What is the ICD 10 code for lupus?
710.0 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the ICD-9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 710.0 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 710.0 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for auto immune disease?
autoimmune disease, single organ or single cell-type -code to relevant condition category. Systemic connective tissue disorders. M32. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M32. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code.

What is ICD-10 code for systemic lupus erythematosus?
Systemic lupus erythematosus, unspecified M32. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M32. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the difference between lupus and systemic lupus erythematosus?
When people use the term “lupus,” they usually refer to systemic lupus erythematosus, or “SLE.” Throughout this website, the term “lupus” is used to signal systemic lupus, since SLE constitutes the most common form of the disease. Systemic lupus is so-named because it affects many different organ systems in the body.
How do you code lupus unspecified?
Systemic lupus erythematosus, organ or system involvement unspecified. M32. 10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is systemic lupus erythematosus pathology?
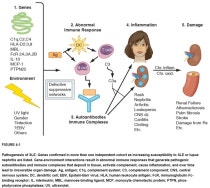
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, lupus) is characterized by a global loss of self-tolerance with activation of autoreactive T and B cells leading to production of pathogenic autoantibodies and tissue injury. Innate immune mechanisms are necessary for the aberrant adaptive immune responses in SLE.
What are the 4 types of lupus?
But there are four kinds of lupus:Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the most common form of lupus.Cutaneous lupus, a form of lupus that is limited to the skin.Drug-induced lupus, a lupus-like disease caused by certain prescription drugs.Neonatal lupus, a rare condition that affects infants of women who have lupus.
What are the 3 types of lupus?
There are three types: Acute cutaneous lupus. Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, or discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
What is systemic lupus erythematosus unspecified?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is the most common type of lupus. SLE is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. It can affect the joints, skin, brain, lungs, kidneys, and blood vessels.
What does unspecified mean in ICD-10 codes?
An “unspecified” code means that the condition is unknown at the time of coding. An “unspecified” diagnosis may be coded more specifically later, if more information is obtained about the patient's condition.
What is diagnosis code m32 9?
9: Systemic lupus erythematosus, unspecified.
Why is SLE called lupus?
Because the location of this rash is the same as the common markings of a wolf, the name "lupus" (wolf in Latin) was given to this disease many years ago. Other skin problems that may happen include large red, circular rashes (plaques), which may scar (called discoid lupus).
What are the top 5 signs of lupus?
Fatigue. About 90 percent of people with lupus experience some level of fatigue. ... Unexplained fever. One of the early symptoms of lupus is a low-grade fever for no apparent reason. ... Hair loss. ... Skin rash or lesions. ... Pulmonary issues. ... Kidney inflammation. ... Painful, swollen joints. ... Gastrointestinal problems.More items...
What are the 11 symptoms of lupus?
The 11 Signs of Lupus: What You Need to KnowA butterfly-shaped rash across both sides of the face.Raised, red skin patches.Sensitivity to light.Ulcers in the mouth or nose.Arthritis plus swelling or tenderness in two or more joints.Seizures or other nervous system problems.Excessive protein in urine.More items...•
What is the most serious form of lupus?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the most common and most serious type of lupus. SLE affects all parts of the body. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus, which affects only the skin.
Are there different stages of lupus?
Lupus nephritis is divided into 6 different stages or classes based on the results of a kidney biopsy. These classes are different from the stages of chronic kidney disease. Some signs and symptoms associated with the different classes of lupus nephritis can be found in the table below.
How do you get lupus erythematosus?
It's likely that lupus results from a combination of your genetics and your environment. It appears that people with an inherited predisposition for lupus may develop the disease when they come into contact with something in the environment that can trigger lupus. The cause of lupus in most cases, however, is unknown.
What is the most common type of lupus?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is the most common type of lupus. SLE is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs.
What happens if you have lupus?
If you have lupus, your immune system attacks healthy cells and tissues by mistake. This can damage your joints, skin, blood vessels and organs. There are many kinds of lupus. The most common type, systemic lupus erythematosus, affects many parts of the body. Discoid lupus causes a rash that doesn't go away. Subacute cutaneous lupus causes sores after being out in the sun. Another type can be caused by medication. Neonatal lupus, which is rare, affects newborns.
What does the no map flag mean?
No Map Flag - The no map flag indicates that a code in the source system is not linked to any code in the target system. Combination Flag - The combination flag indicates that more than one code in the target system is required to satisfy the full equivalent meaning of a code in the source system.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is a see also note?
A “see also” instruction following a main term in the index instructs that there is another main term that may also be referenced that may provide additional index entries that may be useful. It is not necessary to follow the “see also” note when the original main term provides the necessary code.
What is a discoid lupus?
Clinical Information. A chronic inflammatory connective tissue disease marked by skin rashes, joint pain and swelling, inflammation of the kidneys, inflammation of the fibrous tissue surrounding the heart (i.e., the pericardium), as well as other problems.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
ICD-9-CM 695.4 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim , however, 695.4 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What is the name of the disease that affects the skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, heart, and
Not all affected individuals display all of these problems. Also called systemic lupus erythematosus. An autoimmune, connective tissue chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, heart, and the peripheral blood cells. It is more commonly seen in women than men.
How long does it take to diagnose Lupus?
joint pain or swelling. muscle pain. fever with no known cause. red rashes, often on the face (also called the "butterfly rash") there is no one test to diagnose lupus, and it may take months or years to make the diagnosis.
What is pericardial inflammation?
A chronic inflammatory connective tissue disease marked by skin rashes, joint pain and swelling, inflammation of the kidneys, inflammation of the fibrous tissue surrounding the heart (i.e., the pericardium ), as well as other problems. Not all affected individuals display all of these problems.
Does lupus erythematosus go away?
This can damage your joints, skin, blood vessels and organs. There are many kinds of lupus. The most common type, systemic lupus erythematosus, affects many parts of the body. Discoid lupus causes a rash that doesn't go away. Subacute cutaneous lupus causes sores after being out in the sun.
Can a newborn get Lupus?
Neonatal lupus, which is rare, affects newborns. Anyone can get lupus, but women are most at risk. Lupus is also more common in african american, hispanic, asian and native american women. The cause of lupus is not known. Lupus has many symptoms. Some common ones are. joint pain or swelling. muscle pain.
What is a chronic, relapsing, inflammatory, and often febrile multisystemic disorder of
A chronic, relapsing, inflammatory, and often febrile multisystemic disorder of connective tissue, characterized principally by involvement of the skin, joints, kidneys, and serosal membranes. It is of unknown etiology, but is thought to represent a failure of the regulatory mechanisms of the autoimmune system.
What is a sle?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (sle) Clinical Information. A chronic inflammatory connective tissue disease marked by skin rashes, joint pain and swelling, inflammation of the kidneys, inflammation of the fibrous tissue surrounding the heart (i.e., the pericardium), as well as other problems. Not all affected individuals display all of these problems.
What is sle in the body?
A chronic, inflammatory, connective tissue disease that can affect many organs including the joints, skin, heart, lungs, kidneys, and nervous system. It is marked by many different symptoms; however, not everyone with sle has all of the symptoms.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for chronic ingrown toenail
- 2. icd 10 code for history of partial parathyroidectomy
- 3. icd 10 code for grade 3 ac joint separation right
- 4. 2015 icd 10 code for lipoma
- 5. icd 10 code for possible retinal detachment unspecified
- 6. icd-10 code for iv drug use
- 7. icd-10 code for cardiogenic shock
- 8. icd 9 code for vision loss
- 9. what is the icd-10 code for costochondritis
- 10. icd 10 code for phytophotodermatitis