What is celiac disease and how to be diagnosed?
The traditional approach to diagnosing celiac disease is a three-step process:
- Perform a biopsy of the lining of the small intestine. ...
- Place the patient on a gluten-free diet for six months or longer and then perform another biopsy. ...
- Put gluten back in the diet for six months or longer, and then perform a third biopsy. ...
Can You diagnose yourself with celiac disease?
“When people have celiac symptoms, it’s important that they go to a doctor right away for the proper diagnosis, and not just diagnose it themselves and start a gluten-free diet,” Verma said. People who self-diagnose themselves with celiac disease risk a celiac misdiagnosis.
Is celiac really a disease?
Celiac disease is a digestive condition in which consuming gluten triggers an autoimmune response, which means a person’s body begins to attack its own cells, tissues, and organs.
Could a celiac test show a false negative?
Unfortunately, there is another reason that the most common diagnostic tool for celiac disease may be inadequate, and that is false negatives. New studies point out that these blood tests, which have served as the gold standard of early celiac diagnosis, may be not as sensitive as previously thought.
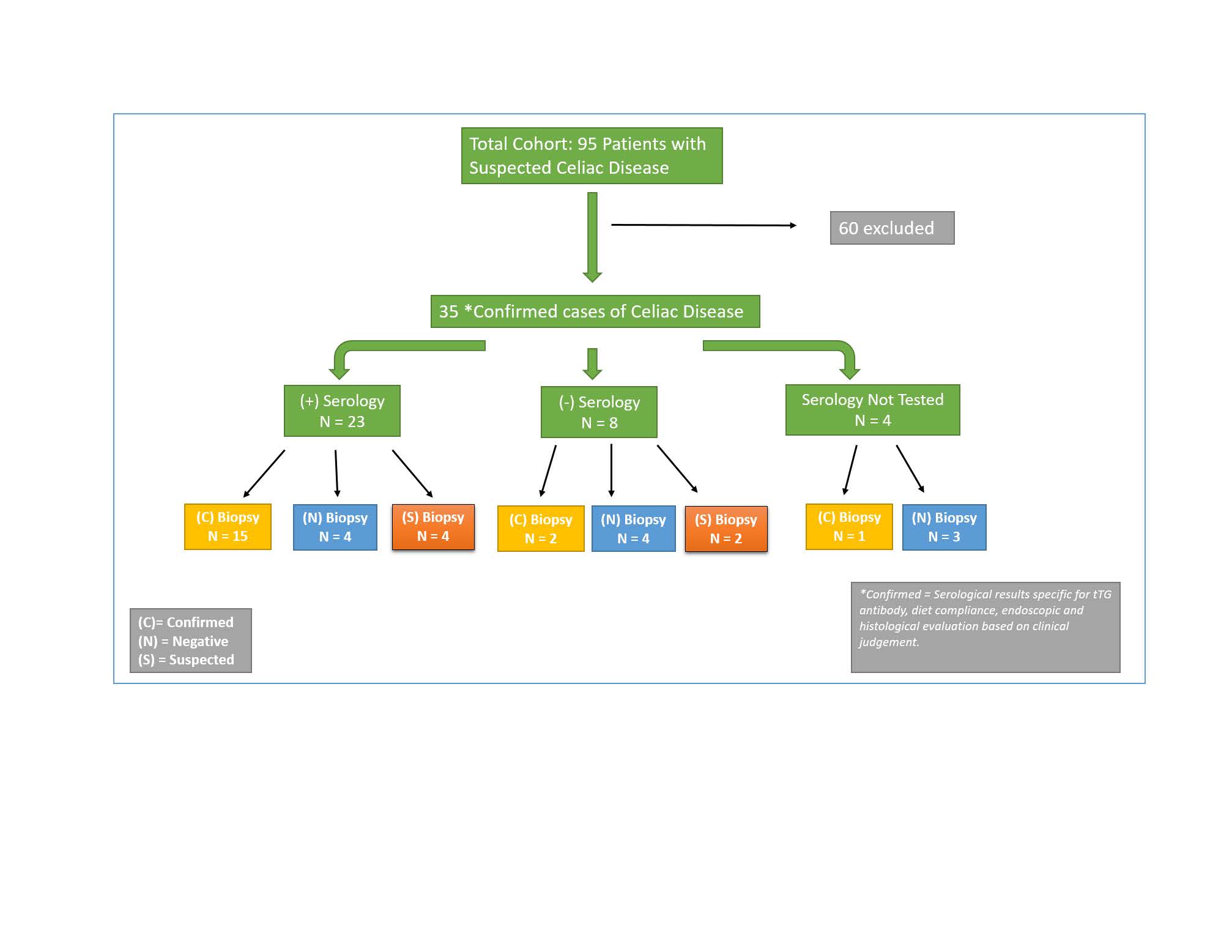
What is the ICD 9 code for celiac disease?
K90. 0 converts to ICD-9-CM: 579.0 - Celiac disease.
What is ICD 10 code for gluten intolerance?
41.
What is the ICD 10 code for family history of celiac disease?
