What is the ICD 10 code for Turner syndrome?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code Q96 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the seven child codes of Q96 that describes the diagnosis 'turner's syndrome' in more detail.
What is Turner's syndrome?
Turner's syndrome, unspecified. A syndrome in which the affected patients have only 45 chromosomes, the loss of one of the x chromosomes producing an xo chromosome constitution. The syndrome occurs in 1/2500 female births and nearly 99% of xo fetuses are aborted. Gonadal agenesis and short stature are the main features in the surviving infants.
What are the diagnosis index entries for Turner's syndrome?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to Q96.9: Anomaly, anomalous (congenital) (unspecified type) Q89.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Q89.9 Deficiency, deficient short stature homeobox gene (SHOX) with Turner's syndrome Q96.9 Dysgenesis gonadal (due to chromosomal anomaly) Q96.9
How is Turner syndrome diagnosed prenatally?
One of two procedures can be performed to test prenatally for Turner syndrome: Chorionic villus sampling. This involves taking a small piece of tissue from the developing placenta. The placenta contains the same genetic material as the baby.
What is the ICD 10 code for Turner's syndrome?
ICD-10 Code for Turner's syndrome- Q96- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD 10 code for Mosaic Turner Syndrome?
Turner's syndrome, unspecified Q96. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q96. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How is Mosaic Turner Syndrome diagnosed?
A genetic test called a karyotype analysis can confirm a Turner syndrome diagnosis. This test requires a blood draw. It can determine whether one of the X chromosomes is fully or partially missing. A complete heart evaluation is also part of diagnosis.
What are streak gonads?
Streak gonads are a form of aplasia, resulting in hormonal failure that manifests as sexual infantism and infertility, with no initiation of puberty and secondary sex characteristics. Gonadal dysgenesis. Specialty.
What is the ICD-10 code for arterial tortuosity syndrome?
ICD-10-CM Code for Arterial tortuosity syndrome Q87. 82.
What is the ICD-10 code for short stature?
ICD-10-CM Code for Short stature (child) R62. 52.
What is the difference between Turner syndrome and mosaic Turner syndrome?
In classical Turner syndrome, an X chromosome is completely missing. This affects about half of all people with TS. Mosaic Turner syndrome, mosaicism, or Turner mosaicism is where the abnormalities occur only in the X chromosome of some of the body's cells.
What are three symptoms of Turner's syndrome?
Signs of Turner syndrome at birth or during infancy may include:Wide or weblike neck.Low-set ears.Broad chest with widely spaced nipples.High, narrow roof of the mouth (palate)Arms that turn outward at the elbows.Fingernails and toenails that are narrow and turned upward.More items...•
What causes Turner syndrome?
Turner syndrome is caused by partial or complete loss (monosomy) of the second sex chromosome. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of all body cells. They carry the genetic characteristics of each individual and they come in pairs. We receive one copy from each parent.
What is Swyer syndrome?
Listen to pronunciation. (SWY-er SIN-drome) A rare genetic condition in which people who have an X chromosome and a Y chromosome (the usual pattern for males) look female. They have normal female reproductive organs, including a uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina.
What is the karyotype for Turners syndrome?
Turner syndrome is associated with a 45,X karyotype, with a single X chromosome. Mosaicism is not uncommon, however, with a separate cell line containing either a normal 46,XX or XY karyotype, or 46 chromosomes including a structurally rearranged X or Y.
What does Cri du Chat mean?
Introduction. The disorder was first described in the medical literature in 1963 by doctor Lejeune who named the disorder after the distinctive cat-like cry. In French, Cri du chat translates into “cry of the cat”.
What are the symptoms of Turner syndrome?
