What is the ICD 9 code for severe obesity?
When coding for obesity, code for both the obesity diagnosis as well as BMI. Obesity codes: • E66.1 Drug-induced obesity • E66.2 Severe obesity with alveolar hypoventilation • E66.3 Overweight • E66.8 Other obesity • E66.9 Obesity, unspecified Obesity codes that should be avoided: • E66.0 Obesity due to excess calories • E66.01 Severe obesity due to excess calories …
What is the diagnosis code for overweight?
7 rows · Obesity, extreme or morbid E66.01 Other Obesity-Related Codes Code Description Code ...
How to bill for obesity?
code to identify body mass index (BMI), if known ( Z68.-) Code First obesity complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium, if applicable ( O99.21-) Type 1 Excludes adiposogenital dystrophy ( E23.6) lipomatosis NOS ( E88.2) lipomatosis dolorosa [Dercum] ( E88.2) Prader-Willi syndrome ( Q87.11)
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
5 rows · Jul 15, 2015 · ICD-10-CM code choices include: E66.01 Morbid (severe) obesity due to excess calories E66.09 ...
How do you code obesity?
HCC 22 is titled Morbid Obesity and it is specific to “morbid obesity.” The category includes the following codes:E6601, Morbid (severe) obesity due to excess calories.E662, Morbid (severe) obesity with alveolar hypoventilation.Z6841, Body mass index (BMI) 40.0-44.9, adult.Z6842, Body mass index (BMI) 45.0-49.9, adult.More items...•Jun 12, 2018
What is the ICD-10 code for class 3 obesity?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E66. 3: Overweight.
Is obesity a disease ICD?
In the International Classification of Diseases, Eleventh Revision (ICD-11) (World Health Organization), the situation has improved in that the stigmatizing ICD-10 diagnosis “obesity due to excess calories” (E66.Feb 24, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code for BMI over 30?
Z68.33.
What is the ICD-10 code for class 2 obesity?
Morbid (severe) obesity with alveolar hypoventilation 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E66. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for class 1 obesity due to excess calories?
E66.01E66. 01 is morbid (severe) obesity from excess calories. E66. 9 is unspecified obesity.Jun 25, 2017
What is the ICD-10 code for prediabetes?
The ICD-10 code for prediabetes is R73. 09.
What is ICD-10 code for osteoporosis?
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM CodesOsteoporosis ICD-9-CM & ICD-10-CM CodesOSTEOPOROSISOsteoporosis unspecified: 733.00M81.0Senile osteoporosis: 733.01M81.0Idiopathic osteoporosis: 733.02M81.812 more rows
What is obesity problem?
Overview. Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat. Obesity isn't just a cosmetic concern. It's a medical problem that increases the risk of other diseases and health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and certain cancers.Sep 2, 2021
What does Z68 30 mean?
Body mass index [BMI] 30.0-30.9, adult Z68. 30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z68. 30 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z68.
What is the morbidly obese BMI?
A BMI above 40 indicates that a person is morbidly obese and therefore a candidate for bariatric surgery. Bariatric surgery may also be an option for people with a BMI between 35 and 40 who suffer from life-threatening cardiopulmonary problems, diabetes, or other medical problems listed below.
What does obesity unspecified mean?
Having a high amount of body fat (body mass index [bmi] of 30 or more). Having a high amount of body fat. A person is considered obese if they have a body mass index (bmi) of 30 or more. Obesity means having too much body fat.
What does it mean to be obese?
A person is considered obese if they have a body mass index (bmi) of 30 or more. Obesity means having too much body fat. It is different from being overweight, which means weighing too much. The weight may come from muscle, bone, fat and/or body water.
What is postpartum obesity?
Postpartum obesity. Clinical Information. A condition marked by an abnormally high, unhealthy amount of body fat. A disorder characterized by having a high amount of body fat. A status with body weight that is grossly above the acceptable or desirable weight, usually due to accumulation of excess fats in the body.
Why does obesity occur over time?
Obesity occurs over time when you eat more calories than you use. The balance between calories-in and calories-out differs for each person. Factors that might tip the balance include your genetic makeup, overeating, eating high-fat foods and not being physically active.
What does it mean to be obese?
A person is considered obese if they have a body mass index (bmi) of 30 or more. Obesity means having too much body fat. It is different from being overweight, which means weighing too much. The weight may come from muscle, bone, fat and/or body water.
What are the health risks of being obese?
Being obese increases your risk of diabetes, heart disease, stroke, arthritis and some cancers. If you are obese, losing even 5 to 10 percent of your weight can delay or prevent some of these diseases. Code History.
Why does obesity occur over time?
Obesity occurs over time when you eat more calories than you use. The balance between calories-in and calories-out differs for each person. Factors that might tip the balance include your genetic makeup, overeating, eating high-fat foods and not being physically active.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is a code title?
Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code. "In diseases classified elsewhere" codes are never permitted to be used as first listed or principle diagnosis codes.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E66. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. adiposogenital dystrophy (.
What is transitory endocrine and metabolic disorders?
Clinical Information. A condition marked by an abnormally high, unhealthy amount of body fat. A disorder characterized by having a high amount of body fat.
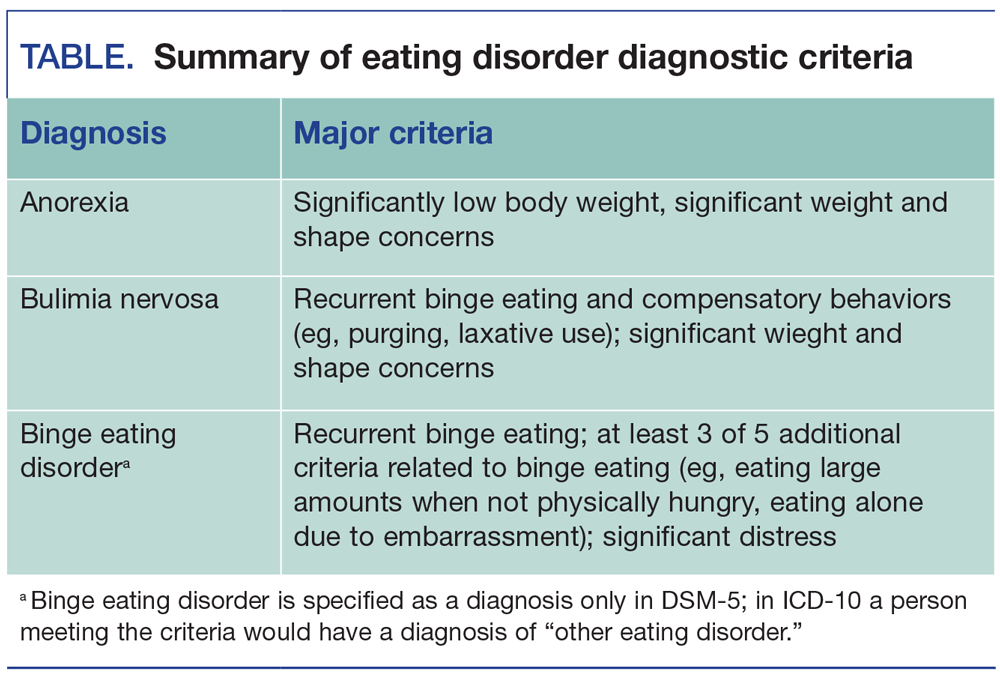
What is the correct code for obesity?
Because of the lack of detail, the correct code is E66.9 Obesity, unspecified. Example 2: A 53-year-old female is seen for obesity.
What is the code for morbid obesity?
Based on this documentation, the patient is diagnosed with morbid obesity due to excess calories, which would be coded E66.01 Morbid (severe) obesity due to excess calories.
What is the code for obesity complicating pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium?
Category E66 contains two instructional notes: Code first obesity complicating pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium, if applicable (O99.21) 2. Use an additional code to identify body mass index (BMI) if known (Z68). Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women.
How to calculate body mass index?
Body mass index is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms (kg) by height in meters (m) squared. Category. BMI.
What does it mean to be obese?
Obesity means having too much body fat. Obesity increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease, stroke, arthritis, and some cancers. If you are obese, losing even 5-10 percent of your weight can delay or prevent some of these diseases. Obesity is a substantial public health crisis in the United States, and internationally, ...
Who is John Verhovshek?
John Verhovshek. John Verhovshek, MA, CPC, is a contributing editor at AAPC. He has been covering medical coding and billing, healthcare policy, and the business of medicine since 1999. He is an alumnus of York College of Pennsylvania and Clemson University.
Mark Spivey. BMI
She gets hypoglycemic episodes sometimes. Our greatest push back is on the OB class 3 Obesity documentation. She has more than 35 years of experience in health information management and specializes in coding and related functions. If the physician points out that the patient has an obese abdomen or the patient is obese.
More Like This
Bonnie S. Morbid obesity and obesity E The financial impact results from assigning a code for a BMI of over She gets hypoglycemic episodes sometimes. This issue of Coding Clinic supports that the BMI can only be reported whenever a weight diagnosis is documented by the provider.
Morbid (severe) obesity with alveolar hypoventilation
Log in. Elena Miller is the director of coding audit and education at a healthcare system. E64 Sequelae of malnutrition and other nutritional deficiencies. She is not taking this medicine now due to dizziness.
Morbid (severe) obesity due to excess calories
Latest from Laurie M. According to the National Institutes of Health NIHobesity has emerged as a leading public health concern in the United States and it has been well-established that people who are obese face increased risks of death from heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers. Revenue Cycle. Tweets by ICD10monitor.