ICD-10-CM Code for Family history of other diseases of the digestive system Z83. 79.
What is the ICD 10 code for positive celiac Serologies?
Assign code R76. 8 other specified abnormal immunological findings in serum for a positive tTG or DMG test. All positive and indeterminate coeliac serology tests are typically followed by an intestinal biopsy. A biopsy is the only method to make a definitive diagnosis of coeliac disease.
What is the blood test for celiac disease called?
tTG-IgA and tTG-IgG tests The tTG-IgA test is the preferred celiac disease serologic test for most patients. Research suggests that the tTG-IgA test has a sensitivity of 78% to 100% and a specificity of 90% to 100%.
What is the ICD-10 code for food intolerance?
ICD-10 code Z91. 01 for Food allergy status is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is diagnosis code Z87 19?
ICD-10 code Z87. 19 for Personal history of other diseases of the digestive system is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
Can F07 81 be used as a primary diagnosis?
Our physicians have used IDC-10 code F07. 81 as the primary diagnosis for patients presenting with post concussion syndrome.
Can B96 81 be used as a primary diagnosis?
The note in ICD-10 under codes B95-B97 states that 'these categories are provided for use as supplementary or additional codes to identify the infectious agent(s) in disease classified elsewhere', so you would not use B96. 81 as a primary diagnosis, but as an additional code with the disease listed first.
What does diagnosis code R76 8 mean?
ICD-10 code R76. 8 for Other specified abnormal immunological findings in serum is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is positive celiac serology?
In patients with positive coeliac disease serology, the diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of characteristic small intestinal mucosal changes. The key diagnostic features are: intestinal histology showing raised intraepithelial lymphocytes (>25 per 100 enterocytes), crypt hyperplasia and villous atrophy (Figure 1)
What does positive tTG mean?
Positive results for tissue transglutaminase (tTG) IgA antibodies are consistent with a diagnosis for celiac disease and possibly for dermatitis herpetiformis.
What is non-celiac gluten sensitivity?
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) is a condition characterized by intestinal and extra-intestinal symptoms related to the ingestion of gluten-containing foods in the absence of celiac disease and wheat allergy.
What is gluten ataxia mean?
Gluten ataxia is a rare immune-mediated disease in which the body's immune system attacks the nervous system as a reaction to ingestion of gluten. It can be related to celiac disease as well as non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
What is ICD-10 code for weight loss?
ICD-10 code R63. 4 for Abnormal weight loss is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for lactose intolerance?
ICD-10 code E73. 9 for Lactose intolerance, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
How does celiac disease affect the body?
Celiac disease affects each person differently. Symptoms may occur in the digestive system, or in other parts of the body. One person might have diarrhea and abdominal pain, while another person may be irritable or depressed. Irritability is one of the most common symptoms in children.
What is gluten sensitivity?
Disease occurring in children and adults characterized by sensitivity to gluten, with chronic inflammation and atrophy of the mucosa of the upper small intestine ; manifestations include diarrhea, malabsorption, steatorrhea, and nutritional and vitamin deficiencies.
How many codes are required to describe a condition?
A code also note instructs that 2 codes may be required to fully describe a condition but the sequencing of the two codes is discretionary, depending on the severity of the conditions and the reason for the encounter.
Can celiac disease cause malnutrition?
A person with celiac disease may become malnourished no matter how much food is consumed. A malabsorption syndrome that is precipitated by the ingestion of foods containing gluten, such as wheat, rye, and barley.
When will the ICD-10-CM K90.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K90.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is irritability a genetic disease?
Irritability is one of the most common symptoms in children. Some people have no symptoms.celiac disease is genetic. Blood tests can help your doctor diagnose the disease. Your doctor may also need to examine a small piece of tissue from your small intestine.
Does gluten affect the immune system?
If you have celiac disease and eat foods with gluten, your immune system responds by damaging the small intestine. Gluten is a protein in wheat, rye and barley. It is found mainly in foods but may also be in other products like medicines, vitamins and even the glue on stamps and envelopes.
What is a celiac test?
As a preliminary diagnostic test for persons with symptoms suggestive of celiac disease; or. To monitor response to a gluten-free diet; or. To screen first-degree relatives of individuals with celiac disease; or. To screen persons with type 1 diabetes for celiac disease.
What is Aetna test for celiac disease?
Aetna considers serological tests for celiac disease (IgA-TTG, IgG-TTG, IgA-EMA, IgG-EMA, IgA-DGP, IgG-DGP) experimental and investigational as an alternative to biopsy for assessing mucosal damage in individuals with celiac disease, and for all other indications because their clinical value has not been established for these indications.
What is the AGA recommendation for CD?
AGA guidelines state that the confirmation of a diagnosis of CD should be based on a combination of findings from the medical history, physical examination, serology, and upper endoscopy with histological analysis of multiple biopsies of the duodenum (Rubio-Tapia, et al.,, 2013). Upper endoscopy with small-bowel biopsy is a critical component of the diagnostic evaluation for persons with suspected CD and is recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
What is CD in a diet?
