What is the ICD 10 code for difficulty urination?
The ICD-10-CM code R39.198 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like abnormal urination, alteration in patterns of urinary elimination, automatic micturition, bladder pain, difficulty initiating bladder emptying , difficulty passing urine, etc.
What is the ICD 10 code for incontinence?
Urge incontinence
- N39.41 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N39.41 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N39.41 - other international versions of ICD-10 N39.41 may differ.
How to manage stress urinary incontinence?
- A personalized treatment plan targeted to your specific condition. There is no ‘one-size-fits-all’ solution for stress incontinence. ...
- Proper instruction on how to perform pelvic floor muscle exercises. Women with urinary incontinence are less likely to be able to ‘feel’ and contract their pelvic floor muscles and are ...
- Better outcomes. ...
What are the symptoms of stress incontinence?
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Laughing
- Standing up
- Lifting something heavy
- Running
- Having sex
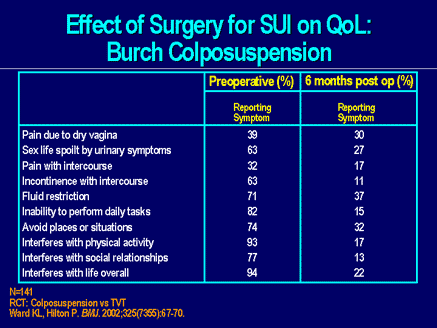
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary stress incontinence?
ICD-10 code N39. 3 for Stress incontinence (female) (male) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is ICD-10 code R32?
ICD-10 code: R32 Unspecified urinary incontinence.
How do you code urinary incontinence?
ICD-10 Code for Other specified urinary incontinence- N39. 498- Codify by AAPC.
What is ICD-10 code N39?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N39: Other disorders of urinary system.
What is stress incontinence?
Stress incontinence happens when physical movement or activity — such as coughing, laughing, sneezing, running or heavy lifting — puts pressure (stress) on your bladder, causing you to leak urine. Stress incontinence is not related to psychological stress.
Which condition is included in code R32 Unspecified urinary incontinence?
This is stress incontinence. If bladder muscles become too active, you may feel a strong urge to go to the bathroom when you have little urine in your bladder. This is urge incontinence or overactive bladder.
What are the 4 types of incontinence?
Types of urinary incontinence include:Stress incontinence. Urine leaks when you exert pressure on your bladder by coughing, sneezing, laughing, exercising or lifting something heavy.Urge incontinence. ... Overflow incontinence. ... Functional incontinence. ... Mixed incontinence.
How is stress incontinence treated?
The treatments your doctor recommends may include:Pelvic floor muscle exercises. Your provider or physical therapist can help you learn how to do Kegel exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles and urinary sphincter. ... Fluid consumption. ... Healthy lifestyle changes. ... Bladder training.
What is CPT code 1090F?
Conducting a bladder control assessment can help detect the presence or absence of urinary incontinence or other bladder control issues in your 65-and-older patients. CPT II code 1090F indicates that the assessment took place and should only be billed on claims for evaluation and management services.
Can N39 0 be a primary diagnosis?
CMS did note that some “unspecified” codes could still be used. For example, one of the codes they reclassified as “acceptable” — Urinary tract infection, site not specified (N39. 0) — is often the primary diagnosis code.
What is the ICD-10 code for voiding dysfunction?
Other difficulties with micturition The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R39. 19 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R39.
What is the ICD-10 code for nocturnal enuresis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Nocturnal enuresis N39. 44.
What is UUI medical term?
[8,9] Urge incontinence (UUI), or “overactive bladder,” is the second most common type of urinary incontinence. UUI is characterized by the unexpected loss of urine while suddenly feeling the need to urinate.
What is the ICD-10 code for OAB?
N32. 81 Overactive bladder - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is nocturia medical term?
Nocturia is a condition in which you wake up during the night because you have to urinate. Causes can include high fluid intake, sleep disorders and bladder obstruction. Treatment of nocturia includes certain activities, such as restricting fluids and medications that reduce symptoms of overactive bladder.
What is mixed urinary incontinence?
The International Continence Society defines mixed urinary incontinence (MUI) as the complaint of involuntary leakage of urine associated with urgency and also with exertion, effort, sneezing, or coughing [1].
