What is the ICD 10 code for macular degeneration?
362.50 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of macular degeneration (senile), unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the ICD 9 code for periph retinal degeneration?
ICD-9 Code 362.60 Peripheral retinal degeneration, unspecified. ICD-9 Index; Chapter: 360–389; Section: 360-379; Block: 362 Other retinal disorders; 362.60 - Periph retina degen NOS
What are the different types of macular degeneration?
Types of Macular Degeneration. Macular degeneration can be classified as dry or wet. Dry macular degeneration is characterized by the presence of yellow deposits, called drusen, in the macula. Macular degeneration generally starts in the dry form and is classified to ICD-9-CM code 362.51.
What is AMD (Macular Degeneration)?
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration ( AMD or ARMD ), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, some people experience a gradual worsening of vision...
How do you code macular degeneration?
Unspecified macular degeneration H35. 30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H35. 30 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified macular degeneration?
ICD-10 code H35. 30 for Unspecified macular degeneration is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
What does Nonexudative age related macular degeneration mean?
Nonexudative AMD is characterized by the degeneration of the retina and the choroid in the posterior pole due to either atrophy or RPE detachment. The atrophy is generally preceded (or coincident in some cases) by the presence of yellow extracellular deposits adjacent to the basal surface of the RPE called drusen.
What is macular disruption?
Macular Degeneration Macular Degeneration (Age-Related Macular Degeneration-AMD) is the breakdown or damage of the macular, the area of the eye that allows you to see fine details clearly and perform activities such as reading and driving. AMD usually does not affect side or peripheral vision.
What is retinal maculopathy?
Maculopathy, or macular degeneration, is a disease related to the central part of the retina, called macula. Maculopathy is characterized by a progressive loss of central vision, usually bilateral, that greatly impairs vision functions.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What is the difference between wet and dry macular degeneration?
The main difference between wet vs dry macular degeneration is simple: dry macular degeneration is the more common type of eye disease and does less damage to your vision while wet macular degeneration can result in serious vision loss.
What is intermediate macular degeneration?
To define intermediate AMD is enough to have one or more large drusen (≥125 µm in the smallest diameter), a distance approximating the width of a major branch retinal vessel crossing the optic disc margin. Abbreviation: AMD, age-related macular degeneration.
Which is worse wet or dry macular degeneration?
AMD is a very common cause of vision loss in older adults. Dry AMD makes up the majority of cases, progressing slowly and causing permanent vision damage. Wet AMD is rarer and more severe but also more treatable than dry AMD.
How many kinds of macular degeneration are there?
There are two main types of age-related macular degeneration: dry (atrophic) and wet (neovascular or exudative.) In Dry Macular Degeneration, fatty deposits called DRUSEN develop on the macula. Researchers believe that these spots are deposits or debris from deteriorating tissue.
What is the macula of the eye?
What is the macula of the eye? The macula is the part of your eye that processes what you see directly in front of you (your central vision). It's part of your retina and is key to your vision. The macula is the round area at the center of your retina, at the back of your eyeball.
Is retinal edema the same as macular edema?
In the retina, blisters of fluid form and swell the retina—this is macular edema. Factors likely to cause macular edema include conditions that: Cause more fluid to leak from blood vessels (diabetes and high blood pressure) Increase inflammation in the eye (surgery, inflammatory diseases)
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is the cause of vision loss in older people?
Macular degeneration, or age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is a leading cause of vision loss in Americans 60 and older. It is a disease that destroys your sharp, central vision. You need central vision to see objects clearly and to do tasks such as reading and driving.
Not Valid for Submission
362.60 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of peripheral retinal degeneration, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Convert 362.60 to ICD-10
The following crosswalk between ICD-9 to ICD-10 is based based on the General Equivalence Mappings (GEMS) information:
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 362.60 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
The retina is a layer of tissue in the back of your eye that senses light and sends images to your brain. In the center of this nerve tissue is the macula. It provides the sharp, central vision needed for reading, driving and seeing fine detail.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is the difference between macular degeneration and exudative macular degeneration?
Blurred vision: Those with nonexudative macular degeneration may be asymptomatic or notice a gradual loss of central vision, whereas those with exudative macular degeneration often notice a rapid onset of vision loss (often caused by leakage and bleeding of abnormal blood vessels).
What percentage of the retina is covered by the macula?
The area of the macula comprises only about 2.1% of the retina, and the remaining 97.9% (the peripheral field) remains unaffected by the disease. Even though the macula provides such a small fraction of the visual field, almost half of the visual cortex is devoted to processing macular information.
What is the term for blurred vision in the center of the eye?
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration ( AMD or ARMD ), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes.
How does genetic testing help with AMD?
