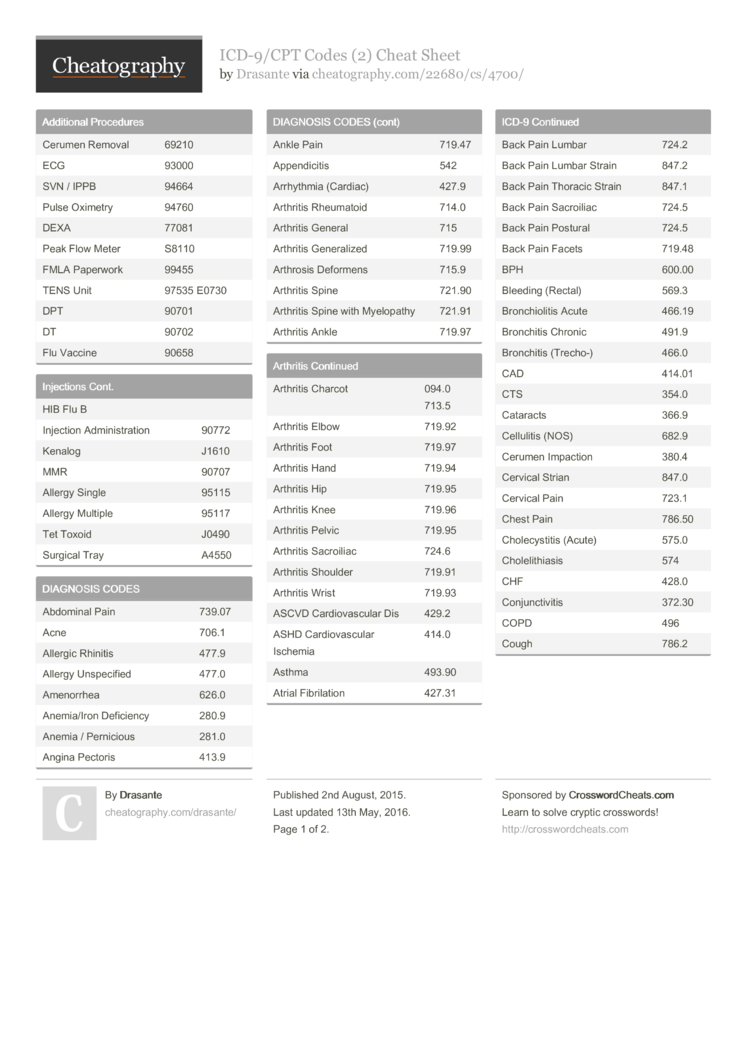
What is the diagnosis code for Schatzki's ring?
Search results for “Schatzki's ring”. Diagnosis Code K222 Billable Diseases of the digestive system / Diseases of esophagus, stomach and duodenum / Other diseases of esophagus.
What is a Schatzki ring?
A Schatzki ring, first identified in 1944 by Dr. Richard Schatzki, is a thin, circular membrane of tissue that forms in the lower esophagus, the tube that connects an individual's mouth to their stomach. A Schatzki ring causes narrowing of the canal of the esophagus.
What is the pathophysiology of Schatzki ring?
A Schatzki ring causes narrowing of the canal of the esophagus (i.e., lumen), and eventually may lead to difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia. The presence of a Schatzki ring in individuals is considered to be the most common cause of episodic solid food dysphagia and food impaction, or blockage of the esophagus by food, in adults.
Can Gerd cause Schatzki ring in esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is a complication of GERD and involves permanent changes to the lining of the esophagus, which may also lead to the formation of a Schatzki ring. Is a Schatzki ring hereditary? A Schatzki ring typically is nonhereditary -- usually it is not passed down from parents to children.
What is the ICD-10 code for schatzki ring?
Congenital stenosis and stricture of esophagus The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q39. 3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for esophageal ring?
K22. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K22. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis code K22 8?
ICD-10 code: K22. 8 Other specified diseases of oesophagus.
What is the code for rupture of the esophagus?
ICD-10 code K22. 3 for Perforation of esophagus is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is Schatzki ring?
A Schatzki's ring is a ring of tissue that forms inside the esophagus, the tube that carries food and liquid to your stomach. This ring makes the esophagus narrow in one area, close to where it meets the stomach. It can make it hard to swallow.
What is a non obstructing Schatzki ring?
