What is the ICD 10 code for high blood pressure with heart disease?
Hypertension with Heart Disease: Hypertension with heart conditions classified to I50.- or I51.4- I51.9, should be assigned to a code from category I11, Hypertensive heart disease.
What is the ICD 10 code for hypertension with kidney disease?
Hypertension “with” ICD-10 Coding. Hypertensive Heart and Chronic Kidney Disease: The codes in category I13, Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease, are combination codes that include hypertension, heart disease and chronic kidney disease, and should be used when there is hypertension with both heart and kidney involvement.
What is the ICD 10 code for hypertension of the eye?
Essential hypertension affecting vessels supplying the eye with blood on the other hand will be represented by the ICD-10 codes H35.0 Hypertensive heart diseases with heart failure will be represented by the ICD-10 code I11.0; this will also be applicable for hypertensive heart failure.
What is the ICD 10 code for hypertensive emergency?
Hypertensive emergency. I16.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I16.1 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I16.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 I16.1 may differ.
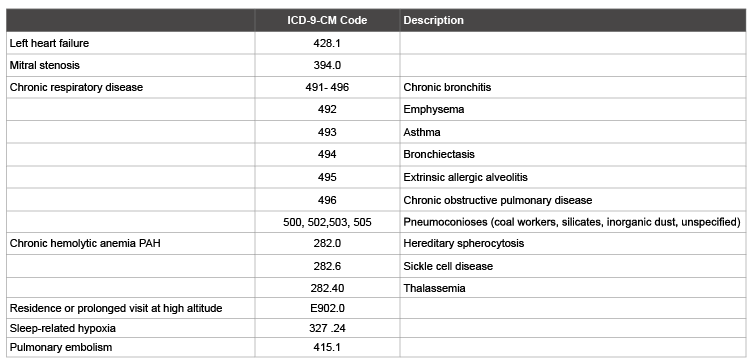
Is there a hypertension table in ICD-10?
In ICD-10, the diagnosis codes are simplified and the hypertension table is no longer necessary. The concept of controlled and uncontrolled are not a part of the coding choice, although good clinical documentation should include the status of the patient and the type of hypertension being treated.
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated blood pressure with hypertension?
That code is I10, Essential (primary) hypertension. As in ICD-9, this code includes “high blood pressure” but does not include elevated blood pressure without a diagnosis of hypertension (that would be ICD-10 code R03. 0).
What is the ICD-10-CM code for benign essential hypertension?
401.1 - Benign essential hypertension.
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated blood pressure without hypertension?
R03. 0: Elevated blood-pressure reading, without diagnosis of hypertension.
What is the CPT code for hypertension?
The two new codes—99473 and 99474—support home blood-pressure monitoring, which provides useful information physicians can use to better diagnose and manage hypertension.
How do you code controlled hypertension?
Essential (primary) hypertension (I10) ICD-10 uses a single code for individuals with HTN who do not have additional disorders like heart or kidney disease. Code I10 includes high blood pressure, but it does not include elevated blood pressure reading without a diagnosis of HTN.
What is unspecified hypertension?
It's also known as idiopathic or essential hypertension. Above-normal blood pressure is typically anything over 120/80 mmHg. This means that the pressure inside your arteries is higher than it should be.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a morbidity classification published by the United States for classifying diagnoses and reason for visits in all health care settings. The ICD-10-CM is based on the ICD-10, the statistical classification of disease published by the World Health Organization (WHO).
How do you code hypertension and heart failure?
Heart failure is assumed to be due to hypertension when coded using I11. 0, “Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure.” In ICD-10, the word “with” presumes a causal relationship between the two conditions linked by this term.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for hypertension due to prescription Albuterol?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R03. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R03.
What is a pathological increase in blood pressure?
Pathological increase in blood pressure; a repeatedly elevated blood pressure exceeding 140 over 90 mmhg.
When will the ICD-10-CM 2022 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I10 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Does high blood pressure cause heart failure?
High blood pressure usually has no symptoms. It can harm the arteries and cause an increase in the risk of stroke, heart attack, kidney failure, and blindness. A disorder characterized by a pathological increase in blood pressure; a repeatedly elevation in the blood pressure exceeding 140 over 90 mm hg.
What is the ICd 10 code for primary hypertension?
ICD Code 110 is a billable ICD-10-CM code that will be used to specify a diagnosis in relation to essential (primary) hypertension. ICD-10 codes 010, 011 and 013-016 in this case will be used to specify any hypertension complication affecting childbirth pregnancy and puerperium. Essential hypertension affecting vessels supplying the brain with blood will be represented by ICD-10 codes 160-169. Essential hypertension affecting vessels supplying the eye with blood on the other hand will be represented by the ICD-10 codes H35.0
What are the two types of hypertension?
There are two main types of hypertension, primary hypertension which has been known to grow gradually with time. The other one is known as secondary hypertension. Both types of hypertension are known to considerably hurt the arteries acting as a major cause for strokes, heart attacks, kidney failure and blindness.
What is the ICd 10 code for kidney disease?
ICD Code I12.0 in ICD-10 codes will be used to indicate hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 5 chronic kidney disease or end stage for renal disease. I12.9 on its part will represent Hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 1 through to stage 4.
How many people have hypertension?
The center for disease Control and prevention puts the number of Americans who suffer from hypertension at 67 million translating to 31% of all adults. It is estimated that more women than men suffer from Hypertensive condition with a high prevalence in people above the ages of 65.
