What is the CPT code for HIV infection?
The code description for B20 is human immunodeficiency virus disease, therefore HIV disease is included in B20, according to the Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting. That excludes note is specifically referring to a patient that has an asymptomatic HIV infection status, also known as HIV positive.
What is the diagnosis code for HIV with no symptoms?
If the provider document without any symptoms like HIV positive, known HIV or HIV test positive, then we need to assign the Z21 code. In this case, the primary diagnosis code will be always O98.7_, followed by HIV (symptomatic-B20 or asymptomatic-Z21) and HIV related condition.
What is the ICD 10 code for HIV B20?
Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease. B20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM B20 became effective on October 1, 2018.
How do you code HIV as an unrelated condition?
If HIV patient met with an accident and admits the hospital then it’s an unrelated condition, in this case the primary diagnosis code will be unrelated condition, secondary diagnoses code will HIV (B20) and followed by any HIV related condition. The sequencing of code will be in below order.
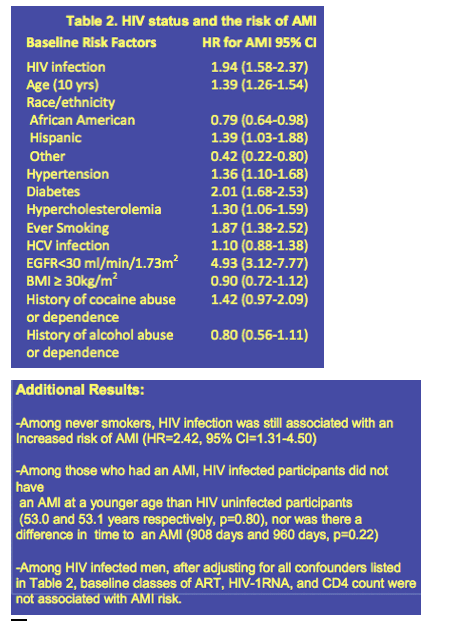
What is the ICD 10 code for AIDS?
B22 Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease resulting in other specified diseases.
Do you always code B20 first?
If a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, B20 Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease should be sequenced first, followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions.
What is ICD 10 code Z21?
Code Z21 is used for patients who are asymptomatic, meaning they are HIV positive but have never had an HIV-related condition. Once that patient experiences an HIV-related condition, the Z21 code is no longer appropriate.
When do you use B20 and Z21?
Following ICD-10 guidelines, if a patient has or has had an HIV related condition, use B20 AIDS. If the patient has a positive HIV status, without symptoms or related conditions, use Z21.
What is code Z71 7?
Z71. 7 — Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] counseling.
What is DX B20?
Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease B20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can Z21 be used as a primary diagnosis?
Z21 is not usually sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
What does code Z12 11 mean?
A screening colonoscopy should be reported with the following International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition (ICD-10) codes: Z12. 11: Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of the colon.
Which code is used for a pain diagnosis?
The ICD-10-CM Index indicates that pain NOS is reported with code R52 (Pain, unspecified).
What is the ICD-10-CM code for malignant neoplasm base of tongue?
C01 - Malignant neoplasm of base of tongue | ICD-10-CM.
What is the primary ICD 10 code for HIV?
The primary ICD 10 code should be HIV B20 and the secondary diagnoses code is HIV related condition.
When should ICD 10 be coded for HIV?
ICD 10 code for HIV should be coded only when it’s confirmed from the provider
What is a symptomatic HIV patient?
A symptomatic HIV patient is at initial visit for sprained left ankle
What is the ICD 10 code for encounter for screening?
ICD 10 code for Encounter for screening is Z11.4
What does asymptomatic mean in a provider?
Asymptomatic means showing no symptoms. If the provider document without any symptoms like HIV positive, known HIV or HIV test positive, then we need to assign the Z21 code.
What is the sequence for HIV?
Sequencing. The proper sequencing for HIV depends on the reason for the admission or encounter. When a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, sequence B20 Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease first, followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions. Conditions always considered HIV-related include ...
What condition must be confirmed to select the code?
In the inpatient setting, HIV is the only condition that must be confirmed to select the code. All other conditions documented as “probable,” suspected,” likely,” “questionable,” “probable,” or “still to rule out” are coded as if they exist in the inpatient setting. Dx. Sequencing. The proper sequencing for HIV depends on the reason for ...
