Does Brugada syndrome have a cure?
Treatment. Brugada syndrome treatment depends on your risk of a serious abnormal heartbeat. You're considered at high risk if you have: A personal history of serious heart rhythm problems; Fainting spells; Survived sudden cardiac arrest; If you don't have any symptoms, you may not need any specific treatment because your risk is likely low.
What are the symptoms of Brugada syndrome?
They often happen during rest or sleep and include:
- Fainting
- Difficulty breathing
- Irregular heartbeats
- Seizures
- Sudden death
What does Brugada syndrome stand for?
Brugada syndrome is a heart condition that causes a disruption of the normal rhythm in the heart's lower chambers (ventricular arrhythmia). Signs and symptoms usually develop in adulthood but the diagnosis may be made at any age. Symptoms and complications often occur during rest or sleep, and may include fainting, seizures, difficulty breathing, or sudden death.
What is the history of Brugada syndrome?
Decreased blood flow to the brain and heart may result in fainting or sudden death. Brugada syndrome is named by the Spanish cardiologists Pedro Brugada and Josep Brugada who reported it as a distinct clinical syndrome in 1992. The genetic basis of Brugada syndrome was established by Ramon Brugada in 1998.
What is the ICD-10 code for Brugada syndrome?
8.
What is the ICD-10 code for arrhythmias?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cardiac arrhythmia, unspecified I49. 9.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for pots?
As you may know, ICD-10 currently lists POTS under “I49. 8 – Other specified cardiac arrhythmias.” ICD-10 notes that this code also “applicable to” Brugada syndrome, coronary sinus rhythm disorder, ectopic rhythm disorder, and nodal rhythm disorder.
What is ICD-10 code for junctional escape rhythm?
ICD-10 code I49. 2 for Junctional premature depolarization is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is Brugada syndrome?
Brugada syndrome is a rare but serious condition that affects the way electrical signals pass through the heart. It can cause the heart to beat dangerously fast. These unusually fast heartbeats – known as an arrhythmia – can sometimes be life threatening.
What is unspecified cardiac arrhythmia?
A heart arrhythmia (uh-RITH-me-uh) is an irregular heartbeat. Heart rhythm problems (heart arrhythmias) occur when the electrical signals that coordinate the heart's beats don't work properly. The faulty signaling causes the heart to beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia) or irregularly.
What is the ICD-10 code for ventricular Trigeminy?
Assign I49. 8 Other specified cardiac arrhythmia for ventricular bigeminy. [Effective 14 August 2009, ICD-10-AM/ACHI/ACS 6th Ed.]
What is the ICD-10 code for complete heart block?
ICD-10 code I44. 2 for Atrioventricular block, complete is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What are the three types of junctional rhythms?
The three types of junctional rhythm are categorized according to the resulting heart rate. In order of ascending beats per minute (bpm), these are junctional rhythm (or junctional escape rhythm), accelerated junctional rhythm, and junctional tachycardia.
What is the difference between accelerated junctional rhythm and junctional escape rhythm?
Junctional escape rhythm arises from the AV junction at a rate of 40 to 60 beats per minute. Accelerated junctional rhythm arises from the AV junction at a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What is a junctional heart rhythm?
A junctional rhythm is where the heartbeat originates from the AV node or His bundle, which lies within the tissue at the junction of the atria and the ventricle. Generally, in sinus rhythm, a heartbeat is originated at the SA node.
The ICD code I498 is used to code Brugada syndrome
Brugada syndrome (BrS) is a genetic disease that is characterised by abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG) findings and an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. It is named by the Spanish cardiologists Pedro Brugada and Josep Brugada.
