What is the ICD 10 code for greenstick fracture?
Short description: Greenstick fracture of shaft of radius, left arm, init The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S52.312A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for shaft of radius fracture?
Greenstick fracture of shaft of radius, right arm, subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing. S52.311D is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM S52.311D became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for distal ulna fracture?
813.42Other closed fractures of distal end of radius (alone)convert 813.42 to ICD-10-CM 813.43Closed fracture of distal end of ulna (alone)convert 813.43 to ICD-10-CM
What is the best radiology code for ulnar fracture?
I personally would use 25605. The distal radius is the main bone that is being manipulated. Also, the ulnar styloid is the typical location of the associated ulnar fracture which may or may not need separate manipulation.
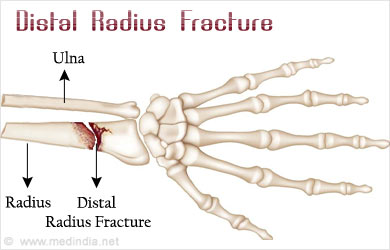
What is a Greenstick fracture of the distal radius?
A greenstick fracture is a partial thickness fracture where only cortex and periosteum are interrupted on one side of the bone but remain uninterrupted on the other. [1] They occur most often in long bones, including the fibula, tibia, ulna, radius, humerus, and clavicle.
What is the ICD-10 code for radius and ulna fracture?
Unspecified fracture of lower end of right ulna, initial encounter for closed fracture. S52. 601A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S52.
What is a Greenstick fracture of the ulna?
A greenstick fracture occurs when a bone bends and cracks, instead of breaking completely into separate pieces. The fracture looks similar to what happens when you try to break a small, "green" branch on a tree.
What is the ICD-10 code for distal radius fracture?
ICD-10 code S52. 5 for Fracture of lower end of radius is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is the ICD 10 code for distal ulna fracture?
Unspecified fracture of lower end of unspecified ulna, initial encounter for open fracture type I or II. S52. 609B is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for both bone forearm fracture?
Table: CodeICD10 Code (*)Code Description (*)S52.60Fracture of lower end of both ulna and radius, closedS52.61Fracture of lower end of both ulna and radius, openS52.7Multiple fractures of forearmS52.70Multiple fractures of forearm, closed26 more rows
What kind of fracture is a greenstick fracture?
What Is a Greenstick Fracture? A greenstick fracture is a type of broken bone. A bone cracks on one side only, not all the way through the bone. It is called a "greenstick" fracture because it can look like a branch that has broken and splintered on one side.
Is greenstick fracture an incomplete fracture?
Greenstick fractures are incomplete fractures of long bones and are usually seen in young children, more commonly less than 10 years of age. They are commonly mid-diaphyseal, affecting the forearm and lower leg. They are distinct from torus fractures.
Is a greenstick fracture the same as a hairline fracture?
Greenstick: A greenstick fracture occurs when there's a crack on one side of a bone that doesn't go all the way through it. Complete: This type of fracture occurs when a bone is fully broken. Stress: This type of fracture, which is a hairline crack, typically occurs because of overuse.
What is the ICD 10 code for nondisplaced distal radius fracture?
Fracture of lower end of radius ICD-10-CM S52. 515A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0):
What is the ICD 10 code for right nondisplaced distal radius fracture?
324D: Nondisplaced transverse fracture of shaft of right radius, subsequent encounter for closed fracture with routine healing.
How do you code a fracture in ICD-10?
In ICD-10-CM a fracture not indicated as displaced or nondisplaced should be coded to displaced, and a fracture not designated as open or closed should be coded to closed. While the classification defaults to displaced for fractures, it is very important that complete documentation is encouraged.
How long does it take to heal a greenstick fracture?
X-rays are required in a few weeks to make sure the fracture is healing properly, to check the alignment of the bone, and to determine when a cast is no longer needed. Most greenstick fractures require four to eight weeks for complete healing, depending on the break and the age of the child.
What is the treatment for a greenstick fracture?
In most cases, greenstick fractures are treated by immobilizing the bone (keeping it from moving) with a cast or a splint. Most casts remain in place for 4-6 weeks.
In which type of individual are you most likely to see a greenstick fracture?
Most greenstick fractures occur in children younger than 10 years of age. This type of broken bone most commonly occurs in children because their bones are softer and more flexible than are the bones of adults.
Is a greenstick fracture open or closed?
In addition to open, closed, and displaced fractures, broken bones are further categorized by other measures. These include: Greenstick fractures – Exclusive to children, greenstick fractures describe bones that have bent but not completely broken.
What is 7th Character Extension?
For codes less than 6 characters that require a 7th character a placeholder 'X' should be assigned for all characters less than 6. The 7th character must always be the 7th position of a code. E.g. The ICD-10-CM code T67.4 (Heat exhaustion due to salt depletion) requires an Episode of Care identifier.
The ICD code S523 is used to code Galeazzi fracture
The Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. It classically involves an isolated fracture of the junction of the distal third and middle third of the radius with associated subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint, the injury disrupts the forearm axis joint.
What is the ICd 10 code for a fractured ulna?
813.04Other and unspecified closed fractures of proximal end of ulna (alone)convert 813.04 to ICD-10-CM
What is the ICD-10 code for a torus fracture of radius and ulnaconvert?
813.47Torus fracture of radius and ulnaconvert 813.47 to ICD-10-CM
What is the ICd 10 code for fractures of the proximal end of the ulna?
