Which is worse a diastolic or systolic heart murmur?
Stenosis of the aortic or pulmonic valves will result in a systolic murmur as blood is ejected through the narrowed orifice. Conversely, regurgitation of the same valves will result in a diastolic murmur as blood flows backward through the diseased valve when ventricular pressures drop during relaxation. Click to see full answer.
Is there surgery for systolic murmur?
Surgery may be needed to correct a damaged or leaky valve that causes a heart murmur. Depending on your heart condition, your doctor may recommend one of several heart valve treatment options. To repair a valve, your doctor may recommend one of the following procedures: Balloon valvuloplasty.
When to worry about a heart murmur?
- chest pain
- trouble doing usual activities/exercise
- shortness of breath
- sudden weight gain
- ankle swelling
- dizziness or fainting
- extreme tiredness
- fever or night sweats
- any symptoms that are out of the ordinary and causing you concern.
What causes systolic murmur?
What are heart murmurs in children?
- Systolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs when the heart contracts.
- Diastolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs when the heart relaxes.
- Continuous murmur. A heart murmur that occurs throughout. the heartbeat. What causes heart murmurs in a child? Heart murmurs may be common in normal, healthy children.
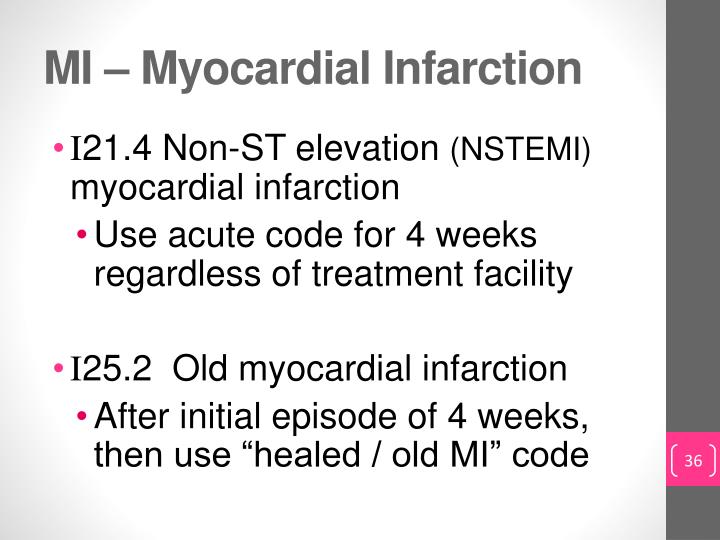
What is the ICD 10 code for systolic murmur?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cardiac murmur, unspecified R01. 1.
Which murmurs are systolic murmur?
Types of murmurs are: Systolic murmur. This happens during a heart muscle contraction. Systolic murmurs are divided into ejection murmurs (because of blood flow through a narrowed vessel or irregular valve) and regurgitant murmurs (backward blood flow into one of the chambers of the heart).
What heart sound is a systolic murmur?
A systolic murmur may sound like a “swish” or “whoosh” after the first heart sound. Blood moving in your heart across a valve is the most common cause of this sound. Often, heart murmurs aren't dangerous. But sometimes, they can point to an underlying heart condition.
What does it mean by systolic murmur?
Definition. A murmur is a series of vibrations of variable duration, audible with a stethoscope at the chest wall, that emanates from the heart or great vessels. A systolic murmur is a murmur that begins during or after the first heart sound and ends before or during the second heart sound.
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic murmurs?
Types of murmurs include: Systolic murmur - occurs during a heart muscle contraction. Systolic murmurs are divided into ejection murmurs (due to blood flow through a narrowed vessel or irregular valve) and regurgitant murmurs. Diastolic murmur - occurs during heart muscle relaxation between beats.
How do you know if a murmur is systolic or diastolic?
Systolic murmurs occur between the first heart sound (S1) and the second heart sound (S2). Diastolic murmurs occur between S2 and S1. In addition, timing is used to describe when murmurs occur within systole or diastole. For example, early systolic, midsystolic or late systolic.
How do you document a heart murmur?
For murmurs, chart where it occurs I the cardiac cycle, loudness, pitch, the location of the where it is heard the best, and other locations where it can be heard. Also record the general type of sound heard and if anything makes the sound change in any way.