Coding Notes for I49.8 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #308-310 - Cardiac arrhythmia and conduction disorders with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'I49.8 - Other specified cardiac arrhythmias'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code I49.8. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code I49.8 and a single ICD9 code, 427.89 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Study Questions
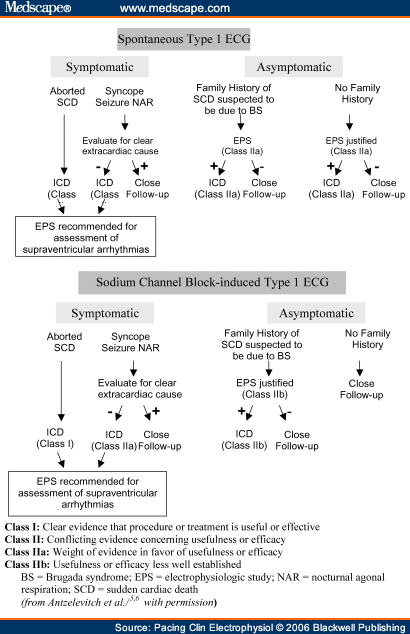
What are the long-term outcomes after implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placement in Brugada syndrome patients?
Methods
In this registry, there were 370 patients with Brugada syndrome. The follow-up was 43 ± 14 years, and 74% were male. A total of 104 patients (28.1%) were treated with ICDs. The authors analyzed the long-term incidence of shocks and complications in patients who underwent ICD implantation.
Results
An ICD was implanted for secondary prevention in 10 patients (10%), and for primary prevention in 94 patients (90%). After a mean follow-up of 9 years, 21 patients (20%) experienced a total of 81 appropriate shocks (incidence rate 2.2% person-year). The rate of appropriate shock was higher in secondary prevention patients (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
ICD therapy is an effective therapy in high-risk patients with Brugada syndrome, but it is associated with a significant risk of device-related complications.
Perspective
Rate of appropriate therapy in Brugada syndrome varies widely across reports, and the indications for ICD implantation for primary prevention in Brugada syndrome remain debatable due to lack of a satisfying risk stratification scheme.
What is Brugada syndrome?
8% of sudden cardiac death. Brugada syndrome ( BrS) is a genetic disorder in which the electrical activity within the heart is abnormal. It increases the risk of abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. Those affected may have episodes of passing out.
What is the abnormal heart rhythm in Brugada syndrome?
The abnormal heart rhythms seen in Brugada syndrome often occur at rest, following a heavy meal, or even during sleep. These situations are linked to periods when the vagus nerve is activated, referred to as periods of high vagal tone. Abnormal heart rhythms may also occur during fever or following excessive alcohol.
What causes Brugada ECG?
A long list of factors that can generate a Brugada ECG pattern have been described, including certain medications, electrolyte disturbances such as a decrease in the levels of potassium in the blood, and a reduction in blood supply to key areas of the heart , specifically the right ventricular outflow tract.
How does Brugada syndrome affect the heart?
As a genetic condition, the syndrome is ultimately caused by changes to a person's DNA, known as genetic mutations. The first mutations described in association with Brugada syndrome were in a gene responsible for a protein or ion channel that controls the flow of sodium ions through the cell membrane of heart muscle cells – the cardiac sodium channel. Many of the genetic mutations that have subsequently been described in association with Brugada syndrome influence the sodium current in some way, or affect other ionic currents.
What does an ICD do?
An ICD can also function as a pacemaker, preventing abnormally slow heart rates that can also occur in people with Brugada syndrome.
What is an ICD device?
In people felt to be at higher risk of sudden cardiac death, an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) may be recommended. These small devices implanted under the skin continuously monitor the heart rhythm. If the device detects a potentially life-threatening arrhythmia it can give the heart a small electric shock, stunning the heart back into a normal rhythm. An ICD can also function as a pacemaker, preventing abnormally slow heart rates that can also occur in people with Brugada syndrome.
Is Brugada syndrome autosomal dominant?
Genetics. Brugada syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that only one copy of the defective gene is needed to produce the syndrome. However, a person diagnosed with the condition may be the first in their family to have Brugada syndrome if it has arisen as a new mutation.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right ureteral stone
- 2. icd 10 code for pseudarthrosis after fusion
- 3. icd 9 code for subscapularis tendon tear
- 4. icd-10 code for external cause drug induced injury
- 5. icd 10 code for left ankle wound
- 6. icd-10 code for porokertosis
- 7. icd 10 code for joseph's disease billable
- 8. icd 10 cm code for fell while going upstairs
- 9. icd 10 code for left finger laceration
- 10. icd 9 code for hypothyroidism due to acquired atrophy of thyroid