What are the common causes of metabolic acidosis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code P74.0 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Late metabolic acidosis of newborn. (fetal) metabolic acidosis of newborn (P19) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code P74.0. Late metabolic acidosis of newborn. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Code on Newborn Record. Type 1 Excludes.
What are the clinical manifestations of metabolic acidosis?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM) 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): No change 2019 (effective 10/1/2018): No change 2020 (effective 10/1/2019): No change 2021 (effective 10/1/2020): No change 2022 (effective 10/1/2021): No ...
How is metabolic acidosis described as?
Mar 28, 2018 · Icd 10 Code For Metabolic Acidosis Unm Hospitalist Wiki / Icd 10 Codes Suggestions. NMVAHCS-Raymond G. Murphy Medical Center. Suggestions collected from... Icd-10 Code For Acidosis. AAPC Coder Complete provides all the coding and reimbursement tools needed for inpatient... Warning: All Sepsis Is ...
How is metabolic alkalosis diagnosed?
Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 276.2. Known As. Metabloic acidosis is also known as acidosis metabolic, alcohol induced ketoacidosis, alcoholic ketoacidosis, ketoacidosis due to acute alcohol intoxication, ketoacidosis due to acute alcoholic intoxication, ketosis, lactic acidosis, metabolic acidosis, metabolic acidosis w increased anion …

What is the metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis develops when too much acid is produced in the body. It can also occur when the kidneys cannot remove enough acid from the body.
What is R68 89 diagnosis code?
ICD-10 code R68. 89 for Other general symptoms and signs is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is diagnosis code E88 81?
ICD-10 | Metabolic syndrome (E88. 81)
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Nagma?
Valid for SubmissionICD-10:E87.2Short Description:AcidosisLong Description:Acidosis
What is the ICD-10 code for lactic acidosis?
Lactic acidosis shares the ICD-10-CM code, E87. 2, Acidosis, with other causes of acidosis, respiratory or metabolic. Mixed acid-base disorders are coded at E87.
What is diagnosis code E28 2?
ICD-10 code: E28. 2 Polycystic ovarian syndrome | gesund.bund.de.
What are the five criteria for metabolic syndrome?
According to the NCEP ATP III definition, metabolic syndrome is present if three or more of the following five criteria are met: waist circumference over 40 inches (men) or 35 inches (women), blood pressure over 130/85 mmHg, fasting triglyceride (TG) level over 150 mg/dl, fasting high-density lipoprotein (HDL) ...
What is the ICD-10 code for metabolic alkalosis?
E87. 3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.
What is the ICD-10 code for renal tubular acidosis?
EntryH00428 DiseaseOther DBsICD-11: GB90.44 ICD-10: N25.8 MeSH: D000141 OMIM: 179800 267300 602722ReferencePMID:19721811AuthorsPereira PC, Miranda DM, Oliveira EA, Silva ACTitleMolecular pathophysiology of renal tubular acidosis.30 more rows
What is the ICD-10 code for starvation ketoacidosis?
The ICD-10-CM code T73. 0XXA might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anemia due to starvation, deprivation of food, starvation, starvation ketoacidosis or starvation-related malnutrition. T73.
What is metabolic acidosis?
A disorder characterized by abnormally high acidity (high hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues. A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up.
What is acid base imbalance?
Acid base imbalance resulting from an accumulation of carbon dioxide secondary to hypoventilation. Acidosis caused by accumulation of lactic acid more rapidly than it can be metabolized. It may occur spontaneously or in association with diseases such as diabetes mellitus, leukemia, or liver failure.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E87.2. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is AAPC coder complete?
