What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is the ICD 10 code for Lyme disease?
- DRG 867 - OTHER INFECTIOUS AND PARASITIC DISEASES DIAGNOSES WITH MCC
- DRG 868 - OTHER INFECTIOUS AND PARASITIC DISEASES DIAGNOSES WITH CC
- DRG 869 - OTHER INFECTIOUS AND PARASITIC DISEASES DIAGNOSES WITHOUT CC/MCC
What is the ICD 10 code for leukemia?
Leukemia, unspecified, in remission. C95.91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C95.91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is ICD 10 code for leukocytosis?
What is the ICD 10 code for leukocytosis? 829 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of elevated white blood cell count, unspecified. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
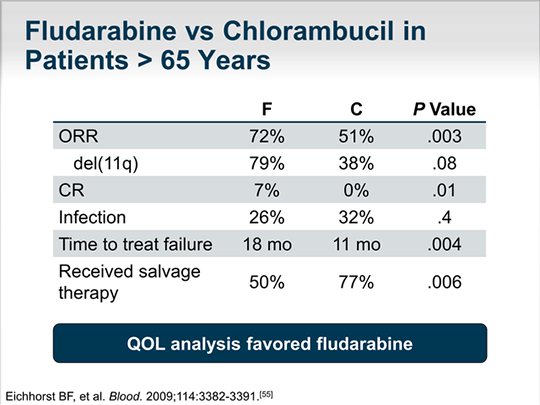
What is lymphoid leukemia?
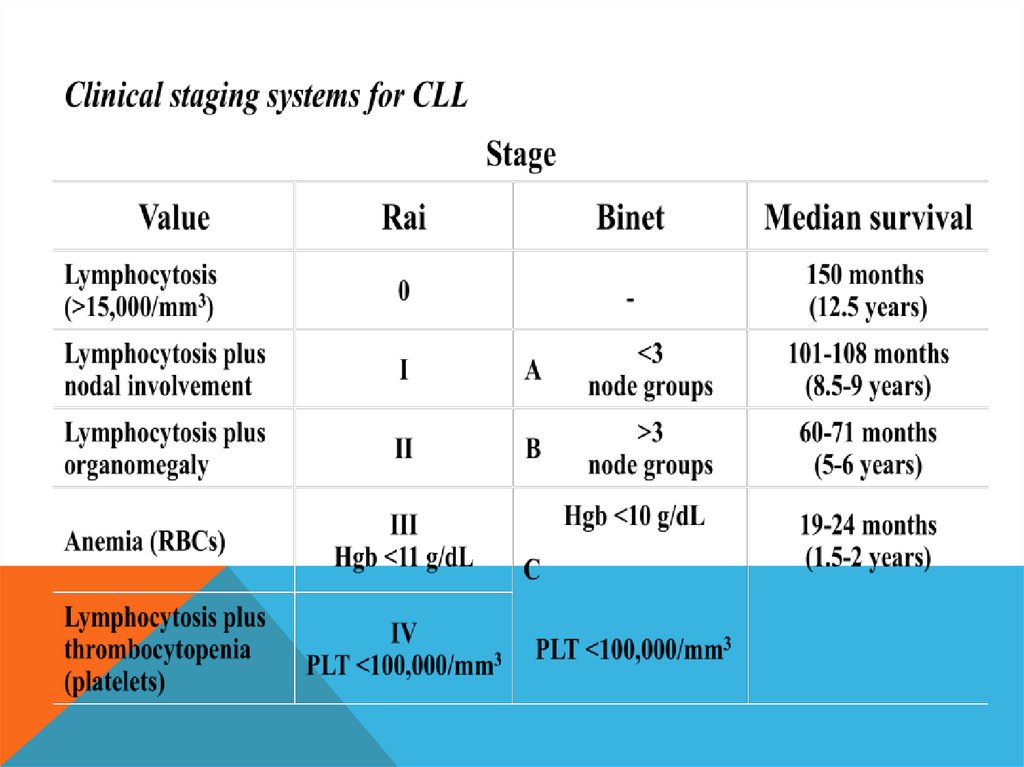
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (also called CLL) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow that usually gets worse slowly. CLL is one of the most common types of leukemia in adults.
How do you code chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Code 9823/3 is used for CLL, SLL, and CLL/SLL.
Is leukemia a lymphoid malignancy?
Leukemia is myeloid or lymphocytic depending on which bone marrow cells the cancer starts in. Lymphocytic leukemias (also known as lymphoid or lymphoblastic leukemia) start in the cells that become lymphocytes. Lymphomas are also cancers that start in those cells.
What is the ICD-10 code for leukemia?
C95. 9 - Leukemia, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the difference between CLL and SLL?
CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) and SLL (small lymphocytic lymphoma) are the same disease, but in CLL cancer cells are found mostly in the blood and bone marrow. In SLL cancer cells are found mostly in the lymph nodes. CLL/SLL is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
What is the ICD-10 code for SLL?
