The following ICD-9 codes for urinary microalbumin are listed as a convenience for the ordering practitioner. The ordering practitioner should report the diagnosis code that best describes the reason for performing the test and provide the 4th and 5th ICD-9 digit as appropriate. Urinary Microalbumin CPT Code 82043/82570 Sample Type Urine Order Code C919
How to interpret microalbumin urine?
Urine Albumin and Albumin to Creatinine Ratio
- About the Test. The purpose of a urine albumin test is to determine if there is an abnormal amount of the protein albumin in a urine sample.
- Finding a Urine Albumin or Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio Test. Testing for urine albumin levels is normally ordered by a doctor. ...
- Urine Albumin and Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio Test Results. ...
What causes microalbumin in urine?
Urine microalbumin levels can be higher than expected for a variety of reasons, including:
- Blood in your urine (hematuria)
- Certain medications
- Fever
- Recent vigorous exercise
- Urinary tract infection
- Other kidney diseases
What is normal microalbumin urine?
The normal range for a random urine microalbumin test is less than 30 milligrams, says Mayo Clinic. Microalbumin is a blood protein filtered by the kidneys. The urine test measures the amount of protein unfiltered by the kidneys and is used to detect early signs of kidney damage.
How can microalbumin in my urine be reduced?
Reducing Protein In Blood Naturally
- Exercise. This should be done in a regular basis. ...
- Eating healthy. Avoiding food that are rich in sugar, fat, and salt is one of the best ways to reduce albumin levels. ...
- Sleeping adequately. This helps the body function normally.
- Avoid certain drugs that can increase albumin in blood. ...
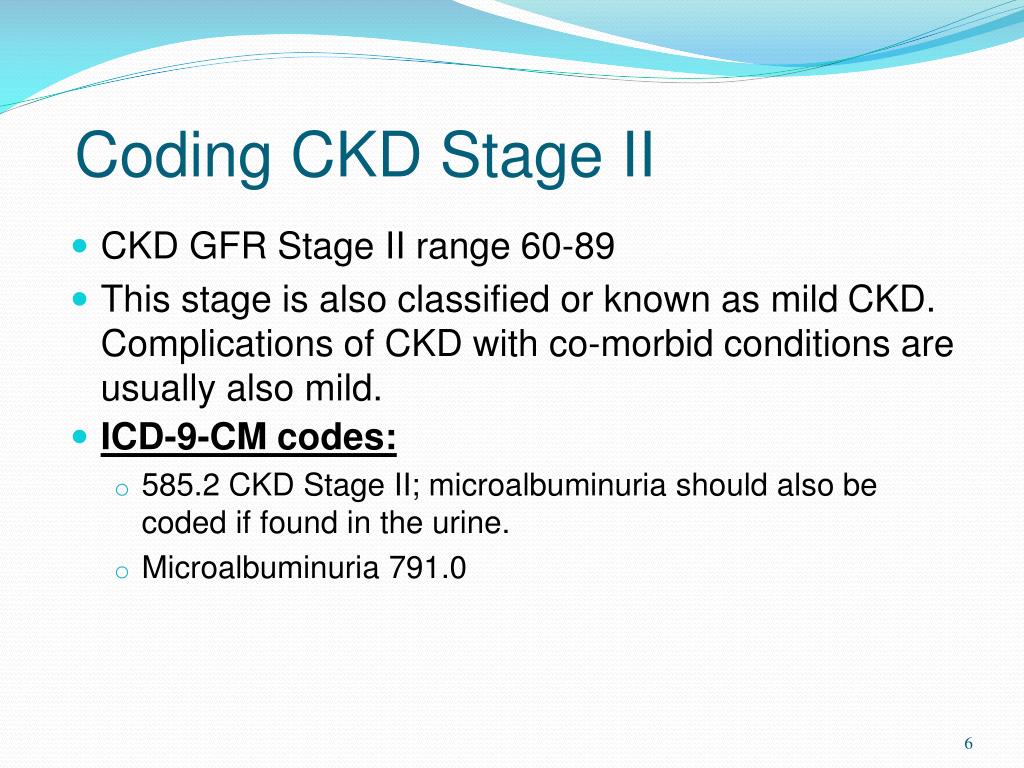
What ICD-10 code covers urine microalbumin?
