stay away from smoking and using tobacco
- Reduce alcohol consumption
- Exercise daily for 30 minutes at least
- Control blood sugar level in case patient is diabetic
- Maintain blood pressure at a healthy level
- Make the diet low-salt and low-fat
- Maintain the best bodyweight
What is the treatment for failing kidneys?
Your treatment plan may include:
- taking medicines
- restricting salt
- limiting certain foods
- getting exercise
What is the ICD 9 code for chronic renal failure?
- acute 584.9
- cortical 583.6 acute 584.6 with abortion - see Abortion, by type, with renal failure ectopic pregnancy (see also categories 633.0 - 633.9) 639.3 molar pregnancy (see also categories 630 - ...
- medullary (papillary) (see also Pyelitis) 590.80 in acute renal failure 584.7 nephritis, nephropathy 583.7
What is acute renal insufficiency?
… Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common clinical condition associated with high morbidity and mortality. The pathogenesis of AKI has not been fully elucidated, with a lack of effective treatment. Renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) play an important role in AKI, and their damage and repair largely determine the progression and prognosis of AKI.
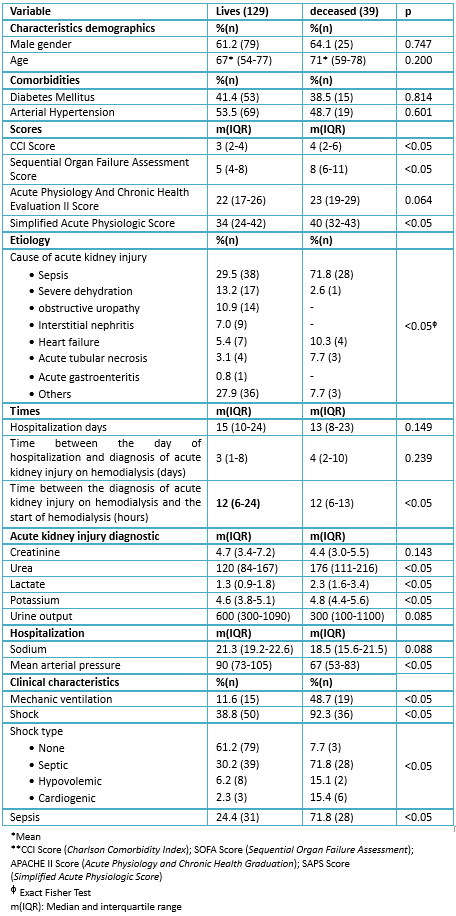
What is the icd10 code for renal insufficiency?
ICD-10-CM code N28. 9 is reported to capture the acute renal insufficiency. Based on your documentation, acute kidney injury/failure (N17.
Is renal insufficiency and renal failure the same thing?
In the case of renal insufficiency (renal failure), a distinction must be made between chronic renal insufficiency and acute renal insufficiency. Chronic renal insufficiency causes a slow loss of renal function.
What is the ICD-9 code for renal failure?
Chronic renal failure (ICD-9-CM: 585; ICD-10: N18), or. Renal failure unspecified (ICD-9-CM: 586; ICD-10: N19)
What is another name for renal insufficiency?
Kidney failure is also called end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Is chronic renal insufficiency the same as chronic kidney disease?
Chronic renal failure is a condition involving a decrease in the kidneys' ability to filter waste and fluid from the blood. It is chronic, meaning that the condition develops over a long period of time and is not reversible. The condition is also commonly known as chronic kidney disease (CKD).
What is the meaning of chronic renal insufficiency?
Chronic renal insufficiency is associated with a progressive inability to excrete normal endogenously produced nonvolatile acid and usually results in systemic acidosis when the GFR is reduced to 0.42 mL/s or less.
What is the ICD-9 code for dialysis?
39.95 Hemodialysis - ICD-9-CM Vol.
Where can I find an ICD code?
If you need to look up the ICD code for a particular diagnosis or confirm what an ICD code stands for, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website to use their free searchable database of current ICD-10 codes.
How do you code a diagnosis?
A Five-Step ProcessStep 1: Search the Alphabetical Index for a diagnostic term. ... Step 2: Check the Tabular List. ... Step 3: Read the code's instructions. ... Step 4: If it is an injury or trauma, add a seventh character. ... Step 5: If glaucoma, you may need to add a seventh character.
How is renal insufficiency diagnosed?
The main test for kidney disease is a blood test. The test measures the levels of a waste product called creatinine in your blood. Your doctor uses your blood test results, plus your age, size, gender and ethnic group to calculate how many millilitres of waste your kidneys should be able to filter in a minute.