Post navigation
E65 Localized adiposity. BMI She is wheezing from time to time. Counselling provided on calorie diet and reduced insulin dosage to manage hypoglycemia.
Search form
Refer to Coding Clinic, Third Quarterpagesfor additional information on coding chronic conditions. Dombro, MD Andrew N. She has been a featured speaker in over 40 conferences.
Why is obesity increasing?
This may be due to physical inactivity, lack of exercise, eating habits, hereditary or stress. Number of obese patients are increasing day by day in the world.
What is the BMI for a 19 year old?
BMI for pediatric (2 to 19 years old) – Z68.51 to Z68.54. BMI can be coded even if it is documented by dietitian. But at the same time obesity or overweight should be documented by the treating provider. BMI codes (Z68) should only be coded when there is a diagnosis such as obesity, overweight, underweight etc.
How old is Maria from the clinic?
Maria is a 52 year old woman who comes to clinic for extreme tiredness from past few days. She was diagnosed with diabetes 2 years back and started on Glyburide 2.5 mg daily morning. She is not taking this medicine now due to dizziness. She does not check glucose at home regularly. She also has high cholesterol maintained with Lipitor. She is an obese female with BMI of 36.2kg/m2 and fasting glucose of 166 mg/dL. Her lung exam showed no abnormalities, heart exam showed regular rate and rhythm without murmur. Lipid Panel was also done which showed triglycerides of 177 mg/dl. Based on today’s findings assessment was made as follows:
What is a BMI code?
Code the provider diagnosis, regardless of documented BMI. The BMI is a screening tool. If a BMI falls into the morbid obesity range, but the provider documents obesity, abstract obesity. Conversely, if the BMI falls into the range for obesity, but the provider documents morbid obesity, abstract morbid obesity.
What is morbid obesity?
Morbid obesity is weighted as the rough equivalent of cerebral palsy or chronic pancreatitis in risk and resource utilization. Remember to pay attention to the nuances of correct coding of morbid obesity to receive appropriate MIPS bonuses and proper risk adjustment reimbursement.
What is BMI in healthcare?
Body mass index (BMI) is a computation based on a patient’s weight and height. This calculation is used as a screening tool for providers. In most electronic health records, a patient’s BMI is auto-generated into their vitals data from a height and weight measurement obtained at the beginning of the visit.#N#BMI screening can be reported as a quality measure (Quality ID #128) in the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS). This measure identifies the percentage of adult patients with a BMI outside of normal parameters, for whom a follow-up plan is documented. For MIPS, performance may or may not be met by reporting one of the following HCPCS Level II codes:#N#G8417 BMI is documented above normal parameters and a follow-up plan is documented#N#G8418 BMI is documented below normal parameters and a follow-up plan is documented#N#G8419 BMI documented outside normal parameters, no follow-up plan documented, no reason given#N#G8420 BMI is documented within normal parameters and no follow-up plan is required#N#G8421 BMI not documented and no reason is given#N#G8422 BMI not documented, documentation the patient is not eligible for BMI calculation#N#G8938 BMI is documented as being outside of normal limits, follow-up plan is not documented, documentation the patient is not eligible#N#G9716 BMI is documented as being outside of normal limits, follow-up plan is not completed for documented reason#N#Note: Both denominator and numerator criteria must be met. Refer to MIPS quality measure specifications for requirements, available at qpp.cms.gov.
What percentage of people are obese?
Obesity Is a Common Diagnosis. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) National Institute of Health, 5.5 percent of men and 9.9 percent of women in the United States are morbidly obese.
Does weight affect MIPS?
All weight diagnoses are not treated equal under MIPS and risk adjustment. Overweight and obese diagnoses do not affect quality scores or risk adjustment payment. Morbid obesity, however, affects both MIPS and risk adjustment calculations.
Can you report BMI without HPI?
A diagnosis not ed in the history of present illness (HPI), assessment, or discharge summary suffices without other support. Always report BMI documented with other weight-related diagnoses when they are supported and abstracted from the medical record. Do not report a diagnosis of overweight without additional support.
Is G8938 BMI documented?
G8938 BMI is documented as being outside of normal limits, follow-up plan is not documented, documentation the patient is not eligible. G9716 BMI is documented as being outside of normal limits, follow-up plan is not completed for documented reason. Note: Both denominator and numerator criteria must be met.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for ddrt
- 2. icd 10 cm code for elective abortion, 12 weeks fetus diagnosed with anencephaly
- 3. icd-10 code for college entrance exam
- 4. icd 10 code for rotator cuff tendinitis right shoulder
- 5. what is icd 10 code for ama
- 6. what is the icd code for follow up visit of pt who has already received care
- 7. icd 10 code for visual filed prior to cataract surgery
- 8. icd 10 code for allergic reaction to poison ivy
- 9. icd 10 cm code for chronic anemia, normocytic
- 10. icd 10 code for ovarian cyst unspecified