Turner syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects a girl's development. The cause is a missing or incomplete x chromosome. Girls who have it are short, and their ovaries don't work properly. Most are infertile. They are at risk for health difficulties such as high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes, cataracts, osteoporosis and thyroid problems.other physical features typical of turner syndrome are#N#short, "webbed" neck with folds of skin from tops of shoulders to sides of neck#N#low hairline in the back#N#low-set ears#N#swollen hands and feet#N#there is no cure for turner syndrome, but there are some treatments for the symptoms. Growth hormone often helps girls reach heights that are close to average. Hormone replacement can stimulate sexual development. Assisted reproduction techniques can help some women with turner syndrome get pregnant. nih: national institute of child health and human development 1 short, "webbed" neck with folds of skin from tops of shoulders to sides of neck 2 low hairline in the back 3 low-set ears 4 swollen hands and feet
What are the physical features of turner syndrome?
They are at risk for health difficulties such as high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes, cataracts, osteoporosis and thyroid problems.other physical features typical of turner syndrome are. short, "webbed" neck with folds of skin from tops of shoulders to sides of neck. low hairline in the back. low-set ears.
What is the name of the syndrome where the absence of a part of the sex chromosome is
A gonadal dysgenesis syndrome occurring in phenotypic females, characterized by the absence of a part or all of one of the sex chromosomes. Signs and symptoms include short stature, webbing of neck, low-set ears, hypogonadism, and sterility. A gonadal dysgenesis syndrome occurring in phenotypic females, characterized by the complete absence ...
Is noonan syndrome inherited?
Noonan syndrome (also called pseudo-turner syndrome and male turner syndrome) resembles this disorder; however, it occurs in males and females with a normal karyotype and is inherited as an autosomal dominant.
The ICD code Q96 is used to code Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example when having 45 or 47 chromosomes when 46 is expected in a human cell. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes, which is called euploidy.
Coding Notes for Q96 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Type-1 Excludes mean the conditions excluded are mutually exclusive and should never be coded together. Excludes 1 means "do not code here."
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'Q96 - Turner's syndrome'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code Q96. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
What is Turner syndrome?
Listen. Turner syndrome is a chromosomal disorder that affects development in females. It results when a female's cells have one normal X chromosome and the other sex chromosome is either missing or structurally altered (females without Turner syndrome have two normal X chromosomes in each cell, and males have one X and one Y chromosome ).
What is the FDA approved indication for Turner syndrome?
FDA-approved indication: For the treatment of short stature associated with Turner syndrome in patients whose epiphyses are not closed. In addition, for the treatment of short stature or growth failure in children with cuases of SHOX (short stature homeobox -containing gene) deficiency whose epiphyses are not closed.
How many chromosomes does Turner syndrome have?
Some females with Turner syndrome have two X chromosomes, but one of them is missing a piece (has a deletion ). Depending on the specific gene (s) that are missing, features of Turner syndrome may or may not be present. A deletion may occur sporadically (not inherited) or it may be inherited from a parent.
Can genetic testing identify Turner syndrome?
Genetic testing of an affected fetus or child can identify the type of Turner syndrome present and may help to estimate the risk of recurrence. People with questions about genetic testing or recurrence risks for Turner syndrome are encouraged to speak with a genetics professional.
Is Turner syndrome inherited?
Most affected girls and women have normal intelligence, but some have developmental delays, learning disabilities, and/or behavior problems. Turner syndrome is typically not inherited, but it can be inherited in rare cases.
What is the diagnosis of Turner syndrome?
A diagnosis is sometimes made during fetal development. Certain features on an ultrasound image may raise suspicion that your baby has Turner syndrome or another genetic condition affecting development in the womb. Prenatal screening tests that evaluate the baby's DNA in the mother's blood (prenatal cell-free DNA screening or noninvasive prenatal ...
What is Turner Syndrome Society?
The Turner Syndrome Society of the United States and other organizations provide educational materials, resources for families and information about support groups. Groups for parents provide an opportunity to exchange ideas, develop coping strategies and locate resources.
How does Oxandrolone help Turner syndrome?
