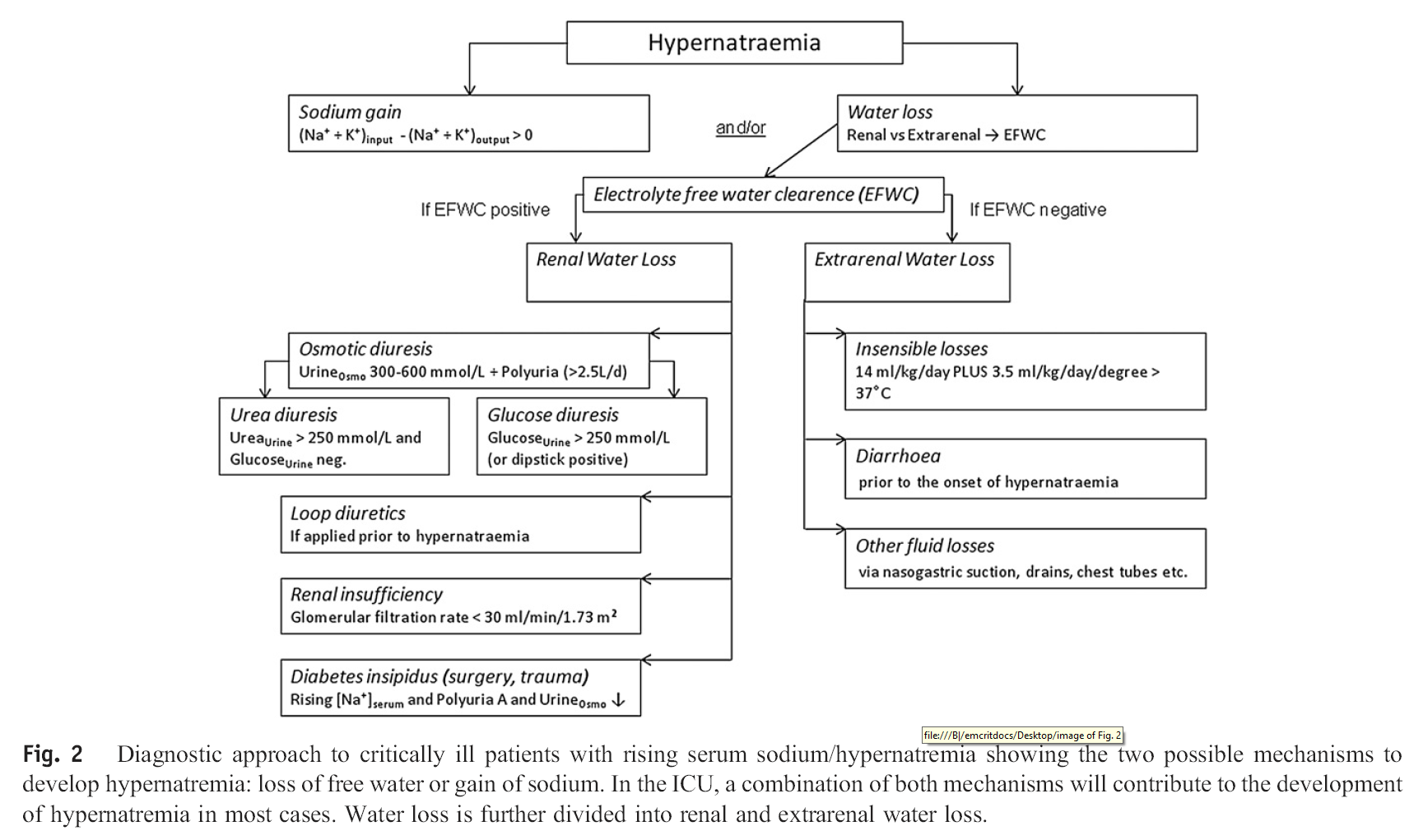
Failed back syndrome is also referred to as postlaminectomy syndrome. The correct ICD-9 code for this would be 722.8, but there are also fifth-digit classifications depending on the region of the spine that is affected. the code for foreign body present in auditory canal is 931.
