Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Q79.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.0 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for congenital diaphragmatic hernia?
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Q79.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.0 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for hernia without obstruction?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K44.9. Diaphragmatic hernia without obstruction or gangrene. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. K44.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for hiatal hernia?
The most common kind of hiatal hernia in which the esophagogastric junction slides above the diaphragm into the thorax. diaphragmatic hernia ( K44 .-) Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for hernia with gangrene?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K44.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 K44.0 may differ. Hernia with both gangrene and obstruction is classified to hernia with gangrene.
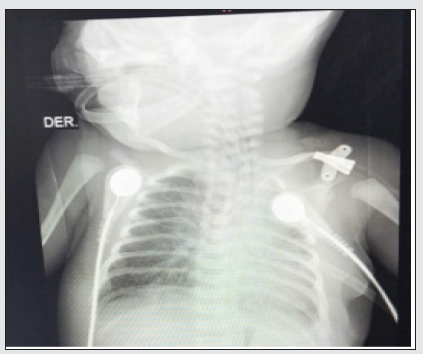
What is the diaphragmatic hernia?
Diaphragmatic hernia is a birth defect where there is a hole in the diaphragm (the large muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen). Organs in the abdomen (such as intestines, stomach, and liver) can move through the hole in the diaphragm and upwards into a baby's chest.
Is diaphragmatic and hiatal hernia the same?
In a hiatal hernia (also called hiatus or diaphragmatic hernia), a portion of the stomach penetrates (herniates) through a weakness or tear in the hiatus of the diaphragm, the small opening that allows the esophagus to pass from the neck and chest to its connection with the stomach.
What is a diaphragmatic hernia in adults?
A diaphragmatic hernia occurs when one or more of your abdominal organs move upward into your chest through a defect (opening) in the diaphragm. This kind of defect can be present at birth or acquired later in life. It's always a medical emergency and requires prompt surgery to correct.
What is the ICD-10 code for esophageal hernia?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K40 K40.
What is another name for diaphragmatic hernia?
Congenital diaphragmatic herniaOther namesCDHMorgagni hernia seen on a chest radiograph.SpecialtyMedical genetics, pediatrics1 more row
What are the types of diaphragmatic hernia?
The 2 most common types of diaphragmatic hernia are:Bochdalek hernia. This involves the side and back of the diaphragm. The stomach, liver, spleen, or intestines move up into your child's chest cavity.Morgagni hernia. This involves the front part of the diaphragm.
Do adults get diaphragmatic hernia?
The exact cause of diaphragmatic hernias is unknown. Research suggests that a combination of nutrition, environmental factors, and genetic abnormalities can all play a role. However, this condition can also be acquired by adults through an injury.
How common is a diaphragmatic hernia in adults?
The incidence of diaphragmatic injury occurs in up to 7% in those who suffer blunt abdominal/thoracic trauma and in 3% to 15% for those with penetrating injury.
Why is congenital diaphragmatic hernia on left?
A left-sided CDH allows for the possibility of the stomach, intestines, and sometimes the liver to move (herniate) up into the baby's chest. The other 17% of babies with CDH have a defect on the right side of the diaphragm. A right-sided CDH almost always allows the liver to move into the chest.
What is the correct code for a diaphragmatic hernia with obstruction without gangrene?
ICD-10 Code for Diaphragmatic hernia with obstruction, without gangrene- K44. 0- Codify by AAPC.
What is a paraesophageal hernia?
A paraesophageal hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach protrudes up through an opening in the diaphragm (called the hiatus) into the chest. Although many people with this type of hernia don't notice symptoms, others may experience heartburn resulting from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What are three types of hiatal hernias?
Type 3 (mixed, sliding, and paraesophageal hiatal hernia) is the EGJ and stomach is located above the diaphragm and 2 cm or more of the fundus is located cephalad to the lower esophageal sphincter and esophagus.
Are there different types of hiatal hernias?
There are two main types of hiatal hernias: sliding and paraesophageal. Ordinarily, your esophagus (food pipe) goes through the hiatus and attaches to your stomach. In a sliding hiatal hernia, your stomach and the lower part of your esophagus slide up into your chest through the diaphragm.
What is the difference between a hernia and a hiatal hernia?
Unlike ventral hernias, which protrude through the abdominal wall, a hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach pushes up into the chest through a small opening in the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the abdomen from the chest.
What is similar to a hiatal hernia?
With a hiatal hernia, this can occur fairly easily since the following conditions show similar symptoms: Angina, a heart condition in which heart muscles don't get the oxygen they need. Indigestion, which results in burping, vomiting, and heartburn. Biliary colic, in which a gallstone blocks the bile duct.
What is a hernia in the chest called?
Hiatal hernia. Paraesophageal hernia. Clinical Information. A congenital or acquired weakness or opening in the diaphragm which allows abdominal contents to protrude into the chest cavity; congenital diaphragmatic hernias are caused when the embryonic diaphragm fails to fuse.
What is a hernia with both gangrene and obstruction?
Hernia with both gangrene and obstruction is classified to hernia with gangrene. A congenital or acquired weakness or opening in the diaphragm which allows abdominal contents to protrude into the chest cavity; congenital diaphragmatic hernias are caused when the embryonic diaphragm fails to fuse.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for left retroauricular adenopathy
- 2. icd 10 cm code for cephalhematoma
- 3. icd 10 code for aggressive behavior in adult
- 4. icd 9 code for eye watering
- 5. icd 10 code for assault by blunt object
- 6. icd 10 code for n41.1
- 7. icd-10-cm code for r460
- 8. icd 9 code for methemoglobinemia
- 9. icd code for post partum
- 10. icd 10 code for airway protection