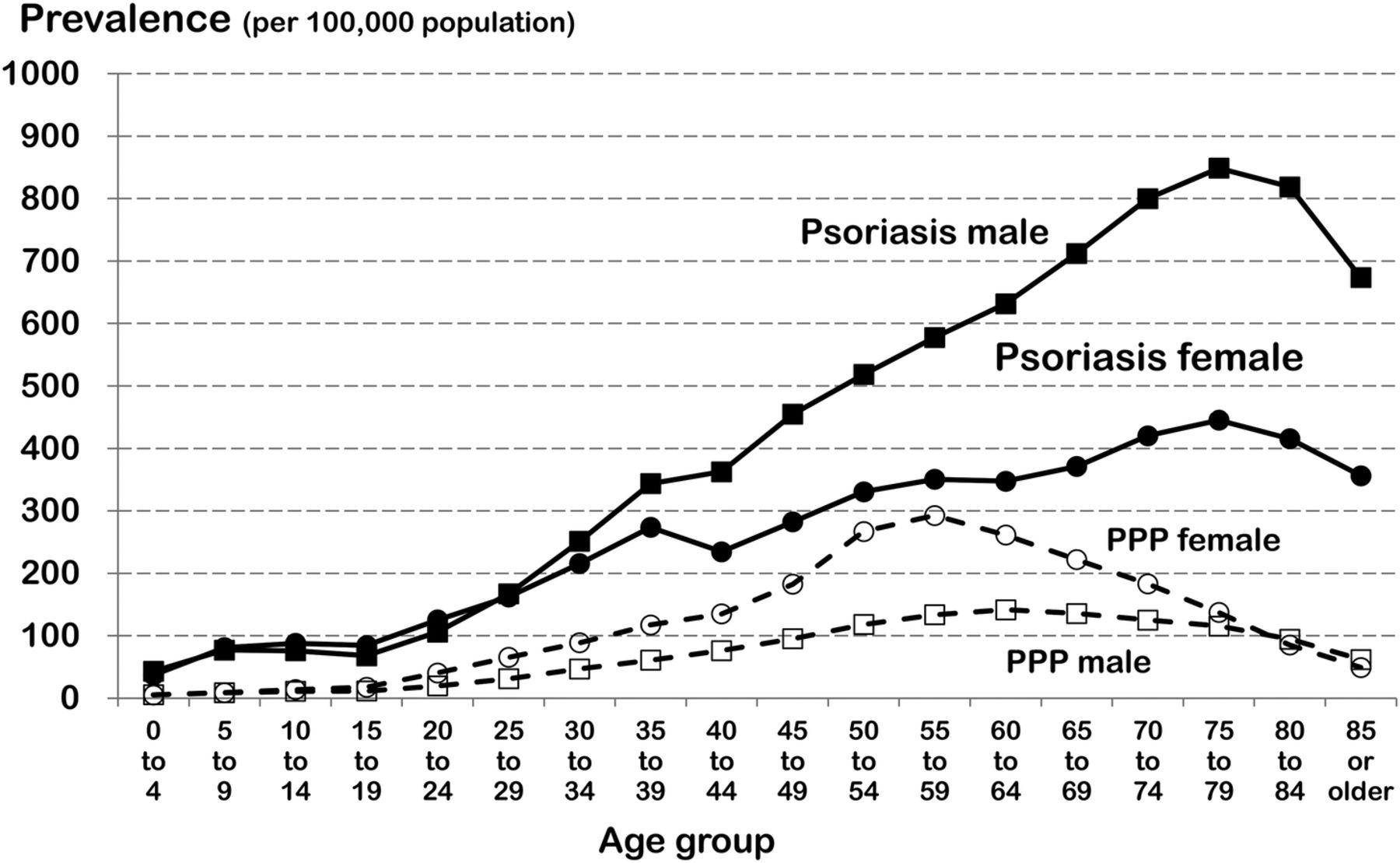
What is the ICD 9 code for retinal telangiectasia?
Long Description: Retinal telangiectasia. This is the 2014 version of the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code 362.15. Code Classification. Diseases of the sense organs (360–389) Disorders of the eye and adnexa (360-379) 362 Other retinal disorders.
What is the ICD 10 code for telangiectasia verrucous?
Telangiectasia, telangiectasis (verrucous) I78.1. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I78.1. Nevus, non-neoplastic. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Araneus nevus. Senile nevus. Spider nevus. Stellar nevus.
What is the ICD 10 code for hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. I78.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I78.0 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I78.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 I78.0 may differ.
What are the characteristics of telangiectasia?
It is characterized by the presence of telangiectasias in the skin, mucous membranes, lungs, brain, liver, and gastrointestinal tract. It results in hemorrhages from the affected areas. An autosomal dominant vascular anomaly characterized by telangiectases of the skin and mucous membranes and by recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding.
Not Valid for Submission
448.0 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 448.0 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are defects in your vascular system. The vascular system includes arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart to other organs; veins carry blood back to the heart. Capillaries connect the arteries and veins. An AVM is a snarled tangle of arteries and veins.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is Mac Tel type 2?
In Mac Tel type 2, fundoscopic exam is initially significant for a decrease of foveal pit, with subsequent foveal or perifoveal ectatic vessels with possible presence of venules diving at a right angle into deeper retinal layers. Grayish discoloration of temporal perifoveal area is the earliest sign present. Ectatic vessels with evidence of venules diving at a right angle into deeper retinal layers. Of note, these findings may be subtle on routine retinal exam. Subretinal neovascularization temporal to fovea may be seen in this disease and can be associated with exudates or hemorrhage. RPE hyperplasia can also be seen at the fovea or temporal perifovea. Also, in later stages, pseudolamellar holes can develop into full-thickness macular holes.
What is the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Mac Tel type 2?
The Mac Tel Project found a prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) of 28% and hypertension (HTN) of 52% in Mac Tel type 2. Such high prevalence of DM, HTN and the age of onset of the disease can point toward a long-term vascular stress as the etiology for this entity. These vascular changes are associated with disruption of the outer nuclear layer, ellipsoid zone and lead to pseudolamellar macular holes. RPE hyperplasia and migration into the inner retinal layers is also seen with time.
What is the visual acuity of type 2?
According to the Mac Tel Project, 50% of type 2 patients with have a visual acuity of 20/32 or better, with a mean visual acuity of 20/40. Mac Tel can rarely lead to 20/200 or worse vision when associated with full-thickness macular hole or subretinal neaovascularization that can lead to a disciform scar in very advanced stages.
What is the most common type of Mac tel?
Mac tel is usually divided into 3 main groups: Type 1: congenital and unilateral. Thought to be similar to and/or possibly a variant of Coats disease. Uncommon. Type 2: acquired and bilateral. The most common form of the three types. Usually found in middle-aged or older patients.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right side clavicle
- 2. icd 10 code for primary open angle glaucoma right eye
- 3. icd 9 code for gait
- 4. icd 10 code for reflux esophagitis secondary to sliding hiatal hernia
- 5. icd 10 code for welder flash
- 6. icd-10 code for allergy to nuts
- 7. icd 10 code for diet low sodium
- 8. icd 10 code for contractures
- 9. icd 10 code for axillary mass
- 10. icd 10 cm code for allergic reaction, right hand