How to fix failed back syndrome?
Transfer Lesion to Another Level after a Spine Fusion
- This degeneration is most likely to happen after a two-level fusion (e.g. ...
- It is much less likely to happen if only the L5-S1 level is fused, as this segment typically does not have much motion and fusing this level does not change ...
- Most of the motion in the spine is at the L4-L5 level, and to a lesser extent at L3-L4. ...
How to diagnose failed back surgery syndrome?
- Medical history
- Review of emotional wellbeing and lifestyle habits
- Physical exam
- Neurological exam
- Review of current symptoms
- Imaging (eg, x-ray)
What causes failed back syndrome?
What are some of the causes of failed back surgery syndrome?
- Causes of failed back surgery syndrome. In general, there are two primary reasons chronic pain may persist after someone undergoes a major back operation.
- When to consider a follow-up surgical procedure. ...
- Browse Related Resources. ...
What are the symptoms of failed back surgery syndrome?
Symptoms of FBSS. Common symptoms of failed back surgery syndrome include: Persistent, chronic pain that is not associated with the healing process. New pain at a different location from where surgery occurred. Restricted mobility. Numbness or pain radiating through the lower back and into the legs. Back spasms.
What is failed back surgery syndrome?
Failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS) is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as lumbar spinal pain of unknown origin either persisting despite surgical intervention or appearing after surgical intervention for spinal pain originally in the same topographical location.
What is diagnosis code Z98 89?
Other specified postprocedural statesICD-10 code Z98. 89 for Other specified postprocedural states is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for post laminectomy syndrome?
ICD-10 code: M96. 1 Postlaminectomy syndrome, not elsewhere classified.
What is Postlaminectomy syndrome NEC m961?
ICD-10 Code for Postlaminectomy syndrome, not elsewhere classified- M96. 1- Codify by AAPC. Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue. Intraoperative and postprocedural complications and disorders of musculoskeletal system, not elsewhere classified.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic back pain?
ICD-10 Code M54. 5 for Chronic Low Back Pain | CareCloud.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for status post back surgery?
Other specified postprocedural states The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for degenerative disc disease?
ICD-10 code M51. 36 for Other intervertebral disc degeneration, lumbar region is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Dorsopathies .
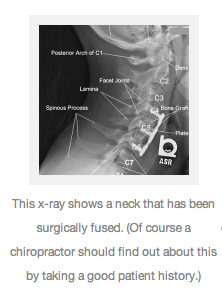
Is laminectomy the same as decompression?
Cervical laminectomy Laminectomy is surgery that creates space by removing the lamina — the back part of a vertebra that covers your spinal canal. Also known as decompression surgery, laminectomy enlarges your spinal canal to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Is failed back syndrome the same as post-laminectomy syndrome?
This persistent pain is called post laminectomy syndrome. Post-laminectomy syndrome is also called Failed Back Surgery Syndrome, or FBSS.
What is the treatment for failed back surgery syndrome?
Treatment for failed back surgery syndrome may include physical therapy, nerve blocks, medications, injections, or a chronic pain management program. If the pain is possibly coming from the facet or sacroiliac joints, chiropractic care may be recommended.
What is back syndrome?
Failed back surgery syndrome (also called FBSS, or failed back syndrome) is a misnomer, as it is not actually a syndrome - it is a very generalized term that is often used to describe the condition of patients who have not had a successful result with back surgery or spine surgery and have experienced continued pain ...
What is a failed back?
Failed back syndrome (FBS) is a well-recognized complication of surgery of the lumbar spine. It can result in chronic pain and disability, often with disastrous emotional and financial consequences to the patient. Many patients have traditionally been classified as "spinal cripples" and are consigned to a life of long-term narcotic treatment with little chance of recovery. Despite extensive work in recent years, FBS remains a challenging and costly disorder.
