The guidelines state that if the type of diabetes is not documented, the default is type 2. The guidelines also instruct to use additional codes to identify long-term control with insulin (Z79.4) or oral hypoglycemic drugs (Z79.84).
What is the ICD 9 code for type 2 diabetes?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 250.00 : Diabetes mellitus without mention of complication, type II or unspecified type, not stated as uncontrolled. Home > 2015 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes > Endocrine, Nutritional And Metabolic Diseases, And Immunity Disorders 240-279 > Diseases Of Other Endocrine Glands 249-259 > Diabetes mellitus 250-.
What is the ICD 10 code for insulin use?
Use additional code for long-term (current) use of insulin (Z79.4) ICD-10 Code Z79.4, Long-term (current) use of insulin should be assigned to indicate that the patient uses insulin for Type 2 diabetes. mellitus (Category E11* codes). Z79.4 should NOT be used for Type 1 diabetes mellitus (Category E10* codes).
What is the ICD 10 code for diabetes mellitus?
ICD-10-CM Codes. ›. E00-E89 Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases. ›. E08-E13 Diabetes mellitus. ›. E11- Type 2 diabetes mellitus. ›. 2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E11.9.
What is the CPT code for Secondary diabetes mellitus?
Secondary diabetes — DM that results as a consequence of another medical condition — is addressed in Chapter 4 guidelines. These codes, found under categories E08, E09, and E13, should be listed first, followed by the long-term therapy codes for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
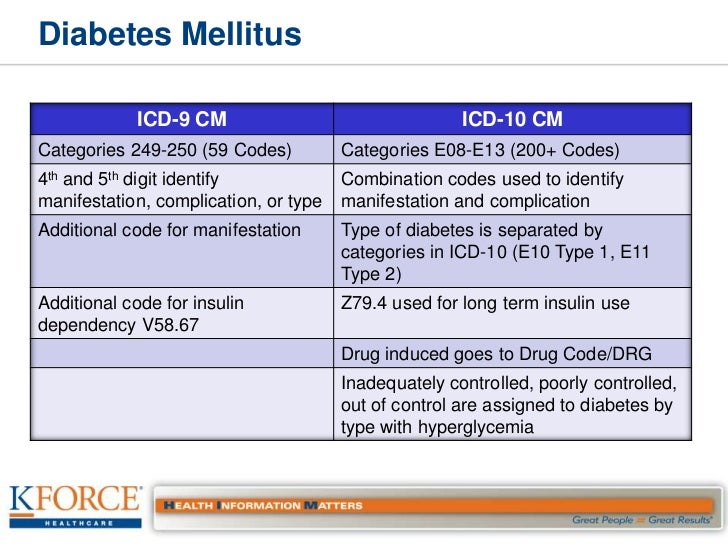
What is the ICD-10 code for insulin dependent type 2?
ICD-10 Code Z79. 4, Long-term (current) use of insulin should be assigned to indicate that the patient uses insulin for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (Category E11* codes). Z79.
What is the diagnosis code for insulin dependent diabetes?
E10 Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for insulin?
ICD-10 code Z79. 4 for Long term (current) use of insulin is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What are the ICD-9 codes for diabetes?
Table 5ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes defining diabetesDescriptionICD-9-CM codeDiabetes mellitus without mention of complications250.0xDiabetes with ketoacidosis250.1xDiabetes with hyperosmolarity250.2xDiabetes with other coma250.3x8 more rows
What is the ICD 9 code for type 2 diabetes?
Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250.
Is type 2 diabetes insulin dependent?
In type 2 diabetes (which used to be called adult-onset or non-insulin-dependent diabetes) the body produces insulin, but the cells don't respond to insulin the way they should.
What is the CPT code for type 2 diabetes?
E11, Type 2 diabetes mellitus. E13, Other specified diabetes mellitus.
What are ICD-10 codes for diabetes?
Common Diabetes ICD-10 Diagnosis Codes.E10.22/E11.22 Diabetes, Renal Complication.PLUS.Diabetes, Circulatory/Vascular Complication.Diabetes, Neurological Complication.E10.9. Type 1 Diabetes, w/o complication. E11.9. ... Diabetes, with other Spec. Complications.Type 1 Diabetes with Hypoglycemia.More items...
What is the code for type 2 diabetes without complications with insulin use?
ICD-10 code E11. 9 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the proper ICD 10 code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with multiple complications?
E11. 69 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication. ICD-10-CM.
Is E11 9 a valid ICD 10 code?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications E11. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is R73 09?
ICD-10 code R73. 09 for Other abnormal glucose is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the code for gestational diabetes?
Codes for gestational diabetes are in subcategory O24.4. These codes include treatment modality — diet alone, oral hypoglycemic drugs, insulin — so you do not need to use an additional code to specify medication management. Do not assign any other codes from category O24 with the O24.4 subcategory codes.
What is the default type of diabetes?
The guidelines state that if the type of diabetes is not documented, the default is type 2. The guidelines also instruct to use additional codes to identify long-term control with insulin (Z79.4) or oral hypoglycemic drugs (Z79.84). You would not assign these codes for short-term use of insulin or oral medications to bring down a patient’s blood ...
How does the pancreas respond to hyperglycemia?
The pancreas responds by making more insulin to try and manage the hyperglycemia , but eventually, the pancreas can’t keep up and blood sugar levels rise. Left uncontrolled, the disease progresses into prediabetes and, eventually, type 2 diabetes.
What is secondary diabetes?
Secondary diabetes — DM that results as a consequence of another medical condition — is addressed in Chapter 4 guidelines. These codes, found under categories E08, E09, and E13, should be listed first, followed by the long-term therapy codes for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
What is the cause of high blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetics?
This is called insulin resistance, which causes high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
What hormones are released when blood sugar is elevated?
This elevation in blood sugar signals the pancreas to release insulin, a hormone that acts like a key to enable the glucose to enter the body’s cells so it can be used as an energy source. Lack of insulin or inability of glucose to enter the cells causes sugar to build up in the blood, which, over time, can lead to complications. ...
What are the complications of chronic hyperglycemia?
The longer someone has diabetes, and the less controlled their blood sugar is, the higher their risk of serious health complications, including: Cardiovascular disease . Kidney damage ( nephropathy)

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for staphylococcus aureus uti
- 2. icd-10-cm code for benign neoplasm of the hepatic flexure
- 3. icd 9 code for cough with hemorrhage
- 4. icd 10 pcs code for thoracoscopic mechanical pleurodesis, right
- 5. icd 10 code for alcohol abuse
- 6. icd 10 cm code for falling from monkey bars
- 7. icd 10 cm code for poor weight gain in infant
- 8. icd 10 cm code for epstein barr mononucleosis
- 9. icd 10 code for gsw to head
- 10. icd 9 code for tee