Estrogen therapy. Most girls with Turner syndrome need to start estrogen and related hormone therapy in order to begin puberty. Often, estrogen therapy is started around age 11 or 12 years.
Why is Turner syndrome important?
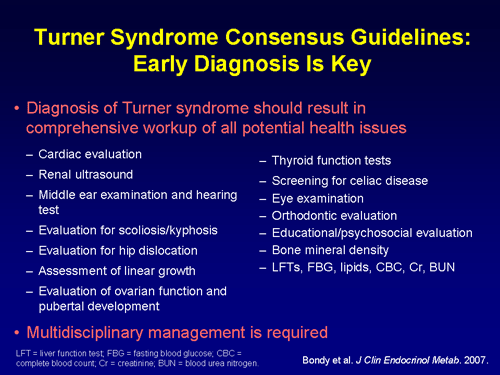
Because Turner syndrome can result in various developmental problems and medical complications, several specialists may be involved in screening for specific conditions, making diagnoses, recommending treatments and providing care. Teams may evolve as the needs of girls with Turner syndrome change throughout life.
What test is done to determine if a child has Turner syndrome?
If, based on signs and symptoms, the doctor suspects that your child has Turner syndrome, a lab test will typically be done to analyze your child's chromosomes. The test involves a blood sample. Occasionally, your doctor also may request a cheek scraping (buccal smear) or skin sample. The chromosome analysis determines whether or not there is ...
Why is it important to have regular checkups for Turner syndrome?
It's important to help your child prepare for the transition from care with your pediatrician to adult medical and mental health care.
Can you get pregnant with Turner syndrome?
Some women with Turner syndrome can become pregnant with the donation of an egg or embryo. This requires a specially designed hormone therapy to prepare the uterus for pregnancy. A reproductive endocrinologist can discuss options and help evaluate the chances of success.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
ICD-9-CM 759.81 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim , however, 759.81 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What is Prader Willi syndrome?
Prader Willi syndrome. Clinical Information. A genetic syndrome caused by deletions or disruptions of chromosome 15. It is characterized by reduced fetal activity, mental retardation, hypotonia, short stature, and hypogonadism. A syndrome characterized at birth by the lack of spontaneous movements and protective reflexes, ...
What is the name of the disorder that causes a person to have a rounded face and low forehead?
Congenital neurobehavioral disorder characterized by rounded face, low forehead, almond shaped eyes, squinting, hypogonadism, hypotonia, insatiable appetite leading to obesity, and mental retardation; chromosomal disorder usually associated with a deletion of the proximal portion of the long arm of chromosome 15.
Overview
Chromosomal anomalies (758–758)
• 758 Chromosomal anomalies
Nervous system (740–742)
• 740 Anencephalus and similar anomalies
• 741 Spina bifida
• 742 Other congenital anomalies of nervous system
Eye, ear, face and neck (743–744)
• 743 Congenital anomalies of eye
• 744 Congenital anomalies of ear, face, and neck
Circulatory system (745–747)
• 745 Bulbus cordis anomalies and anomalies of cardiac septal closure
• 746 Other congenital anomalies of heart
• 747 Other congenital anomalies of circulatory system
Respiratory system (748–748)
• 748 Congenital anomalies of respiratory system
Digestive system (749–751)
• 749 Cleft palate
• 750 Other congenital anomalies of upper alimentary tract
• 751 Other congenital anomalies of digestive system
Genital organs (752–752)
• 752 Congenital anomalies of genital organs
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for e coli bacteremia with sepsis
- 2. 2016 icd 10 code for chronic eye pain.
- 3. icd 10 code for sa node dysfunction
- 4. icd 10 code for history of tooth neuropathy
- 5. 2015 icd 9 code for retroverted
- 6. icd 9 code for surgical wound of foot
- 7. icd 10 code for fracture of left foot
- 8. icd 10 code for choronic anemia
- 9. icd 10 code for severe aortic ressis
- 10. icd 10 code for decreased tsh level