What are the four types of heart murmurs?
What Are the Different Types of Murmurs?Systolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during a heart muscle contraction. ... Diastolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during heart muscle relaxation between beats. ... Continuous murmur. A heart murmur that occurs throughout the cardiac cycle.
What are the two types of heart murmurs?
Types of murmurs include: Systolic murmur. This happens during a heart muscle contraction. Systolic murmurs are divided into ejection murmurs (due to blood flow through a narrowed vessel or irregular valve) and regurgitant murmurs (backward blood flow into one of the chambers of the heart).
What is a 1/6 systolic murmur?
Systolic Murmurs. Systolic murmurs are graded on their intensity using the following method: Grade 1/6 - Barely audible. Grade 2/6 - Audible, but faint. Grade 3/6 - Easily heard.
What is S1 and S2 murmur?
S1 is normally a single sound because mitral and tricuspid valve closure occurs almost simultaneously. Clinically S1 corresponds to the pulse. The second heart sound (S2) represents closure of the semilunar (aortic and pulmonary) valves (point d).
How do you grade a systolic murmur?
A grade 1 murmur is barely audible, a grade 2 murmur is louder and a grade 3 murmur is loud but not accompanied by a thrill. A grade 4 murmur is loud and associated with a palpable thrill. A grade 5 murmur is associated with a thrill, and the murmur can be heard with the stethoscope partially off the chest.
Is mitral regurgitation a systolic murmur?
Mitral regurgitation is a systolic murmur, best heard at the left 5th midclavicular line with possible radiation to the left axilla. It is commonly associated with infective endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease, congenital anomalies, and inferior wall myocardial infarctions.
Is aortic stenosis a systolic murmur?
Midsystolic murmurs — also known as systolic ejection murmurs, or SEM — include the murmurs of aortic stenosis, pulmonic stenosis, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy and atrial septal defects.
What are the four types of heart murmurs?
What Are the Different Types of Murmurs?Systolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during a heart muscle contraction. ... Diastolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during heart muscle relaxation between beats. ... Continuous murmur. A heart murmur that occurs throughout the cardiac cycle.
Is tricuspid regurgitation a systolic murmur?
The murmur of tricuspid regurgitation is similar to that of mitral regurgitation. It is a high pitched, holosystolic murmur however it is best heard at the left lower sternal border and it radiates to the right lower sternal border.
What are the symptoms of a heart murmur?
The sounds can vary widely and can be heard with a stethoscope. Symptoms of a heart murmur are chest pain, breathlessness, fatigue, bluish skin color, and rapid heartbeat.
When will ICD-10 CM 785.2 be replaced?
Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 785.2.
What is the ICd 10 code for cardiac murmurs?
785.2 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of undiagnosed cardiac murmurs. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is a code also note?
Code also note - A "code also" note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction.
How many valves does the heart have?
Your heart has four valves. Normally, these valves open to let blood flow through or out of your heart, and then shut to keep it from flowing backward. But sometimes they don't work properly. If they don't, you could have
Can congenital heart defects cause no symptoms?
Many congenital heart defects cause few or no signs and symptoms. They are often not diagnosed until children are older.
What causes a heart murmur?
Heart sounds caused by vibrations resulting from the flow of blood through the heart. Heart murmurs can be examined by heart auscultation, and analyzed by their intensity (6 grades), duration, timing (systolic, diastolic, or continuous), location, transmission, and quality (musical, vibratory, blowing, etc).
What is a postpartum heart murmur?
Clinical Information. A periodic humming or blowing sound heard on auscultation of the heart that can indicate the presence of cardiac disease ; murmurs are the result of vibrations caused by the turbulent flow of blood in the heart or great vessels.
When will the ICD-10-CM R01.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R01.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for anterior talofibular ligament tear
- 2. 2017 icd 10 code for enterocolitis
- 3. icd 10 code for bug bites on neck
- 4. icd 10 dx code for lymphedema in arm
- 5. icd 9 code for palpitation
- 6. icd 10 code for profound visual loss
- 7. icd 10 code for fetal mobility
- 8. icd 10 cm code for: sustanted a first degree burn from a hot drink
- 9. icd 10 code for glioblastoma
- 10. 2015 icd 10 code for crushed by a horse