Genetic testing can help identify whether a patient with AMD is at a greater risk of developing the condition and can inform disease progression. Genetic testing can also allow researchers to identify whether patients are more or less likely to respond to treatments, such anti-VEGF medication or complement inhibitors. However, there remain several challenges to using predictive tools which incorporate genetic variation in clinical practice. As well as our limited understanding of the way that different genetic variants and environmental factors interact to influence AMD risk, the single nucleotide polymorphisms which are common in the population have small effects on individual patients with AMD. Therefore, there is increasing interest in understanding the functional consequences of rare mutations, which often have more pronounced effects. Genetic testing to guide clinical management is not currently recommended.
What is distortion of vision?
Distorted vision in the form of metamorphopsia, in which a grid of straight lines appears wavy and parts of the grid may appear blank: Patients often first notice this when looking at things like miniblinds in their home or telephone poles while driving. There may also be central scotomas, shadows or missing areas of vision
Is macular degeneration more prevalent in Europeans than in Asians?
more than 240. The prevalence any age-related macular degeneration is higher in Europeans than in Asians and Africans. There is no difference in prevalence between Asians and Africans. The incidence of age-related macular degeneration and its associated features increases with age and is low in people <55 years of age.
Can macular degeneration be diagnosed early?
Diagnosis of age-related macular degeneration depends on signs in the macula, not necessarily vision. Wet AMD is typically the advanced progression of dry AMD and will require additional diagnostic tools. Additionally, early diagnosis of wet AMD can prevent further visual deterioration and potentially improve vision.
How to tell if you have wet macular degeneration?
The symptoms for wet macular degeneration include the following: • visual distortions; • decrease in or loss of central vision; and. • central blurry spot. Diagnosis. Macular degeneration is diagnosed during a thorough eye examination. The physician will look for drusen and mottled pigmentation in the macula.
What does a doctor look for in a macular test?
The physician will look for drusen and mottled pigmentation in the macula. In addition, the physician may have the patient look at an Amsler grid , which looks like a checkerboard. This test can determine the location and extent of the macular damage.
What is the cause of vision loss in older people?
Macular degeneration is a chronic eye condition that occurs because of deterioration of the tissue in the macula—the central portion of the retina responsible for central vision. Sometimes referred to as age-related macular degeneration , it is the leading cause of severe vision loss in people aged 60 and older.
What test is used to determine the extent of damage to the macula?
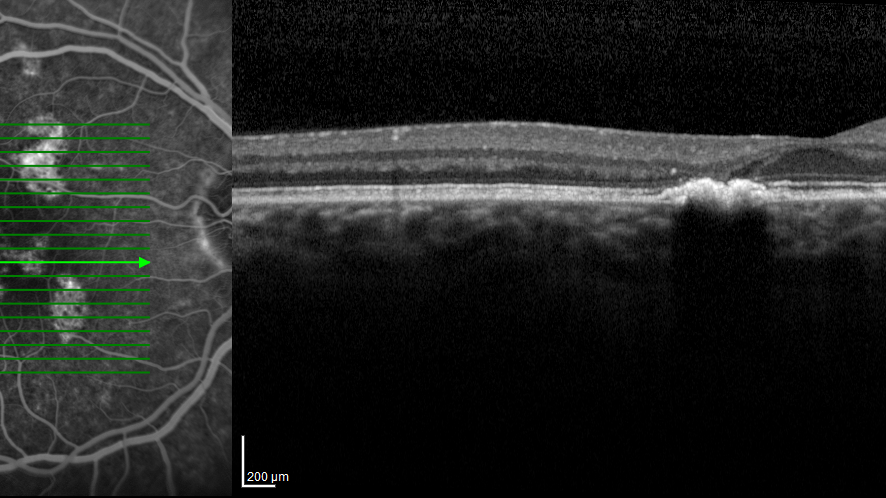
The physician may also choose to perform a fluorescein angiography to evaluate the extent of the damage to the macula. Another test that may be done is optical coherence tomography which identifies the area of retinal thickening or thinning. It is extremely beneficial to diagnosis macular degeneration early.
Can macular degeneration cause blindness?
Although it does not lead to total blindness, it can cause blurred central vision or a blind spot in the center of the visual field. Typically, the condition does not affect peripheral vision. Macular degeneration is a gradually progressive disease that is nonreversible.
Can macular degeneration be reversed?
Although the damage from macular degeneration cannot be reversed, early treatment can slow progression.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left radius fracture
- 2. icd 10 code for tachypnea
- 3. icd-10-cm code for rheumatoid bursitis unspecified site
- 4. icd 10 code for r63.0
- 5. icd 10 code for f5109
- 6. icd 10 code for mobility deficit
- 7. icd 10 code for pulmonary artery hypertension
- 8. icd 10 code for indwelling suprapubic catheter
- 9. icd-10-pcs code for lysis of abdominal adhesions
- 10. what is the icd 10 code for occult blood feces