What is the ICD 10 code for retinal hyperpigmentation?
Midperipheral retinal hyperpigmentation often seen in retinitis pigmentosa ICD-10 Diagnosis Code: H35.52–Pigmentary retinal dystrophy
What is the ICD 10 code for retinal dystrophy?
Pigmentary retinal dystrophy. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code. H35.52 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM H35.52 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is retinitis pigmentosa (R pigmentosa)?
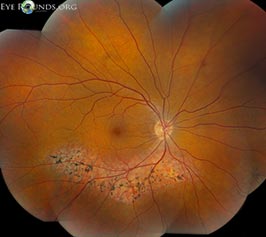
Retinitis pigmentosa is a rod-cone dystrophy that results in cell death, predominately in the rod photoreceptors. The genetic defects that cause retinitis pigmentosa can also affect the cone photoreceptors and the retinal pigment epithelium. Fundus images are from a 47-yer-old Hispanic male with retinitis pigmentosa.
What is the ICD 10 code for retinitis chorioretinal?
Retinitis - see also Inflammation, chorioretinal. albuminurica N18.9. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N18.9. Chronic kidney disease, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Chronic renal disease. Chronic renal failure NOS. Chronic renal insufficiency.
Is retinitis pigmentosa the same as retinal dystrophy?
Retinitis pigmentosa: It is the most commonly seen retinal dystrophy. RP is a progressive rod-cone disease with rods affected first and has a high level of clinical and genetic heterogeneity. The age of presentation and the prognosis depends on the type of inheritance.
What is the ICD-10 code for retinitis?
Unspecified chorioretinal inflammation The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H30. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is typical retinitis pigmentosa?
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a group of rare eye diseases that affect the retina (the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of the eye). RP makes cells in the retina break down slowly over time, causing vision loss.
What is the ICD-10 code for retinitis left eye?
92: Unspecified chorioretinal inflammation, left eye.
Is there any treatment for retinitis pigmentosa?
At this time, there is no specific treatment for retinitis pigmentosa. However, protecting your eye's retina by using UV sunglasses may help delay the start of symptoms. A retinal prosthesis (artificial retina) has been developed for individuals with very advanced disease and severe vision loss.
What is the ICD-10 code for blindness?
If “blindness” or “visual loss” is documented without any information about whether one or both eyes are affected, assign code H54. 7, Unspecified visual loss.
What are the different types of retinitis pigmentosa?
Researchers have identified several major types of nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa, which are usually distinguished by their pattern of inheritance: autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked. Less commonly, retinitis pigmentosa occurs as part of syndromes that affect other organs and tissues in the body.
How do you diagnose retinitis pigmentosa?
DiagnosisEye examination: An ophthalmologist (eye doctor) can diagnose retinitis pigmentosa (RP). ... If RP is suspected, an ophthalmologist may confirm a diagnosis by performing an electroretinogram (ERG). ... Visual tests can also be performed to determine the severity of vision loss.More items...
Is retinitis pigmentosa an autoimmune disease?
We conclude that although retinitis pigmentosa is genetically determined, patients develop autoimmunity against retinal tissue due to suppression of cell-mediated immunity. Association of rheumatoid factor in 8% of the cases further confirms the loss of homeostatic control owing to suppressed cell-mediated immunity.
What is the ICD-10 code for maculopathy?
Toxic maculopathy, unspecified eye H35. 389 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H35. 389 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic retinopathy?
E11. 31 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus with unspecified diabetic retinopathy. ICD-10-CM.
What is the correct ICD-10 code for pigmentary retinal dystrophy?
H35.52ICD-10-CM Code for Pigmentary retinal dystrophy H35. 52.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for trained night feeder
- 2. icd 9 code for possible dementia
- 3. 2017 icd 10 code for tear right posterior horn and body of the medial meniscus.
- 4. icd 10 code for retinal disorder
- 5. icd 10 code for hyperlipidemia
- 6. icd-10 code for polypharmacy unspecified
- 7. icd 10 code for spondylolisthesis l4-l5
- 8. icd 10 code for history of renal stent
- 9. icd 10 cm code for brachial artery stenosis
- 10. icd-10-cm code for alzheimer's disease with delirium