What is the ICD 9 code for encephalopathy Nos?
Encephalopathy, unspecified Short description: Encephalopathy NOS. ICD-9-CM 348.30 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 348.30 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. You are viewing the 2012 version of ICD-9-CM 348.30.
What is the ICD 9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 348.30 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 348.30 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What are the ICD-9-CM Diagnosis codes for the nervous system?
Home> 2015 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes> Diseases Of The Nervous System And Sense Organs 320-389> Other Disorders Of The Central Nervous System 340-349> Other conditions of brain 348-
How is the diagnosis of encephalopathy made?
The diagnosis of encephalopathy starts with the history provided by the patient or family. We will have a better understanding of the possible etiology based on the information provided about the patient’s symptoms. When did they start?
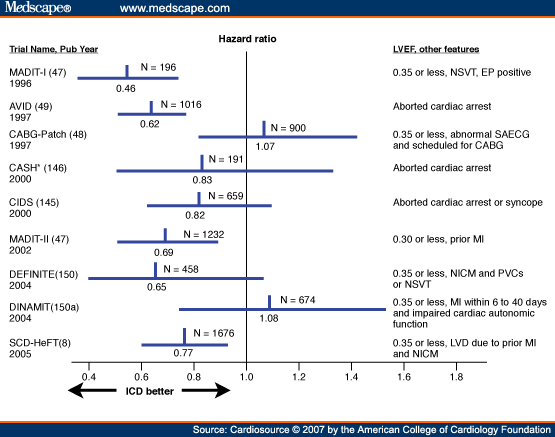
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for Encephalopathy?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encephalopathy, unspecified G93. 40.
What is the ICD 10 code for infectious encephalopathy?
Encephalitis and encephalomyelitis, unspecified G04. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G04. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for septic encephalopathy?
Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy D065166.
How do you code infectious encephalopathy?
Coding Clinic, Second Quarter 2018, pp. 24-25 advises coders to assign G93. 49, Other encephalopathy, for documentation of “encephalopathy due to urinary tract infection (UTI).” Can code G93.
What is infectious encephalopathy?
Encephalitis refers to inflammation in the brain, which often results from a viral infection. Encephalopathy refers to permanent or temporary brain damage, disorder, or disease. It affects the brain's function or structure and may be degenerative.
Can encephalopathy be used as principal diagnosis?
When encephalopathy is the principal diagnosis, the UTI can be added as a CC. When the encephalopathy is a principal diagnosis, auditor denials are not the issue; the real concern is with the documentation not supporting it as a reportable condition.
What is diagnosis code G93 40?
G93. 40 - Encephalopathy, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What is acute metabolic encephalopathy?
Acute toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (TME), which encompasses delirium and the acute confusional state, is an acute condition of global cerebral dysfunction in the absence of primary structural brain disease [1].
What does toxic-metabolic encephalopathy mean?
Acute toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (TME) is a condition of acute global cerebral dysfunction manifested by altered consciousness, behavior changes, and/or seizures in the absence of primary structural brain disease or direct central nervous system (CNS) infection.
Can encephalopathy be used as principal diagnosis?
When encephalopathy is the principal diagnosis, the UTI can be added as a CC. When the encephalopathy is a principal diagnosis, auditor denials are not the issue; the real concern is with the documentation not supporting it as a reportable condition.
What is g04 81?
81 Other encephalitis and encephalomyelitis.
What is acute metabolic encephalopathy?
Acute toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (TME), which encompasses delirium and the acute confusional state, is an acute condition of global cerebral dysfunction in the absence of primary structural brain disease [1].
What does NEC mean in code?
NEC "Not elsewhere classifiable" - This abbreviation in the Alphabetic Index represents "other specified". When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Alphabetic Index directs the coder to the "other specified” code in the Tabular List.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion terms - List of terms is included under some codes. These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used. The terms may be synonyms of the code title, or, in the case of "other specified" codes, the terms are a list of the various conditions assigned to that code. The inclusion terms are not necessarily exhaustive. Additional terms found only in the Alphabetic Index may also be assigned to a code.
What does "see also" mean in the alphabet?
See Also - A "see also" instruction following a main term in the Alphabetic Index instructs that there is another main term that may also be referenced that may provide additional Alphabetic Index entries that may be useful. It is not necessary to follow the "see also" note when the original main term provides the necessary code.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
Type 1 Excludes Notes - A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!" An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What does the combination flag mean?
Combination Flag - The combination flag indicates that more than one code in the target system is required to satisfy the full equivalent meaning of a code in the source system.
What does the approximate flag mean?
Approximate Flag - The approximate flag is on, indicating that the relationship between the code in the source system and the code in the target system is an approximate equivalent.
What is the ICD-10 code for encephalopathy?
348.30 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of encephalopathy, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is a static encephalopathy?
Static encephalopathy. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by a pathologic process involving the brain. A disorder of the brain that can be caused by disease, injury, drugs, or chemicals.
When will the ICd 10 G93.40 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G93.40 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the different types of encephalopathy?