AAPC Coder Complete provides all the coding and reimbursement tools needed for inpatient coders, outpatient coders and CDI experts. Quickly view the OPPS fee schedules for freestanding ASCs and hospital based outpatient services in one place. For each CPT code, you can identify the applicable modifiers, status indicators and payment indicators. For procedures that require devices, you can view if there is a credit adjustment policy for the device. Avoid bundling and determine proper modifier use by using the OPPS CCI checker for up to 25 codes at one time. The cross-reference tools allow you to forward and backward map CPT to ICD-9-CM Volume 1 and 3, ICD-9-CM Volume 1 to ICD-10-CM and ICD-9-CM Volume 1 to the appropriate DRG options. Easily identity the DRG options, including CC and MCC, for each ICD-9-CM Volume 1 code. APC look up provides necessary detail on one page including long descriptor, payment and coverage info and more. CPT Assistant is the official word from the AMA on proper CPT code usage. AAPC Coder's Code Connect add-on allows you to search all CPT Assistant articles from 1990 to present by CPT code to narrow the options to only related articles for quick coding guidance. The HCPCS Coding Clinic delivers the official guidance published quarterly by the American Hospital Association (AHA) Central Office on correct HCPCS level II code usage. Each issue offers consistent and accurate advice for the proper use of HCPCS and includes information on HCPCS reporting for hospitals HCPCS Level 1 (CPT) and Level II codes, the latest code assignments from emerging technologies, and real examples. Continue reading >>
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes. It means 'NOT CODED HERE!' An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A type 2 Excludes note represents 'Not included here'. An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A code also note instructs that 2 codes may be required to fully describe a condition but the sequencing of the two codes is discretionary, depending on the severity of the conditions and the reason for the encounter. Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology. For such conditions the ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first followed by the manifestation. Wherever such a combination exists there is a 'use additional code' note at the etiology code, and a 'code first' note at the manifestation code. These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation. In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, 'in diseases classified elsewhere.' Codes with this title area component of the etiology / manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code. 'In disease Continue reading >>
Known As
Metabloic acidosis is also known as acidosis metabolic, alcohol induced ketoacidosis, alcoholic ketoacidosis, ketoacidosis due to acute alcohol intoxication, ketoacidosis due to acute alcoholic intoxication, ketosis, lactic acidosis, metabolic acidosis, metabolic acidosis w increased anion gap, metabolic acidosis increased anion gap, metabolic acidosis increased anion gap (IAG), and respiratory acidosis..
Metabolic Acidosis Definition and Symptoms
Metabolic acidosis is when there is a disruption in the body’s normal acid/base balance. Symptoms include headache, lack of energy, sleepiness, shallow breathing, loss of appetite, coma, or death.
What is metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis, increased anion gap (IAG) (met-ah-bol-ik as-id-o-sis) a condition in which the blood is too acidic. It may be caused by severe illness or sepsis (bacteria in the bloodstream) A disorder characterized by abnormally high acidity (high hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up A state due to excess retention of carbon dioxide in the body Acidosis caused by accumulation of lactic acid more rapidly than it can be metabolized; may occur spontaneously or in association with diseases such as diabetes mellitus, leukemia, or liver failure Acidosis resulted from any pathologic condition interfering with normal ventilation, e.g. In case of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease An abnormal increase in the acidity of the body's fluids An abnormally high acidity (excess hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues An abnormally high acidity of the blood and other body tissues. Acidosis can be either respiratory or metabolic Excess retention of carbon dioxide in the body resulting from ventilatory impairment Pathologic condition resulting from accumulation of acid or depletion of the alkaline reserve (bicarbonate) content of the blood and body tissues, and characterized by an increase in hydrogen ion concentration (decrease in ph) Continue reading >>
What is the name of the condition in which the blood is too acidic?