A Schatzki ring is a thin ring of tissue that forms in your esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach. The ring is noncancerous and made of tissue that lines your esophagus.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for esophageal stricture?
530.3 - Stricture and stenosis of esophagus | ICD-10-CM.
What K31 89?
ICD-10 code K31. 89 for Other diseases of stomach and duodenum is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD 10 code for irregular Z line?
89.
Why is it called a Mallory Weiss tear?
Mallory Weiss tears are named after two physicians named Kenneth Mallory and Soma Weiss. In 1929, they described tears in the lower esophagus in people who experienced forceful retching or vomiting after drinking too much alcohol.
Is rupture in the esophagus assigned code K22 3?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K22. 3: Perforation of esophagus.
What is the ICD-10 code for hiatal hernia?
Q40. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q40. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does thickening of the esophageal wall mean?
Accurate description of the esophageal mural thickening will encourage referring physicians to consider infection, inflammation, and neoplasm – rather than fibrotic stricture or abnormal motility – as the cause of any dysphagia reported by the patient.
What is eosinophilic esophagitis?
Eosinophilic esophagitis is an allergic condition that happens in the esophagus. The esophagus becomes inflamed and does not contract properly. It can get narrowed and develop rings or abscesses. The symptoms happen when your immune system makes white blood cells in reaction to an allergen.
What is the ICD 10 code for hiatal hernia?
Q40. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q40. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is next to the esophagus?
Just below the junction of the throat and the esophagus is a band of muscle called the upper esophageal sphincter. Slightly above the junction of the esophagus and the stomach is another band of muscle called the lower esophageal sphincter.
What is the code for Schatzki's Ring?
Although the default code for unspecified Schatzki's Ring is the congenital code ,#N#1. Unless it meets the UHDDS criteria, I wouldn't code it.#N#2. If it meets the UHDDS criteria, perhaps a query would be appropriate for clarification as to whether it is congenital or acquired.
What is the congenital version of Schatzki's Ring?
The congenital version of Schatzki's ring (750.3) is a MCC and includes the following terms: Absent esophagus. Atresia of esophagus. Congenital: esophageal ring. stenosis of esophagus. stricture of esophagus. Congenital fistula: esophagobronchial.
When are diagnoses coded?
AHA coding guidelines specify that diagnoses are only coded when they#N#are: evaluated, treated, complicate another condition, affect LOS,#N#require increased nursing care, etc. If a diagnosis is present but does#N#not affect patient's treatment in anyway, it should not be reported.#N#Hope this helps.
What is the most common type of Schatzki ring?
The most common type is a sliding hia tal hernia, or type 1, which can result in irritation of the esophagus due to the rise of acidic stomach contents. ...
Where is the Schatzki Ring?
A Schatzki ring, first identified in 1944 by Dr. Richard Schatzki, is a thin, circular membrane of tissue that forms in the lower esophagus, the tube that connects an individual's mouth to their stomach.
What is the treatment for a Schatzki ring?
Treatment is aimed at widening the diameter of the Schatzki ring and can include balloon dilation. If acid reflux is also present, the use of proton pump inhibitor medications may be indicated.
Why does my esophagus get a Schatzki ring?
Prolonged irritation of the esophagus due to acid reflux may result in Schatzki ring formation. Barrett’s esophagus is a complication of GERD and involves permanent changes to the lining of the esophagus, which may also lead to the formation of a Schatzki ring.
Can a Schatzki ring be asymptomatic?
While most individuals who have a Schatzki ring are asymptomatic, those who have symptoms usually experience difficulty swallowing, the sensation that food is stuck in their chest after swallowing, heartburn, and regurgitation of food. Diagnosis involves a thorough discussion of symptoms and additional testing if necessary.
Is a Schatzki ring hereditary?
A Schatzki ring typically is nonhereditary -- usually it is not passed down from parents to children. However, the potential underlying causes, such as GERD and Barrett’s esophagus, can be hereditary.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for osteoarthritis of bilateral knees
- 2. icd 10 code for nondisplaced fracture right ankle initial encounter
- 3. icd 10 code for positive ppd skin test
- 4. icd 10 code for lung scarring
- 5. icd 10 code for lac ;ip
- 6. icd-10 code for post op bile leak
- 7. icd 10 code for compression fx t12
- 8. icd 10 code for k76.0
- 9. icd 10 code for sepsis e coli
- 10. icd 10 code for right hip replacement