Some of the different types of encephalopathy include: 1 Metabolic (G93.41): Causes include fever, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, acidosis, hypoxia, infection, and organ dysfunction. 2 Toxic (G92): Causes include effects of non-medicinal drugs and toxins, but not medications. 3 Toxic-Metabolic (G92): Suggests a combination of toxic and/or metabolic factors 4 Septic (93.41): A clinical term that represents a manifestation of severe sepsis. 5 Hepatic (K72.90): Describes a spectrum of neurologic impairment in patients with severe end-stage liver disease, such as altered mental status, confusion, disorientation, inappropriate behavior, combativeness, gait disturbances, and/or altered level of consciousness ranging from drowsiness to deep coma. An elevated level of neurotoxic blood ammonia confirms the diagnosis. 6 Hypertensive (I67.4): An acute or subacute consequence of severe hypertension marked by headache, obtundation, confusion, or stupor, with or without convulsions. Papilledema may be noted. 7 Hypoxic or anoxic (G93.1): A permanent chronic brain damage due to sustained hypoxia. 8 Hypoxic ischemia or HIE (P91.60): Applies to neonates and is an acute or subacute brain injury due to oxygen deprivation at delivery. Seizures are common manifestation. 9 Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) (F07.81): The term used to describe brain degeneration likely caused by repeated head traumas. CTE is a diagnosis only made at autopsy by studying sections of the brain. Some symptoms of CTE are thought to include difficulties with thinking (cognition), physical problems, emotions, and other behaviors.
What is CTE in medical terms?
Seizures are common manifestation. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) (F07.81): The term used to describe brain degeneration likely caused by repeated head traumas. CTE is a diagnosis only made at autopsy by studying sections of the brain.
What is the term for abnormal brain function?
Encephalopathy is a broad term used to describe abnormal brain function or brain structure. The hallmark of encephalopathy is altered mental status. The abnormality may be transient, recurrent, or permanent. There are numerous types of encephalopathy and brain disorders with a variety of different etiologies. ...
What are the symptoms of CTE?
Some symptoms of CTE are thought to include difficulties with thinking (cognition), physical problems, emotions, and other behaviors. In summation, acute encephalopathy is the underlying cause of an acute generalized alteration of mental status for most patients admitted to hospitals.
When should encephalopathy return to baseline?
Certain types of encephalopathy such as metabolic, septic, and hypoxic should return to baseline once the underlying etiology is corrected. Encephalopathy caused by a stroke or vascular encephalopathy or trauma would not be expected to return to the patient’s “normal” baseline.
What is the I67.4?
Hypertensive (I67.4): An acute or subacute consequence of severe hypertension marked by headache, obtundation, confusion, or stupor, with or without convulsions. Papilledema may be noted.
What is K72.90?
Hepatic (K72.90): Describes a spectrum of neurologic impairment in patients with severe end-stage liver disease, such as altered mental status, confusion, disorientation, inappropriate behavior, combativeness, gait disturbances, and/or altered level of consciousness ranging from drowsiness to deep coma.
Which encephalopathy category is unlikely to be fully corrected?
Encephalopathy categories that are unlikely to be fully corrected include: Alcoholic. Ischemic. Structural. Wernicke’s. Remember, though, that this is just a rough approximation and there is likely to be some variation in a patient’s response to treatment even within these two broad categories.
What are the different types of encephalopathy?
A: It’s a common misconception that encephalopathy has only one definition. Encephalopathy can be either metabolic/transient or chronic/progressive/degenerative. There’s no one definition which describes all types of encephalopathy. Let’s look at some examples below: 1 Metabolic 2 Septic 3 Toxic 4 Alcoholic 5 Hypoxic 6 Infectious 7 Ischemic 8 Uremic 9 Structural 10 Wernicke’s 11 Hypertensive
Is metabolic encephalopathy less probable?
If there was no difference between the acute illness phase mental status function and after the metabolic issue was supposedly corrected in a patient with pre-existing dementia or degenerative neurological process, the case for an acute metabolic encephalopathy is less probable. The argument for one of the chronic progressive degenerative types of encephalopathy may still be on the table here though.
Is encephalopathy a metabolic disease?
Encephalopathy can be either metabolic/transient or chronic/progressive/degenerative. There’s no one definition which describes all types of encephalopathy. Let’s look at some examples below:
Is the blanket statement "encephalopathy must be resolved prior to discharge to be considered valid" false?
The only thing I can say for certain is that the blanket statement “encephalopathy must be resolved prior to discharge to be considered valid” is categorically false. If this is the basis of the denials you’re receiving, I absolutely recommend bringing your physician and/or neurologist in on the process of appeal writing and dealing with that particular insurance company.
Can uremic encephalopathy be present at hospice?
For example, think of the diagnosis of uremic encephalopathy where the patient is discharged to hospice still in renal failure . In such a situation, the uremic encephalopathy would still be present at discharge. We can, however, make a rough approximation of two distinct categories—one set which may be reversible and another set which likely isn’t.
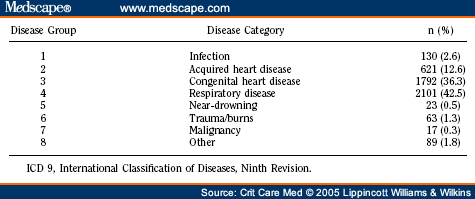
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for pubic cellulitis
- 2. icd 10 code for coag negative staph
- 3. icd 10 code for cellulitis unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for fragments of fibrocartilage lumbar 5
- 5. icd 10 code for humeral head fracture right
- 6. icd 10 code for incontinence of bladder and bowel
- 7. icd-10 code for removal of ortho hardware
- 8. icd 10 code for metacarpal hardware
- 9. icd 10 code for chest wall abrasion
- 10. icd 10 code for rhistory of subdural hemaoma