When will ICD-10 replace ICd 9?
ICD-10-CM officially replaces ICD-9-CM on October 1 2014, therefore, Medical Billers or Medical coders can use 2014 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes for only training or planning purposes until then.
What is the difference between diastolic and systolic pressure?
One is considered to suffer from hypertension if his systolic pressure stands at more than 140mmHG while the diastolic pressure clocks a high of 90mmHg and more. Hypertension causes the heart to work harder to pump blood to the entire body which most of the time result in left sided heart failure.
What Is Controlled Hypertension
Controlled hypertension was defined as an average systolic blood pressure of less than 140 mm Hg and an average diastolic blood pressure of less than 90 mm Hg over two readings in people with hypertension, which is consistent with the definition in both the eighth Joint National Committee guideline.
Hypertension And Hypertensive Heart Disease: I11
When an individual has hypertension and heart disease, it is up to the provider to determine whether there is a causal relationship stated or implied. This relationship determination is spelled out in the Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting . 1
Hypertension And Chronic Kidney Disease: I12
Unlike hypertension and heart disease, where the provider must determine whether a causal relationship exists, if the patient has hypertension and develops chronic kidney disease, ICD-10 presumes a cause and effect relationship and classifies the condition as hypertensive chronic kidney disease.
Diseases Of The Circulatory Systemtype 2 Excludes
symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified
Q& a: Coding Headaches For Patients With Hypertension
Q: If a physician orders a consultation for a patient who is experiencing a headache due to hypertension, which ICD-10-CM codes would be assigned? Would hypertension be coded since headache is a common sign and symptom of hypertension, or would both the headache and hypertension be coded?
Example Of Hypertension And Heart Involvement
Patient is discharged with final diagnosis of exacerbated CHF, and a secondary diagnosis of hypertension. For this patient, CHF and hypertension would be coded as code I11.0, Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure since the causal relationship is assumed due to the word with following the main term in the Alphabetic Index under hypertension.
How Do You Code Borderline Hypertension
ICD-9-CM code 796.2 is assigned for elevated blood pressure without a diagnosis of hypertension and for transient or borderline hypertension. Once hypertension is established by a physician, a code from category 401 is assigned, with a fourth digit required: 0 for malignant, 1 for benign, and 9 for unspecified.
What is the I10 code for hypertension?
Essential hypertension, also known as arterial, benign, idiopathic, primary, or malignant hypertension, has no known or identified cause and is reported with code I10 as long as there are no associated and/or related causal relationships (e.g, heart disease).
What is the code for elevated blood pressure?
If the patient is pregnant, use the appropriate pregnancy codes (O13.- or O14.-) instead of code R03.0.
How is blood pressure measured?
Blood pressure is measured using a sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff with an attached gauge) and a stethoscope. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and documented as systolic over diastolic (e.g., 120/80 mmHg). Both systolic and diastolic pressures can indicate hypertension independently or together. The following table identifies five types of systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings and what they indicate.
What is the measurement of blood pressure when the heart contracts?
Hypertension Definitions . Blood pressure is the measurement of blood pressing on the blood vessel walls when the heart contracts, pushing blood through the arteries (systolic pressure) and when the heart is at rest between heart contractions when it is refilling with oxygenated blood (diastolic pressure).
What are the factors that contribute to high blood pressure?
There are many factors that can contribute to or cause high blood pressure and hypertension (e.g., tobacco use or exposure, obesity, stress, pregnancy) and several ICD-10-CM code categories to report them. Documentation is important for code selection in identifying these additional factors.
What is PHE in coding?
The COVID-19 public health emergency (PHE) has made it interesting and challenging for organizations to keep an eye on the evolving changes to the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting. Have you been keeping up with these changes?
Is hypertension linked to a condition?
The guidelines also state that “For hypertension and conditions not specifically linked by relational terms such as “with,” “associated with” or “due to” in the classification, provider documentation must link the conditions in order to code them as related.”
What is the code for heart failure?
Hypertensive Heart and Chronic Kidney Disease: The codes in category I13, Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease, are combination codes that include hypertension, heart disease and chronic kidney disease, and should be used when there is hypertension with both heart and kidney involvement. If heart failure is present, an additional code ...
Is hypertension a causal relationship?
When assigning diagnosis codes for hypertension (HTN), there is an presumed causal relationship between hypertension and heart involvement, and between hypertension and kidney involvement. The ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting (I.C.9) instruct, “These conditions should be coded as related even in the absence of provider documentation explicitly linking them, unless the documentation clearly states the conditions are unrelated.” The Guidelines further specify:
Can CKD be coded as hypertensive?
CKD should not be coded as hypertensive if the physician has specifically documented a different cause. The appropriate code from category N18 should be used as a secondary code with a code from category I12 to identify the stage of chronic kidney disease.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for l2 l3 discitis
- 2. icd 10 code for abnormal glutathione
- 3. icd 10 code for recurrent ovarian cancer
- 4. icd 10 code for right elbow ulnar collateral ligament tear
- 5. icd 10 code for peripheral edema
- 6. icd 10 code for routine eye exam
- 7. icd 9 code for chronic airway obstruction
- 8. icd 10 cm code for stage 4 endometriosis
- 9. icd 10 code for factor v leiden
- 10. icd 10 code for reverse shoulder arthroplasty