What is acute kidney insufficiency?
Acute kidney failure occurs when your kidneys suddenly become unable to filter waste products from your blood. When your kidneys lose their filtering ability, dangerous levels of wastes may accumulate, and your blood's chemical makeup may get out of balance.
What causes acute renal insufficiency?
Among the most common reasons are: acute tubular necrosis (ATN) severe or sudden dehydration. toxic kidney injury from poisons or certain medications.
Is renal insufficiency life threatening?
Acute kidney failure can be fatal and requires intensive treatment. However, acute kidney failure may be reversible. If you're otherwise in good health, you may recover normal or nearly normal kidney function.
Can renal insufficiency be cured?
There's no cure for chronic kidney disease (CKD), but treatment can help relieve the symptoms and stop it getting worse. Your treatment will depend on the stage of your CKD. The main treatments are: lifestyle changes – to help you stay as healthy as possible.
How is renal insufficiency diagnosed?
The main test for kidney disease is a blood test. The test measures the levels of a waste product called creatinine in your blood. Your doctor uses your blood test results, plus your age, size, gender and ethnic group to calculate how many millilitres of waste your kidneys should be able to filter in a minute.
Known As
Renal insufficiency is also known as abnl renal function, abnl renal tubular function, abnormal renal function, abnormal renal tubular function, disorder of ureter, impaired renal function, kidney disease, kidney lesion, kidney mass, renal failure syndrome, renal function impaired, renal impairment, renal insufficiency, renal mass, and ureteral disorder.
Renal Insufficiency Definition and Symptoms
Renal insufficiency, also referred to as renal failure, is when the kidneys no longer function well enough to maintain a normal state of health. Symptoms of renal insufficiency include fatigue, muscle cramps, skin color changes, difficulty breathing, itchy skin, dry eyes, nocturia, trouble concentrating, easy bleeding, and anemia.
Not Valid for Submission
586 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of renal failure, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 586 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Healthy kidneys clean your blood by removing excess fluid, minerals, and wastes. They also make hormones that keep your bones strong and your blood healthy. But if the kidneys are damaged, they don't work properly. Harmful wastes can build up in your body. Your blood pressure may rise.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
Not Valid for Submission
584.9 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute kidney failure, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Convert 584.9 to ICD-10
The following crosswalk between ICD-9 to ICD-10 is based based on the General Equivalence Mappings (GEMS) information:
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 584.9 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Healthy kidneys clean your blood by removing excess fluid, minerals, and wastes. They also make hormones that keep your bones strong and your blood healthy. But if the kidneys are damaged, they don't work properly. Harmful wastes can build up in your body. Your blood pressure may rise.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is a kidney disease?
A term referring to any disease affecting the kidneys. Conditions in which the function of kidneys deteriorates suddenly in a matter of days or even hours. It is characterized by the sudden drop in glomerular filtration rate. Impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning of the kidney.
Why is my kidney unable to remove waste?
This damage may leave kidneys unable to remove wastes. Causes can include genetic problems, injuries, or medicines. You are at greater risk for kidney disease if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a close family member with kidney disease. chronic kidney disease damages the nephrons slowly over several years.
Where are the kidneys located?
Your kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of your fists. They are located near the middle of your back, just below the rib cage. Inside each kidney about a million tiny structures called nephrons filter blood. They remove waste products and extra water, which become urine.
What is acute renal failure?
Acute renal failure is usually associated with oliguria or anuria, hyperkalemia, and pulmonary edema.
Can kidney failure lead to full life?
But with the help of healthcare providers, family and friends, most people with kidney failure can lead full and active lives. Inability of a kidney to excrete metabolites at normal plasma levels under conditions of normal loading or inability to retain electrolytes under conditions of normal intake.
Can chronic renal failure be cured?
Chronic renal failure develops over many years, may be caused by conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes, and cannot be cured. Chronic renal failure may lead to total and long-lasting renal failure, called end-stage renal disease (esrd).

Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for congenital atrial septal aneurysm
- 2. icd 10 cm code for bullous myringitis.
- 3. icd 10 pcs code for vertical sleeve gastrectomy via laparoscopic
- 4. icd 10 code for mild diarrhea
- 5. icd 10 code for smoker current
- 6. icd 10 code for gestational diabetes in pregnancy
- 7. icd 10 code for tendinitis of elbow
- 8. icd 10 code for elevated bnp level
- 9. icd 10 code for high blood pressure with kidney di
- 10. icd 10 code for radial sensory nerve entrapment