Small cell B-cell lymphoma, unspecified site The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C83. 00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is difference between leukemia and lymphoma?
“The simplest way to think about it is that lymphomas are solid tumors made up of blood cells. This kind of cancer usually causes enlarged lymph nodes or solid masses. Leukemia, on the other hand, is seen in the bloodstream – it's a liquid kind of cancer and it flows and is pumped around with the blood.”
What are the 4 types of leukemia?
The major types of leukemia are:Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). This is the most common type of leukemia in young children. ... Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). AML is a common type of leukemia. ... Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). ... Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). ... Other types.
What is acute lymphocytic leukemia in adults?
Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL; also called acute lymphocytic leukemia) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated. Anatomy of the bone. The bone is made up of compact bone, spongy bone, and bone marrow.
What is the ICD-10 code for History of leukemia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Personal history of leukemia Z85. 6.
What is the CPT code for leukemia?
CPT Codes*: 88184(x1), 88185(x22), 88189(x1). Additional 88185 CPTs may be added if initial screen is abnormal.
What is unspecified leukemia?
Leukemia of unspecified cell type A malignant (clonal) hematologic disorder, involving hematopoietic stem cells and characterized by the presence of primitive or atypical myeloid or lymphoid cells in the bone marrow and the blood.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the term for cancer of the white blood cells?
Chronic leukemia characterized by morphologically mature but immunologically less mature lymphocytes; manifested by an abnormal accumulation of these cells in blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic tissue. leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells help your body fight infection.
What tests are done to diagnose a cll?
tests that examine the blood, bone marrow, and lymph nodes diagnose cll. Your doctor may choose to just monitor you until symptoms appear or change. Treatments include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery to remove the spleen, and targeted therapy.
Is morphology included in the category and codes?
In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
Is lymphocytic leukemia hard on the blood?
These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells, making it hard for blood to do its work. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia ( cll), there are too many lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.cll is the second most common type of leukemia in adults.
What is the term for cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes?
A type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (white blood cells). Leukemia associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue; there are increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts.
What is a B cell neoplasm?
A malignant lymphocytic neoplasm of b-cell or t-cell lineage involving primarily the bone marrow and the peripheral blood. This category includes precursor or acute lymphoblastic leukemias and chronic leukemias. A progressive, proliferative disease of blood cells, originating from lymphoid cells.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
tests that examine the blood and bone marrow diagnose all. Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplants, and targeted immune therapy. Once the leukemia is in remission, you need additional treatment to make sure that it does not come back. nih: national cancer institute.
What is the name of the cancer that is caused by too many lymphoblasts?
An aggressive (fast-growing) type of leukemia (blood cancer) in which too many lymphoblasts (immature white blood cells) are found in the blood and bone marrow. leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells help your body fight infection. Your blood cells form in your bone marrow.
Does leukemia cause white blood cells to crowd out?
In leukemia, however, the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells. These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells, making it hard for blood to do its work. In acute lymphocytic leukemia (all), there are too many of specific types of white blood cells called lymphocytes or lymphoblasts.
What is a malignant lymphocytic neoplasm?
Clinical Information. A malignant lymphocytic neoplasm of b-cell or t-cell lineage involving primarily the bone marrow and the peripheral blood. This category includes precursor or acute lymphoblastic leukemias and chronic leukemias.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the disease associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue?
Leukemia associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue; there are increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Leukemia associated with hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissues and increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Code History.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a B cell neoplasm?
A malignant lymphocytic neoplasm of b-cell or t-cell lineage involving primarily the bone marrow and the peripheral blood. This category includes precursor or acute lymphoblastic leukemias and chronic leukemias. A progressive, proliferative disease of blood cells, originating from lymphoid cells.
What is the disease associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue?
Leukemia associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue; there are increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Leukemia associated with hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissues and increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a B cell neoplasm?
A malignant lymphocytic neoplasm of b-cell or t-cell lineage involving primarily the bone marrow and the peripheral blood. This category includes precursor or acute lymphoblastic leukemias and chronic leukemias. A progressive, proliferative disease of blood cells, originating from lymphoid cells.
What is the disease associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue?
Leukemia associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue; there are increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Leukemia associated with hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissues and increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Code History.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for itching eyes
- 2. icd-10 code for status post right wrist arthroscopy
- 3. icd 10 code for genital herpes
- 4. icd-10-cm code for alpers' disease
- 5. icd 10 code for g63
- 6. icd 10 code for left charcot foot
- 7. icd 10 code for anemia secondary to chronic kidney disease
- 8. icd-10 code for diminished renal excretion
- 9. icd 10 code for t cell pll
- 10. 2017 icd 10 code for hepatitis c with coma