What is the scientific name for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T31.51 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Burns involving 50-59% of body surface with 10 -19% third degree burns. Burns of 50-59% of body surface w 10-19% third degree burns; Burn injury; Burn involving 50-59 percent of body surface, with 10-19 percent of body surface with full thickness burn.
What is the ICD 9 code for medical diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 466.19 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 466.19 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What are the risk factors associated with Stenotrophomonas infections?
041.9 Bacterial infection, unspecified, in conditions classified elsewhere and of unspecified site convert 041.9 to ICD-10-CM Free ICD-9-CM Codes 2015 / Index · 2014 / Index · 2013 / Index
When was Stenotrophomonas first found?
Search Results. 262 results found. Showing 251-262: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T31.30 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Burns involving 30-39% of body surface with 0% to 9% third degree burns. Burns of 30-39% of body surfc w 0% to 9% third degree burns; Burn any degree involving 30-39 percent of body surface; Burn any degree involving 30-39 percent of body surface with third degree less …
What is the ICD-10 code for stenotrophomonas?
B96. 5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B96. 5 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are ICD-9 diagnosis codes?
The International Classification of Diseases Clinical Modification, 9th Revision (ICD-9 CM) is a list of codes intended for the classification of diseases and a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or disease.Aug 1, 2010
What is B96 89?
ICD-10 code B96. 89 for Other specified bacterial agents as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for gram-negative bacteria?
To identify patients with possible Gram-negative bacteremia in the NPR, we used diagnoses of “septicemia/sepsis due to other Gram-negative organisms” (ICD-10 code A41. 5).Feb 12, 2015
How do I find diagnosis codes?
If you need to look up the ICD code for a particular diagnosis or confirm what an ICD code stands for, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website to use their searchable database of the current ICD-10 codes.Jan 9, 2022
What is the difference between ICD-9 codes and ICD-10 codes?
ICD-9-CM codes are very different than ICD-10-CM/PCS code sets: There are nearly 19 times as many procedure codes in ICD-10-PCS than in ICD-9-CM volume 3. There are nearly 5 times as many diagnosis codes in ICD-10-CM than in ICD-9-CM. ICD-10 has alphanumeric categories instead of numeric ones.
What is the ICD-10 code for GPC?
Chronic giant papillary conjunctivitis, bilateral H10. 413 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H10. 413 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for GPC bacteremia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Bacteremia R78. 81.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R50 9?
ICD-10 code: R50. 9 Fever, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
What is GPC bacteremia?
Gram-positive cocci are the most common cause of bloodstream infections in hemodialysis patients, with Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci causing most infections.
What is the correct ICD-10 code for leukocytosis?
288.60 - Leukocytosis, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for bacterial infection?
ICD-10 code: A49. 9 Bacterial infection, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
What is the ICd 9 classification?
The International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) is based on the World Health Organization’s Ninth Revision, International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9). ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. The ICD-9 was used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates until 1999, when use of ICD-10 for mortality coding started.
What is tabular list?
a tabular list containing a numerical list of the disease code numbers in tabular form; an alphabetical index to the disease entries; and. a classification system for surgical, diagnostic, and therapeutic procedures (alphabetic index and tabular list). are the U.S. governmental agencies responsible for overseeing all changes ...

Overview
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is an aerobic, nonfermentative, Gram-negative bacterium. It is an uncommon bacterium and human infection is difficult to treat. Initially classified as Bacterium bookeri, then renamed Pseudomonas maltophilia, S. maltophilia was also grouped in the genus Xanthomonas before eventually becoming the type species of the genus Stenotrophomonas in 1993.
Pathogenesis
S. maltophilia frequently colonizes humid surfaces such as the tubes used in mechanical ventilation and indwelling urinary catheters as well as medical devices such as suction catheters and endoscopes. Infection is usually facilitated by the presence of prosthetic material (plastic or metal), and the most effective treatment is removal of the prosthetic material (usually a central venous catheter or similar device). S. maltophilia adheres strongly and forms biofilmon plastic su…
Treatment
S. maltophilia is naturally resistant to many broad-spectrum antibiotics (including all carbapenems) due to the production of two inducible chromosomal metallo-β-lactamases (designated L1 and L2). This makes treatment of infected patients very difficult. S. maltophilia is ubiquitously present in the environment and impossible to eradicate, which makes prevention also extremely difficult.
Sensitivity testing requires nonstandard culture techniques (incubation at 30 °C). Testing at the …
Epidemiology
Stenotrophomonas infections have been associated with high morbidity and mortality in severely immunocompromised and debilitated individuals. Risk factors associated with Stenotrophomonas infection include HIV infection, malignancy, cystic fibrosis, neutropenia, mechanical ventilation, central venous catheters, recent surgery, trauma, prolonged hospitalization, intensive care unit admission and broad-spectrum antibiotic use.
History
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia has had multiple different names in the past. It was first found in a pleural effusion in 1943 and given the name Bacterium bookeri. It was then renamed to Pseudomonas maltophilia in 1961. It was moved to the genus Xanthomonas in 1983, and most recently to Stenotrophomonas in 1993.
External links
• Stenotrophomonas maltophilia article at eMedicine.
• The genus Stenotrophomonas
• Stenotrophomonas Genome Projects from Genomes OnLine Database
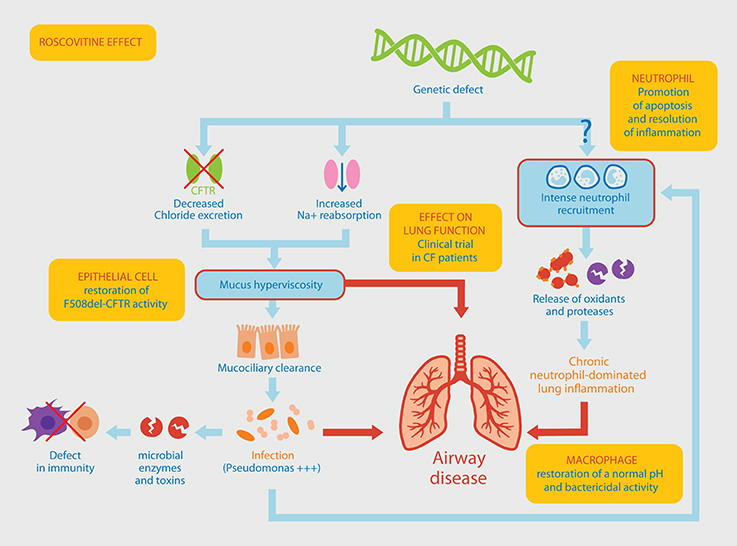
• Relevance to Cystic Fibrosis
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for renal insufficiency.
- 2. icd 10 code for swollen maxillary
- 3. icd 10 code for rt eye pain
- 4. icd-10-cm code for uterine fibroids
- 5. icd 10 code for fell down embankment
- 6. icd 9 code for influenza vaccine
- 7. icd 9 code for inner ear infection
- 8. icd 10 code for screening respiratory
- 9. icd 10 code for suicide risk
- 10. icd 9 code for bilateral leg edema