A condition in which the blood is too acidic. It may be caused by severe illness or sepsis (bacteria in the bloodstream). A disorder characterized by abnormally high acidity (high hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues. A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. A state due to excess retention of carbon dioxide in the body. Acid base imbalance resulting from an accumulation of carbon dioxide secondary to hypoventilation. Acidosis caused by accumulation of lactic acid more rapidly than it can be metabolized. It may occur spontaneously or in association with diseases such as diabetes mellitus, leukemia, or liver failure. Acidosis caused by accumulation of lactic acid more rapidly than it can be metabolized; may occur spontaneously or in association with diseases such as diabetes mellitus, leukemia, or liver failure. An abnormal increase in the acidity of the body's fluids An abnormally high acidity (excess hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues. An abnormally high acidity of the blood and other body tissues. Acidosis can be either respiratory or metabolic. Excess retention of carbon dioxide in the body resulting from ventilatory impairment. Increased acidity in the blood secondary to acid base imbalance. Causes include diabetes, kidney failure and shock. Metabolic acidosis characterized by the accumulation of lactate in the body. It is caused by tissue hypoxia. Pathologic condition resulting from accumulation of acid or depletion of the alkaline reserve (bicarbonate) content of the blood and body tissues, and characterized by an increase in hydrogen ion concentration (decrease in ph). Respi Continue reading >>
What is the ICD-10-CM/PCS MS-DRGv33?
ICD-10-CM/PCS MS-DRGv33 Definitions Manual Newborn (suspected to be) affected by maternal hypertensive disorders Newborn (suspected to be) affected by maternal renal and urinary tract diseases Newborn (suspected to be) affected by other maternal circulatory and respiratory diseases Newborn (suspected to be) affected by maternal nutritional disorders Newborn ( suspected to be) affected by maternal injury Newborn (suspected to be) affected by surgical procedure on mother Newborn (suspected to be) affected by other medical procedures on mother, not elsewhere classified Newborn (suspected to be) affected by periodontal disease in mother Newborn (suspected to be) affected by unspecified maternal condition Newborn (suspected to be) affected by incompetent cervix Newborn (suspected to be) affected by premature rupture of membranes Newborn (suspected to be) affected by oligohydramnios Newborn (suspected to be) affected by polyhydramnios Newborn (suspected to be) affected by ectopic pregnancy Newborn (suspected to be) affected by multiple pregnancy Newborn (suspected to be) affected by maternal death Newborn (suspected to be) affected by malpresentation before labor Newborn (suspected to be) affected by other maternal complications of pregnancy Newborn (suspected to be) affected by maternal complication of pregnancy, unspecified Newborn (suspected to be) affected by placenta previa Newborn (suspected to be) affected by other forms of placental separation and hemorrhage Newborn (suspected to be) affected by unspecified morphological and functional abnormalities of placenta Newborn (suspected to be) affected by other morphological and functional abnormalities of placenta Newborn (suspected to be) affected by placental transfusion syndromes Newborn (suspected to be) affected by pro Continue reading >>
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes. It means 'NOT CODED HERE!' An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A type 2 Excludes note represents 'Not included here'. An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A code also note instructs that 2 codes may be required to fully describe a condition but the sequencing of the two codes is discretionary, depending on the severity of the conditions and the reason for the encounter. Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology. For such conditions the ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first followed by the manifestation. Wherever such a combination exists there is a 'use additional code' note at the etiology code, and a 'code first' note at the manifestation code. These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation. In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, 'in diseases classified elsewhere.' Codes with this title area component of the etiology / manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code. 'In disease Continue reading >>
What is the process of making energy from food?
Respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis Metabolism is the process your body uses to get or make energy from the food you eat. Food is made up of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Chemicals in your digestive system break the food parts down into sugars and acids, your body's fuel. Your body can use this fuel right away, or it can store the energy in your body tissues, such as your liver, muscles, and body fat. A metabolic disorder occurs when abnormal chemical reactions in your body disrupt this process. When this happens, you might have too much of some substances or too little of other ones that you need to stay healthy. There are different groups of disorders. Some affect the breakdown of amino acids, carbohydrates, or lipids. Another group, mitochondrial diseases, affects the parts of the cells that produce the energy. You can develop a metabolic disorder when some organs, such as your liver or pancreas, become diseased or do not function normally. Diabetes is an example. Metabolic acidosis (Medical Encyclopedia) It can be scary when your baby is sick, especially when it is not an everyday problem like a cold or a fever. You may not know whether the problem is serious or how to treat it. If you have concerns about your baby's health, call your health care provider right away. Learning information about your baby's condition can help ease your worry. Do not be afraid to ask questions about your baby's care. By working together with your health care provider, you make sure that your baby gets the best care possible. Brief resolved unexplained event -- BRUE (Medical Encyclopedia) Crying - excessive (0-6 months) (Medical Encyclopedia) Hemorrhagic disease of the newborn (Medical Encyclopedia) Hyperglycemia - infants (Medical Encyclopedia) Continue reading >>
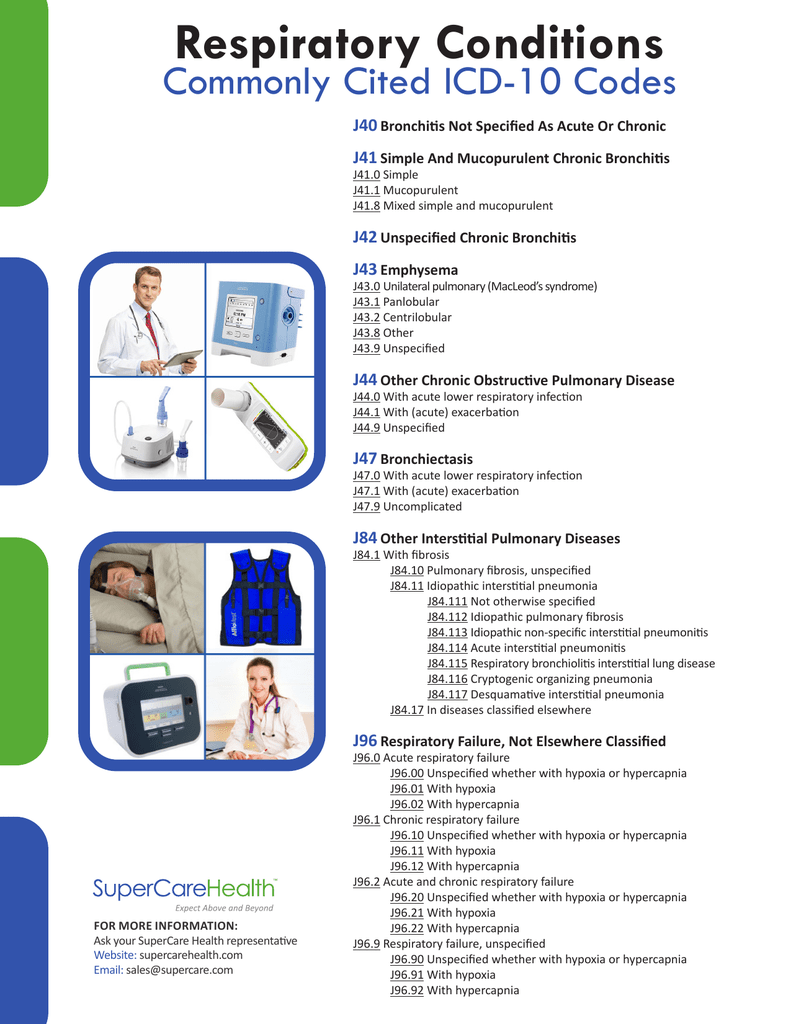
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10-cm code for hepatorenal syndrome
- 2. icd 10 code for ekc left eye
- 3. icd 10 code for m17.0
- 4. 2019 icd 10 code for nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage unspecified
- 5. icd 10 code for exposure to chemicals
- 6. icd 10 cm code for post incision bleeding
- 7. icd 10 code for acute exacerbation of chronic asthmatic bronchitis
- 8. icd 9 code for degenerative arthritis
- 9. icd 10 code for right knee djd
- 10. icd 9 code for acquired deformity of foot