When to use Z21?
Apply Z21 Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] infection status when the patient is HIV positive and does not have any documented symptoms of an HIV-related illness. Do not use this code if the term AIDS is used. If the patient is treated for any HIV-related illness, or is described as having any condition resulting from HIV positive ...
Is HIV a diagnosis?
HIV infection/illness is coded as a diagnosis only for confirmed cases. Confirmation does not require documentation of a positive blood test or culture for HIV; the physician’s diagnostic statement that the patient is HIV positive or has an HIV-related illness is sufficient.#N#In the inpatient setting, HIV is the only condition that must be confirmed to select the code. All other conditions documented as “probable,” suspected,” likely,” “questionable,” “probable,” or “still to rule out” are coded as if they exist in the inpatient setting.#N#Dx. Sequencing#N#The proper sequencing for HIV depends on the reason for the admission or encounter. When a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, sequence B20 Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease first, followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions. Conditions always considered HIV-related include Kaposi’s sarcoma, lymphoma, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), cryptococcal meningitis, and cytomegaloviral disease. These conditions are considered opportunistic infections.#N#If a patient with HIV disease is admitted for an unrelated condition (e.g., fracture), sequence the code for the unrelated condition, first. Report B20 as an additional diagnosis, along with any HIV-related conditions.#N#Apply Z21 Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] infection status when the patient is HIV positive and does not have any documented symptoms of an HIV-related illness. Do not use this code if the term AIDS is used. If the patient is treated for any HIV-related illness, or is described as having any condition resulting from HIV positive status, use B20.#N#Patients with inconclusive HIV serology, and no definitive diagnosis or manifestations of the illness, may be assigned code R75 Inconclusive laboratory evidence of human immunodeficiency virus [HIV].#N#Known prior diagnosis of an HIV-related illness should be coded to B20. After a patient has developed an HIV-related illness, the patient’s condition should be assigned code B20 on every subsequent admission/encounter. Never assign R75 or Z21 to a patient with an earlier diagnosis of AIDS or symptomatic HIV (B20).#N#If a patient is being seen to determine HIV status, use code Z11.4 Encounter for screening for human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]. Should a patient with signs, symptoms or illness, or a confirmed HIV-related diagnosis be tested for HIV, code the signs and symptoms or the diagnosis. If the results are positive and the patient is symptomatic, report B20 with codes for the HIV-related symptoms or diagnosis. The HIV counseling code (Z71.7) may be used if counseling is provided for patients with positive test results. When a patient believes that he/she has been exposed to or has come into contact with the HIV virus, report Z20.6.
What is the ICD-9 code for HIV?
The classification for symptomatic HIV infection consists of a single, three-digit ICD-9-CM code -- code 042, found in Chapter 1, Infectious and Parasitic Diseases, of the ICD-9-CM. This classification places HIV infection at the beginning of the section on viral diseases. Multiple coding of all listed manifestations of HIV infection is required. The new code for asymptomatic HIV infection, V08, is found in the Supplementary Classification of Factors Influencing Health Status and Contact with Health Services; the code for inconclusive serologic tests for HIV, 795.71, is found in Chapter 16, Signs, Symptoms, and Ill-Defined Conditions.
What is the code for HIV serology?
Patients with inconclusive HIV serology, but no definitive diagnosis or manifestations of the illness may be assigned code 795.71.
What is the code for asymptomatic HIV?
Patients with physician-documented asymptomatic HIV infections who have never had an HIV-related illness should be coded to V08, Asymptomatic Human Immunodeficiency Virus {HIV} Infection.
What is the difference between code 795.8 and code 044.9?
Code 795.8 was intended for inconclusive HIV test results, whereas code 044.9 was intended for asymptomatic HIV infection (or a statement of "HIV positive"). However, both of these codes have been widely misused because of the lack of clear instructions and guidelines.
Why are there modifications to the classification of HIV?
The increasing incidence of HIV infection and advances in medical knowledge about the spectrum of illnesses caused by this virus have created demand for continued modifications to the classification. The current modifications will simplify the coding of HIV-related illnesses and should improve the accuracy of reporting, allowing public health officials, clinical researchers, and agencies that finance health care to monitor more reliably the diagnoses of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and other manifestations of HIV infection.
