How to identify atrial fibrillation?
Oct 01, 2021 · Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. I48.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate …
What is the ICD 10 code for rapid AFIB?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48.1. Persistent atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation, persistent; Atrial flutter; Atrial flutter, chronic; Atrial flutter, paroxysmal; Chronic atrial flutter; Paroxysmal atrial …
How to confirm atrial fibrillation?
I48.0 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. The code I48.0 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through …
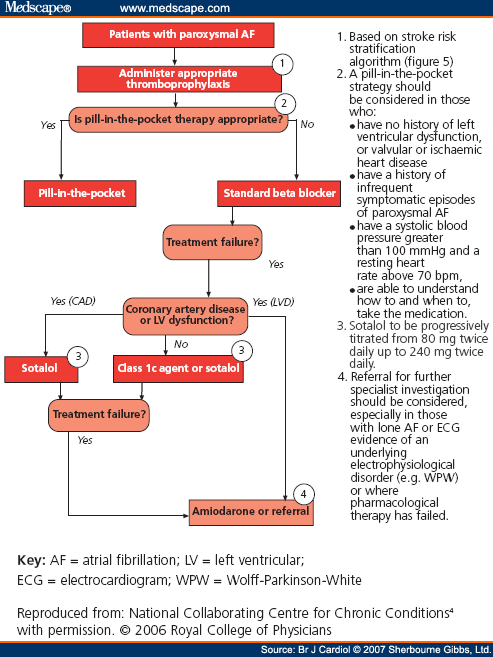
How to treat paroxysmal AFIB?
Codes. I48 Atrial fibrillation and flutter. I48.0 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. I48.1 Persistent atrial fibrillation. I48.11 Longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation. I48.19 Other persistent atrial …

Is paroxysmal atrial fibrillation the same as atrial fibrillation?
What is a paroxysmal AF?
How do you do ICD-10 codes for atrial fibrillation?
What is the difference between paroxysmal and persistent AFib?
What is the ICD 10 code for paroxysmal atrial flutter?
What is paroxysmal arrhythmia?
What is the ICD 10 code for rapid atrial fibrillation?
AFIB with a rapid ventricular response is a kind of irregular heartbeat. The electrical impulses in your heart cannot work correctly if your heartbeat is too fast. This abnormal heartbeat is referred to as “atrial fibrillation” or “AFIB” by doctors.
Can you code atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter together?
What is the ICD 10 code for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response?
Can you have persistent and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation at the same time?
What are the 4 types of AFib?
- Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Paroxysmal AFib comes and goes. ...
- Persistent atrial fibrillation. Persistent AFib also begins spontaneously. ...
- Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. ...
- Permanent atrial fibrillation.
What are the 3 types of AFib?
- Paroxysmal Afib: This type of Afib occurs intermittently and stops on its own within seven days.
- Persistent Afib: This type of atrial fibrillation lasts longer than seven days. ...
- Long-standing persistent Afib: This is similar to persistent Afib, but lasts longer than a year.
Is atrial fibrillation a complication?
Atrial fibrillation is very common in postoperative patients and should be verified as a complication before coding as such. When multiple types of atrial fibrillation are documented in the record select the most specific type. There are other examples of how to code atrial fibrillation when multiple types are documented in the latest issue ...
What causes atrial fibrillation?
The causes of atrial fibrillation is oftentimes unknown, but can be the result of damage to the heart’s electrical system caused by conditions such as uncontrolled hypertension and coronary artery disease.
Can atrial fibrillation cause blood clots?
This arrhythmia can cause a patient to develop blood clots, have a stroke, heart failure or other conditions. The heart rate is most often rapid and causes poor blood flow. When a patient is in atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers of the heart (atria) are beating differently than the lower chambers (ventricles).
Does atrial fibrillation go away?
Sometimes treating and controlling the underlying cause will make the atrial fibrillation go away. If this does not help the erratic rhythm, then the patient may require treatment with beta blockers and calcium channel blockers to help slow the heart rate. The rhythm should be restored to a normal rhythm to reduce the high heart rate.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for right aka
- 2. icd 10 code for dense left hemiparesis
- 3. 2016 icd 10 code for extremity pain
- 4. 2015 icd 10 code for blood vesseel injury
- 5. icd 9 code for history of abdominal cancer
- 6. icd 10 code for herniated nucleus pulposus l4-5
- 7. icd 10 code for corneal transplant
- 8. icd 10 code for vomiting unspecified
- 9. icd 10 cm code for ige mediated allergic asthma
- 10. icd 10 code for fissuring of skin