When did back syndrome become difficult to understand?
Before the advent of CT scanning, the pathology in failed back syndrome was difficult to understand. Computerized tomography in conjunction with metrizamide myelography in the late 1960s and 1970s allowed direct observation of the mechanisms involved in post operative failures.
When was the first lumbar total disc replacement approved?
The procedure was met with great excitement and heightened expectations both in the United States and Europe. In late 2004, the first lumbar total disc replacement received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). More experience existed in Europe. Since then, the initial excitement has given way to skepticism and concern. Various failure rates and strategies for revision of total disc replacement have been reported.
What are the symptoms of FBS?
Common symptoms associated with FBS include diffuse, dull and aching pain involving the back or legs. Abnormal sensibility may include sharp, pricking, and stabbing pain in the extremities. The term "post-laminectomy syndrome" is used by some doctors to indicate the same condition as failed back syndrome.
What causes back pain after a laminectomy?
Failed back syndrome or post-laminectomy syndrome is a condition characterized by chronic pain following back surgeries. Many factors can contribute to the onset or development of FBS, including residual or recurrent spinal disc herniation, persistent post-operative pressure on a spinal nerve, altered joint mobility, joint hypermobility with instability, scar tissue ( fibrosis ), depression, anxiety, sleeplessness, spinal muscular deconditioning and even Cutibacterium acnes infection. An individual may be predisposed to the development of FBS due to systemic disorders such as diabetes, autoimmune disease and peripheral blood vessels (vascular) disease.
Can a disc herniation cause back pain?
Many observers have noted that the most common cause of a failed back syndrome is caused from recurrent disc herniation at the same level originally operated.
Is spine surgery a conflict of interest?
A report from Spain noted that the investigation and development of new techniques for instrumented surgery of the spine is not free from conflicts of interest. The influence of financial forces in the development of new technologies and its immediate application to spine surgery, shows the relationship between the published results and the industry support. Authors who have developed and defended fusion techniques have also published new articles praising new spinal technologies. The author calls spinal surgery the "American Stock and Exchange" and "the bubble of spine surgery". The scientific literature doesn't show clear evidence in the cost-benefit studies of most instrumented surgical interventions of the spine compared with the conservative treatments. It has not been yet demonstrated that fusion surgery and disc replacement are better options than the conservative treatment. It's necessary to point out that at present "there are relationships between the industry and back pain, and there is also an industry of the back pain". Nonetheless, the "market of the spine surgery" is growing because patients are demanding solutions for their back problems. The tide of scientific evidence seems to go against the spinal fusions in the degenerative disc disease, discogenic pain and in specific back pain. After decades of advances in this field, the results of spinal fusions are mediocre. New epidemiological studies show that "spinal fusion must be accepted as a non proved or experimental method for the treatment of back pain". The surgical literature on spinal fusion published in the last 20 years establishes that instrumentation seems to slightly increase the fusion rate and that instrumentation doesn't improve the clinical results in general. We still are in need of randomized studies to compare the surgical results with the natural history of the disease, the placebo effect, or conservative treatment. The European Guidelines for lumbar chronic pain management show "strong evidence" indicating that complex and demanding spine surgery where different instrumentation is used, is not more effective than a simple, safer and cheaper posterolateral fusion without instrumentation. Recently, the literature published in this field is sending a message to use "minimally invasive techniques"; – the abandonment of transpedicular fusions. Surgery in general, and usage of metal fixation should be discarded in most cases.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left breast mass at 3 o clock
- 2. 2016 icd 10 code for stepped into a hole
- 3. icd 10 code for elevated ige level
- 4. icd 10 code for hepatitis acute panel
- 5. icd 10 code for colloid cyst
- 6. icd 10 code for personal history of fibromyalgia
- 7. icd 10 code for potential stroke
- 8. icd 10 code for er follow up
- 9. icd 10 code for cerebral white matter disease
- 10. icd 10 code for atherosclerosis of carotid