813.14Other and unspecified open fractures of proximal end of ulna (alone)convert 813.14 to ICD-10-CM
What is the ICD-10 code for fracture of olecranon process of ulnaconvert?
813.01Closed fracture of olecranon process of ulnaconvert 813.01 to ICD-10-CM
What is the ICD-10 code for fracture of shaft of radius?
813.30Open fracture of shaft of radius or ulna, unspecifiedconvert 813.30 to ICD-10-CM
What is the ICd 10 code for fracture of unspecified part of forearm?
813.80Closed fracture of unspecified part of forearmconvert 813.80 to ICD-10-CM
What is the classification of distal radius and ulna fractures?
Distal radius and ulna fractures are classified according to fracture pattern, type of associated ulnar fracture, and direction of displacement, angulation, and rotation. Most distal radial metaphyseal fractures are displaced dorsally with apex volar angulation. 190 Volar displacement with apex dorsal angulation occurs less commonly with volar flexion mechanisms.
How to reduce greenstick fracture?
With apex volar angulated fractures of the radius, the rotatory deformity is supination. Pronating the radius and applying a dorsal-to-volar reduction force is utilized to restore bony alignment. Conversely, fractures with apex dorsal angulation result from pronation mechanisms of injury. Supinating the distal forearm and applying a volar-to-dorsal force should reduce the incomplete fracture of the radius. 135 Though these fractures are incomplete and patients often present with minimal pain, adequate analgesia will facilitate bony reduction and quality of cast application. Typically this is done with the assistance of conscious sedation. 64, 79, 114
What are the symptoms of a distal radial fracture?
Children with distal radial and/or ulnar fractures present with pain, swelling, and deformity of the distal forearm ( Fig. 11-9 ). The clinical signs depend on the degree of fracture displacement. With a nondisplaced torus fracture in a young child, medical attention may not be sought until several days after injury; the intact periosteum and biomechanical stability is protective in these injuries, resulting in minimal pain and guarding. Similarly, many of the physeal injuries are nondisplaced and present only with pain and tenderness at the physis. 142, 154 With displaced fractures, the typical dorsal displacement and apex volar angulation create an extension deformity that is usually clinically apparent. Careful inspection of the forearm is critical to evaluate for possible skin lacerations, wounds, and open fractures.
What is distal radial stress?
In contrast to the child with an acute, traumatic distal radius fracture, patients with distal radial physeal stress injuries typically report recurring, activity-related wrist pain. Characteristically, this pain is described as diffuse “aching” and “soreness” in the region of the distal radial metaphysis and physis. Pain may be reproduced in the extremes of wrist extension and flexion, and usually there is local tenderness over the dorsal, distal radial physis. Resistive strength testing of the wrist extensors will also reproduce the pain. There may be fusiform swelling about the wrist if there is reactive bone formation. The differential diagnosis includes physeal stress injury, ganglion, ligamentous or TFCC injury, tendinosis or musculotendinous strain, carpal fracture, and osteonecrosis of the scaphoid (Preiser disease) or lunate (Kienbock disease). Diagnosis is made radiographically in the context of the clinical presentation.
What is a metaphyseal fracture pattern?
Metaphyseal fracture patterns are classified as torus, incomplete or greenstick, and complete fractures ( Fig. 11-17 ). This system of classification has been shown to have good agreement between experienced observers. 167 Torus fractures are axial compression injuries. The site of cortical failure is the transition from metaphysis to diaphysis. 128 As the mode of failure is compression, these injuries are inherently stable and are further stabilized by the intact surrounding periosteum. Rarely, they may extend into the physis, putting them at risk for growth impairment. 155, 156, 158
How to treat displaced Salter Harris fracture?
Most displaced Salter–Harris I and II fractures are treated with closed reduction and cast stabilization. Closed manipulation of the displaced fracture is similarly performed with appropriate conscious sedation, analgesia, or, rarely, anesthesia to achieve pain relief and an atraumatic reduction. 64, 79, 114 Most of these fractures involve dorsal and proximal displacement of the epiphysis with an apex volar extension deformity. Manipulative reduction is by gentle distraction and flexion of the distal epiphysis, carpus, and hand over the proximal metaphysis ( Fig. 11-32 ). The intact dorsal periosteum is used as a tension band to aid in reduction and stabilization of the fracture. Unlike similar fractures in adults, finger trap distraction with pulley weights is often counterproductive. However, finger traps can help stabilize the hand, wrist, and arm for manipulative reduction and casting by applying a few pounds of weight for balance. Otherwise, an assistant is helpful to support the extremity in the proper position for casting.
How long does it take for a nondisplaced fracture to heal?
11-26 ). Serial radiographs are obtained in the first 2 to 3 weeks to confirm maintenance of acceptable radiographic alignment. In general, most fractures will heal within 4 to 6 weeks.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for xeroderma pigmentosum
- 2. icd 10 code for mid back lipoma
- 3. icd 10 code for snowboarding fall
- 4. icd 10 code for 90846
- 5. is there one procedure code icd 10 code for egd and biopsy of stomach?
- 6. icd-10 code for passenger injured in rollover accident
- 7. icd-9 code for fibrofatty breast tissue
- 8. icd-10-cm code for rectal pain
- 9. icd 10 code for hyperdipeden
- 10. icd 10 code for swelling of lips