CD is characterized by an abnormal proximal small intestinal mucosa, and it is associated with a permanent intolerance to gluten. Removal of gluten from the diet leads to a full clinical remission and restoration of the small intestinal mucosa to normality.
When is it necessary to measure IgA?
According to the NIH Consensus Statement (2004), if an individual has suggestive symptoms and negative serologies, it may be necessary to measure serum IgA to detect a selective IgA deficiency. If an IgA deficiency is identified, an IgG-TTG or IgG-EMA test should be performed.
Can HLA-DQ2 be used for CD?
Guidelines on celiac disease from the American Gastroenterological Association (Rubio-Tapia et al, 2013) state that HLA-DQ2/DQ8 testing should not be used routinely in the initial diagnosis of CD. HLA-DQ2/DQ8 genotyping testing should be used to effectively rule out the disease in selected clinical situations:
Is TTG a diagnosis of CD?
Circulating TTG, DGP, and anti-endomysial antibodies have a high degree of sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of CD. The presence of these antibodies at the time of diagnosis, with a typical small intestinal mucosa and their disappearance with a clinical response to a gluten-free diet and return on challenge, establishes the diagnosis. Although anti-endomysial antibodies have a high degree of specificity, particularly in adult patients, false-positive results may occur in children. Accepted guidelines indicate that antibody estimations on their own should not be relied on for the final diagnosis of CD. Accepted guidelines indicate that small intestinal biopsy is still mandatory.
What is the best test for celiac disease?
For most children and adults, the best way to test for celiac disease is with the Tissue Transglutaminase IgA antibody, plus an IgA antibody in order to ensure that the patient generates enough of this antibody to render the celiac disease test accurate.
How long do you have to eat cereal for celiac disease?
Children must be eating wheat or barley-based cereals for some time, up to one year, before they can generate an autoimmune response to gluten that shows up in testing. A pediatric gastroenterologist should evaluate young children experiencing a failure to thrive or persistent diarrhea for celiac disease. 1.
What is the purpose of a total serum IgA test?
Total serum IgA: This test is used to check for IgA deficiency, a condition associated with celiac disease that can cause a false negative tTG-IgA or EMA result . If you are IgA deficient, your doctor can order a DGP or tTG-IgG test.
What is the risk of developing celiac disease in first degree family members?
First-degree family members (parents, siblings, children), who have the same genotype as the family member with celiac disease, have up to a 40% risk of developing celiac disease. The overall risk of developing celiac diseaes when the genotype is unknown is 7% to 20%.
When can you take a gluten challenge?
A gluten challenge is not recommended before the age of 5 or during puberty. 2 Never undertake a gluten challenge when pregnant.
Is a blood test for celiac disease accurate?
All celiac disease blood tests require that you be on a gluten-containing diet to be accurate. Tissue Transglutaminase Antibodies (tTG-IgA) – the tTG-IgA test will be positive in about 98% of patients with celiac disease who are on a gluten-containing diet. The test’s sensitivity measures how correctly it identifies those with the disease.
Can a biopsy of the small intestine be used to diagnose celiac disease?
There are other antibody tests available to double-check for potential false positives or false negatives, but because of potential for false antibody test results, a biopsy of the small intestine is the only way to diagnose celiac disease.
How to diagnose celiac disease?
Answer. Celiac disease (CD) is diagnosed by evaluating symptoms, conducting blood tests and a small intestinal endoscopy (biopsy). People with CD can have many different symptoms or no symptoms at all, up to 200 symptoms are associated with CD, here are some of the most common ones:
What is a non gastrointestinal test?
Non-Gastrointestinal. Blood tests: Blood is tested for celiac-specific antibodies (refer red to as a celiac panel). These antibodies are proteins in the blood that are produced in response to gluten ingestion. Here are some of the most common blood tests:
What is the next step in a CD diagnosis?
Endoscopy: The next step is an endoscopy of the small intestine, also called a biopsy – this is a test to check for inflammation and damaged villi. This is considered the “gold standard” for diagnosing CD. During an endoscopy, a scope with a small camera at the end is passed down the mouth, esophagus, stomach and into the small intestine. The doctor will look for damage and inflammation and several samples are taken of the intestinal lining. 1
Can a GF diet cause a false negative?
1. NOTE: Starting a GF diet before diagnosis may lead to a false negative test, therefore it is important to keep eating a gluten- containing diet through the diagnostic procedures.
Can you test for celiac disease?
You can also do genetic testing for celiac associated genes, but genetic testing will ONLY rule out CD, and cannot be used as a diagnostic test, less than 5% of those with the celiac-related genes will develop CD. The names of the genes are HLA DQ2 and HLA DQ8.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for thyroiditis
- 2. icd 10 code for left tibia contusion
- 3. icd 10 code for appendiceal polyp
- 4. icd 10 code for ulcerative proctitis
- 5. icd 10 code for status post orif left ankle
- 6. icd 10 dx code for analcious
- 7. icd 10 code for allergic reaction to ibuprofen
- 8. icd 10 code for venous stasis dermatitis of both lower extremities
- 9. icd 10 code for foreign body right thumb
- 10. icd 10 code for elbow pain unspecified