R80.99 - see also Proteinuria. Microalbuminuria R80. 9.
What is the ICD-10 code for albuminuria?
ICD-10 | Proteinuria, unspecified (R80. 9)
What microalbuminuria means?
Abstract. Microalbuminuria (MA) is defined as persistent elevation of albumin in the urine, of 30-300 mg/day (20-200 microg/min). These values are less than the values detected by routine urine dipstick testing, which does not become positive until protein excretion exceeds 300-500 mg/day.
What is diabetes mellitus with microalbuminuria?
[6,7] Microalbuminuria is the strong predictor of diabetic nephropathy, which is the main cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. Microalbuminuria is also characterized by increased prevalence of arterial hypertension, proliferative retinopathy, and peripheral neuropathy.
What diagnosis covers Microalbumin?
The urinary microalbumin/creatinine ratio may be performed on individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, hypertension, a family history of chronic kidney disease, those at intermediate (10-20%) risk for CVD or those with known vascular disease.
What is diagnosis code R31 29?
ICD-10 code R31. 29 for Other microscopic hematuria is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Is Microalbumin the same as albuminuria?
Early of its mostly albumin because of its small size. Later on its lots of albumin but also other proteins. Microalbuminuria is now called moderately increased albuminuria while albuminuria (macroalbuminuria) or proteinuria is now called severely increased albuminuria.
What is the clinically significant value of Microalbumin?
Persistent microalbuminuria indicates a high probability of damage to the glomerular filtration capacity of the kidney and is of great diagnostic relevance: (a) in diabetes, for early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy; (b) in patients with hypertension, as an indicator of end-organ damage associated with a lowered life ...
What is the cause of microalbuminuria?
Microalbuminuria is caused by kidney damage. Some medical conditions that can lead to kidney damage include: High blood pressure. Type I and type II diabetes.
How do you code diabetes with microalbuminuria?
E11. 29 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 29 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the difference between microalbuminuria and proteinuria?
Proteinuria indicates an elevated presence of protein in the urine (normal excretion should be < 150 mg/d), while albuminuria is defined as an “abnormal loss of albumin in the urine.”1 Albumin is a type of plasma protein normally found in the urine in very small quantities.
Is microalbuminuria a nephropathy?
Diabetic nephropathy presents in its earliest stage with low levels of albumin (microalbuminuria) in the urine.
What is the value of microalbuminuria?
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has defined microalbuminuria as a microalbumin value of 30-300 mg/g creatinine.7 A persistent microalbumin of >30 mg/g indicates a loss of kidney function and is used in the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease.8
What is the purpose of microalbumin?
Microalbumin is the quantification of small amounts of albumin, a serum protein, in urine that can be used to identify microvascular endothelial dysfunction. The presence of small amounts of albumin in the urine may suggest the presence of systemic endothelial dysfunction – an early indicator of heart disease.1 This test is more sensitive than a standard dipstick test routinely performed in an office setting.
How often should I check for microalbumin?
Microalbumin testing is determined by an individual’s medical history, but may be performed semi-annually or annually as necessary. If the initial test result is abnormal, then follow-up testing may be performed within 3-6 months following treatment.
Can microalbumin be performed on a diabetic?
Microalbumin may be performed on individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, hypertension, a family history of chronic kidney disease, those at intermediate (10-20%) risk for CVD, or those with known vascular disease.

Popular Posts:
- 1. what's the icd-10 code for
- 2. icd 10 diagnosis code for eustachian tube dysfunction
- 3. icd 9 code for right carotid endarterectomy
- 4. icd 10 diagnostic code for prediabetes
- 5. icd 10 code for low vision both etes
- 6. icd 10 code for exposure to hep c
- 7. icd 10 code for pneumonia due to covid
- 8. icd-10 code for parkinson's dementia
- 9. icd 10 code for second degree pro lapsed hemorrhoids
- 10. 2018 icd 10 code for infant renal disease found after birth