What is the criteria for NSQIP database?
ACS NSQIP database. Criteria:TheIDNusedisatthediscretionoftheparticipatinghospital,althoughitiscommontoenterthepatient’s Medical Record Number (MRN) in this field. If the IDN or MRN are not available, a site may elect to assign a
What is the effective date for NSQIP operations?
ACS NSQIP OPERATIONS MANUAL EFFECTIVE DATE: OPERATION DATE (July 1, 2013 –December 31, 2013)Page 31 PREOPERATIVE RISK ASSESSMENT There are differing timeframes for preoperative risk factors. Please be aware of the specific times frames when assigning these variables.
When to contact the patient or physician for NSQIP postoperative occurrences?
If a patient returns a 30-day follow-up letter and reports that they developed one of the NSQIP postoperative occurrences within 30-days of the principal operative procedure, the patient or physician should be contacted to determine if they meet the criteria of the definition to assign the postoperative
What is the NSQIP closure variable?
matching NSQIP data to other data systems. This also allows more relevant classification of postoperative infections. Definition: This variable classifies three layers of wound closure. Criteria:Code the most complete closure of any incision based on the criteria below: A.
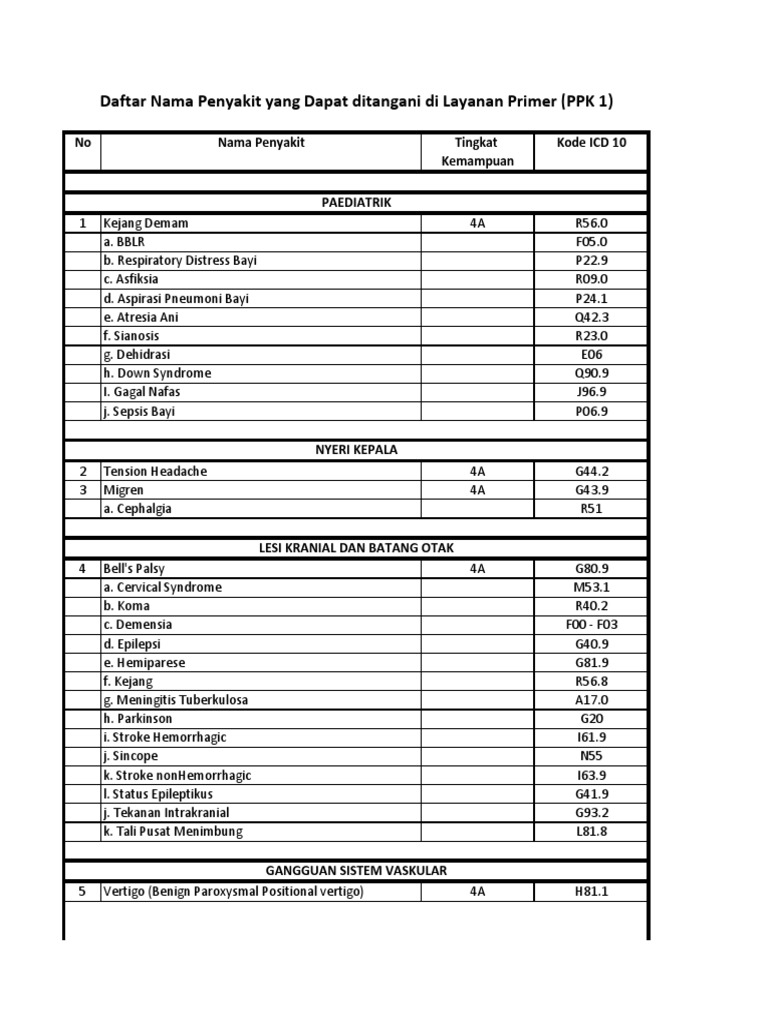
What is the sixth character of a code?
For most codes that require laterality, you report this number as the sixth character (e.g., H21.22- Degeneration of ciliary body ), but there are some codes where it appears as the fifth character (e.g., H26.3-, Drug-induced cataract ). And for other codes, you don’t report laterality at all.
What is CPT code 66982?
When you submit CPT code 66982, local coverage determinations (LCDs) require more than the traditional cataract diagnosis codes. To indicate why the surgery qualifies as complex, you also must report one of the following codes:
Abstract
The Emergency General Surgery (EGS) population is particularly at high risk for readmission. Currently, no system exists to predict which EGS patients are most at risk. We hypothesized that a subset of EGS patients could be identified with increased 30-day unplanned readmission.
Introduction
Emergency general surgery (EGS) encompasses a broad scope of surgical diagnoses and procedures. From 2001 to 2010, there was a 27% increase in EGS admissions over time. 1 Previous studies have identified that 80% of the EGS operative burden consists of seven common procedure types.
Material and methods
A retrospective data analysis was performed using the American College of Surgeons’ NSQIP Participant User File (PUF) from January 1, 2011-September 30, 2015.
Results
We identified 383,726 patients who met inclusion criteria and underwent nonelective general surgery procedures in NSQIP during the time period. Three patients were excluded based on readmission data being missing or contradictory. There was an 8.1% unplanned readmission rate ( Fig. 1 ).
Discussion
We have identified several risk factors for unplanned readmission in the EGS population using the NSQIP database. 8.1% of the NSQIP EGS population had an unplanned readmission from 2011 to 2015 (See Fig. 1 ). Most unplanned readmissions within this population were related to the primary procedure (73% related versus 27% unrelated).
Conclusions
The rate of unplanned readmission in patients undergoing EGS procedures in our NSQIP database was 8.1%. We hypothesized that a high-risk subpopulation could be identified, which may provide a window of opportunity for intervention and improvement.
Acknowledgment
Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for protein electrolyte screening
- 2. icd 10 cm code for fracture, midshaft left clavicle
- 3. icd 10 code for sarcoidosis with secondary nodules in the brain
- 4. icd 10 code for osteomyelitis due to diabetes
- 5. icd 10 code for amnesia unspecified
- 6. icd code 10 for urinary tract infection
- 7. icd 10 code for stress reaction grief
- 8. icd 9 code for autoimmune asthma
- 9. icd 10 code for infected of shoulder after prosthesis
- 10. icd-10 code for migraines