Not Valid for Submission
625.6 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of stress incontinence, female. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Convert 625.6 to ICD-10
The following crosswalk between ICD-9 to ICD-10 is based based on the General Equivalence Mappings (GEMS) information:
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 625.6 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Pain is a feeling triggered in the nervous system. Pain may be sharp or dull. It may come and go, or it may be constant. You may feel pain in one area of your body, such as your back, abdomen or chest or you may feel pain all over, such as when your muscles ache from the flu.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
Not Valid for Submission
788.30 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of urinary incontinence, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 788.30 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Urinary incontinence (UI) is loss of bladder control. Symptoms can range from mild leaking to uncontrollable wetting. It can happen to anyone, but it becomes more common with age. Women experience UI twice as often as men.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What happens if you have no urinary retention?
If no leakage occurs, and there is no urinary retention, the patient is discharged from the hospital. When the procedure is performed under general anesthesia and the bladder is filled, an 8F feeding tube is inserted to empty the bladder and then removed. All patients receive perioperative antibiotics.
What is urodynamics in urology?
European Association of Urology guidelines on urinary incontinence (EAU, 2013) stated that “'urodynamics is generally used as a collective term for all tests of bladder and urethral function. These guidelines will review both non-invasive estimation of urine flow, i.e., uroflowmetry, and invasive tests, including multichannel cystometry, ambulatory monitoring and video-urodynamics, and different tests of urethral function, such as urethral pressure profilometry, Valsalva leak point pressure estimation and retrograde urethral resistance measurement. Multichannel cystometry, ambulatory monitoring and video-urodynamics aim to observe the effects on intra-vesical and intra-abdominal pressures while reproducing a patient's symptoms. Bladder filling may be artificial or physiological and voiding is prompted. Any incontinence observed may be categorized as SUI, detrusor overactivity (DO) incontinence, a mixture of SUI/DO incontinence, or, rarely, urethral relaxation incontinence. A test may fail to reproduce a patient's symptoms because of poor diagnostic accuracy or because the symptoms are not directly attributable to a urodynamically measurable phenomenon. Urodynamic testing is widely used as an adjunct to clinical diagnosis, to direct decisions about treatment and to provide prognostic information. When clinical diagnosis is difficult because of an unclear history or inconclusive examination, urodynamics may provide the only 'diagnosis' available. Although it is unlikely that carrying out a test, in itself, would alter the outcome of treatment, it remains possible that the test results would influence treatment decisions to such an extent that better outcomes would be achieved. This has been the rationale for using urodynamics prior to surgery."
What is multi channel urodynamics?
Clinicians may perform multi-channel urodynamics in patients with both symptoms and physical findings of stress incontinence who are considering invasive, potentially morbid or irreversible treatments . (Option; Evidence Strength: Grade C)#N#Clinicians should perform stress testing with reduction of the prolapse in women with high grade pelvic organ prolapse (POP) but without the symptom of SUI. Multi-channel urodynamics with prolapse reduction may be used to assess for occult stress incontinence and detrusor dysfunction in these women with associated lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). (Option; Evidence Strength: Grade C)
What is UI in nursing?
Urinary incontinence (UI) is the inability to voluntarily control voiding of urine from the bladder. It affects people of all ages especially elderly women. Urinary incontinence is not part of the normal aging process; however, age-related changes in the functioning of the lower urinary tract make the elderly more susceptible to this malady. There are 4 prevalent types of UI in adults:
Does Aetna recommend multichannel urodynamics?
Aetna considers multi-channel urodynamic studies medically necessary when the member has both symptoms and physical findings of urinary incontinence/voiding dysfunctions (such as stress incontinence, overactive bladder, lower urinary tract symptoms) and there is consideration by the provider to perform invasive, potentially morbid or irreversible treatments after conservative management has been tried and failed.
Is a vaginal cone considered a DME?
Vaginal Cones. Aetna considers weighted vaginal cones (vaginal weights) medically necessary DME when they are used in combination with a structured pelvic floor muscle exercise (Kegel's exercise) program for the treatment of simple (pure) stress UI.
Does Aetna have an artificial urethral sphincter?
Aetna considers the implantation of an artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) medically necessary for the treatment of urinary incontinence (UI) due to intrinsic urethral sphincter deficiency (IUSD) for members with any of the following indications:

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left anterior thigh strain
- 2. icd 10 code for left shoulder tendinitis unspecified
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for thyroid nodules
- 4. icd 10 code for adult onset diabetes
- 5. icd code for autusm
- 6. icd 10 code for thyroglobulin antibody positive
- 7. icd 10 code for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for symptomatic fibroids?
- 9. icd 10 code for left toe paronychia
- 10. icd 10 cm code for acute lymphadenitis secondary to hiv infection