What is the code for HIV counseling?
If the results are negative, use code V65.44, HIV counseling. If the results are positive, code V08, Asymptomatic HIV infection, should be used unless the patient has symptoms of HIV disease. If the test result is positive and the patient has an HIV-related illness, code 042, HIV disease, should be used.
What is the new HIV code?
In addition, a new code, V08, has been created for asymptomatic HIV infection. The new code, 795.71, is applicable only to those patients who test positive on a preliminary screening test, but whose HIV infection status is not yet confirmed.
What is the asymptomatic code for HIV?
Once a patient is coded to B20, they will always have B20 coded on their record; they will never go back to being coded using the asymptomatic code Z21. Code Z21 is used for patients who are asymptomatic, ...
What is the Z21 code?
Code Z21 is used for patients who are asymptomatic, meaning they are HIV positive but have never had an HIV-related condition. Once that patient experiences an HIV-related condition, the Z21 code is no longer appropriate.
Can you code B20 for HIV?
says that patients who are HIV positive with any known prior diagnosis of an HIV related illness should be coded to code B20. Only confirmed cases are coded using code B20. HIV is one of three conditions that cannot be coded based on the documented terminology, “possible, probable, or suspected,” or any other similar terminology.
Can HIV be coded?
HIV is one of three conditions that cannot be coded based on the documented terminology, “possible, probable, or suspected,” or any other similar terminology. It is not required that any form of testing be documented, such as a positive serology test.
What is coding clinic 2000?
Coding Clinic 2000 3Q#N#When coding for physician services, whether provided in the hospital inpatient setting or in the physician office, coders should be guided by the Diagnostic Coding and Reporting Guidelines for Outpatient Services (Hospital-Based and Physician Office). The inpatient guidelines are for hospital coding. Therefore, in the outpatient settings do not code diagnoses documented as "probable," "suspected," "questionable," "rule out," or "working diagnosis." Rather, code the condition (s) to the highest degree of certainty for that encounter/visit, such as symptoms, signs, abnormal test results, or other reason for the visit. V-codes may be assigned when appropriate. Please refer to the V-code article published in Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 1996 and Fourth Quarter 1998, respectively, for further discussion.
Is V67.X a follow up?
no to the acute renal failure and no to the hyperkalemia, these would be follow up following treatment a V67.x code
Can a physician code a possible diagnosis?
Physician coding may never code a possible diagnosis, they may code only confirmed diagnosis or signs and symptoms. As far as a resolved dx then it will depend on what it is. If the patient is returning for an infection and it is documented as resolved at this encounter then we code the infection since that is why the patient is returning and it not deemed resolved until after exam. However for other conditions such as post surgical we code a follow up code from the V67.xx category or an aftercare code such as a V54.x or V58.xx.
Can an outpatient coder code "possible"?
Outpatient coders should not code "possible", "probable", "suspected", "question of". We should choose a diagnosis from symptoms instead.
Can you bill for resolved inpatient coding?
Resolved: unless continuing care, cannot bill for resolved in either the facility inpatient coding or physician coding, non facililty.
Do outpatients code probable?
Therefore, in the outpatient settings do not code diagnoses documented as "probable," "suspected," "questionable," "rule out," or "working diagnosis.". Rather, code the condition (s) to the highest degree of certainty for that encounter/visit, such as symptoms, signs, abnormal test results, or other reason for the visit.
Do you code a V67.x?
yes we are coding the reason for the visit which was the infection, if the patient is instructed to return yet again just to be sure then that visit gets a V67.x code for follow up following completed therapy. There is an old coding clinic on this which is where I learned, but I do not remember the year, sorry.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 pcs code for below the knew amputation
- 2. icd 10 code for fall and striking object
- 3. icd 10 code for left foot blister
- 4. what is the icd 10 code for long term use of aspirin
- 5. what is the icd 10 cm code for hypothyroidism
- 6. icd 10 code for colon cancer in remission
- 7. icd 10 code for pathologic fracture of ankle 2016
- 8. icd 10 code for abnormal mcm
- 9. icd 9 code for depression nos
- 10. icd-10-cm code for hallux valgus of left great toe metatarsal