Hyperglycemia Icd 9 Code. E11.65 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code E11 is used to code Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state...
What type of medication is used for type 2 diabetes?
Mar 29, 2018 · Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. E11.65 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the code for type 2 diabetes?
Mar 09, 2020 · Moreover, what is the ICD 9 code for hyperglycemia? ICD - 9 -CM 790.29 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 790.29 should only be used for claims with a …
What are common causes of high blood sugar levels?
2014 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes 250.*. : Diabetes mellitus. (dye-a-bee-teez) a disease in which the body does not properly control the amount of sugar in the blood. As a result, the level of sugar in the blood is too high. This disease occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use it properly.
What is type 2 diabetes?
E11.9 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. What is the code for diabetes? Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition (E08.-) Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus (E09.-)
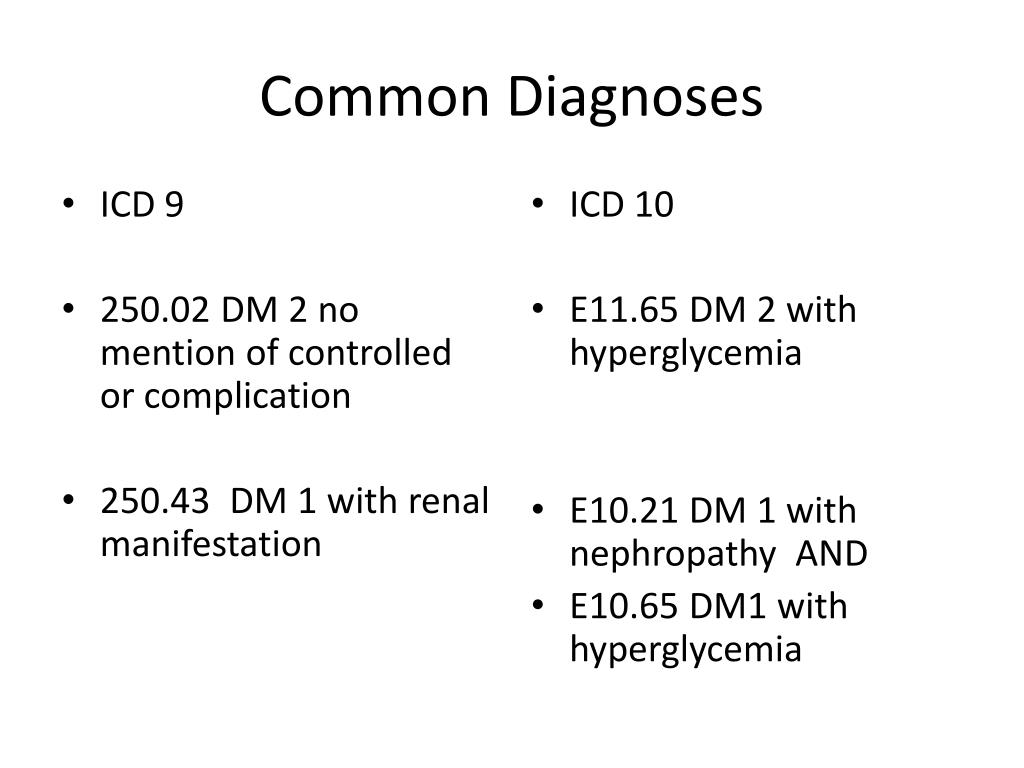
What is the ICD-9 code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus?
ICD-9 Code 250.00 -Diabetes mellitus without mention of complication, type ii or unspecified type, not stated as uncontrolled- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes with hyperglycemia?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia E11. 65 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you code diabetes with hyperglycemia?
In this situation, it might be more accurate to code Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia (E11. 65). ICD-10 does not currently define hyperglycemia, but it considers hyperglycemia to be a complication of diabetes, which is why code E11. 65 is found in the E11.
What is the ICD-9 code for hyperglycemia?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 790.29 : Other abnormal glucose.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes mellitus 2?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications E11. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
When do you code E11 9?
9: Type 2 diabetes mellitus Without complications.
What is the code for diabetes mellitus?
E08, Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition. E09, Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus. E10, Type 1 diabetes mellitus. E11, Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes without complications with insulin use?
ICD-10 code E11. 9 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is ICD-10 code for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus?
ICD-10 Code Z79. 4, Long-term (current) use of insulin should be assigned to indicate that the patient uses insulin for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (Category E11* codes).
What is icd10 code for hyperglycemia?
R73. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute hyperglycemia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Hyperglycemia, unspecified R73. 9.
Is elevated glucose the same as hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia doesn't cause symptoms until glucose values are significantly elevated — usually above 180 to 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 10 to 11.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Symptoms of hyperglycemia develop slowly over several days or weeks.Jun 27, 2020
What is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance
A metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels due to diminished production of insulin or insulin resistance/desensitization. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or sugar, levels are too high.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose comes from the foods you eat . Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well.
Can diabetes cause heart disease?
It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb.
What are the symptoms of hyperglycemia?
Symptoms include frequent hunger, blurred vision, dry mouth, itchy skin, erectile dysfunction, increased volume of urine, and weight loss.
What is the name of the disorder where an excessive amount of glucose is in the blood plasma?
Hyperglycemia is a disorder where an excessive amount of glucose is in the blood plasma. Symptoms include frequent hunger, blurred vision, dry mouth, itchy skin, erectile dysfunction, increased volume of urine, and weight loss.
What is the ICd 9 code for diabetes?
Resistin is thus a hormone that potentially links obesity to diabetes. ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions.
What is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance
A metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels due to diminished production of insulin or insulin resistance/desensitization. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or sugar, levels are too high.
How to control diabetes?
Exercise, weight control and sticking to your meal plan can help control your diabetes. You should also monitor your glucose level and take medicine if prescribed. nih: national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases. Diabetes mellitus.
Which group of disorders share glucose intolerance in common?
Heterogeneous group of disorders that share glucose intolerance in common. Type 2 diabetes, characterized by target-tissue resistance to insulin, is epidemic in industrialized societies and is strongly associated with obesity; however, the mechanism by which increased adiposity causes insulin resistance is unclear.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose comes from the foods you eat . Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well.
Can diabetes cause heart disease?
It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes.a blood test can show if you have diabetes.
What does it mean when your blood sugar is too high?
diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, is too high. With type 2 diabetes , the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E11. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is mellitus in medical terms?
diabetes (mellitus) due to insulin secretory defect. diabetes NOS. insulin resistant diabetes (mellitus) Clinical Information. A disease in which the body does not control the amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in the blood and the kidneys make a large amount of urine.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose comes from the foods you eat . Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well.
Can high blood glucose cause heart problems?
Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth.you have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes if you are older, obese, have a family history of diabetes, or do not exercise.the symptoms of type 2 diabetes appear slowly.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lle wounds
- 2. icd-10 code for macrocytosis without anemia
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for cellulitis of nec
- 4. icd 9 code for ascus pap
- 5. icd 10 pcs code for swan ganz catheter insertion
- 6. icd 10 code for delayed milestones
- 7. icd 10 code for a right occipital craniotomy
- 8. icd 10 code for borderline diabetes
- 9. icd 10 code for axiety
- 10. icd 10 code for car seat