What is Procedure Code 10e0xzz?
- DRG 805 - VAGINAL DELIVERY WITHOUT STERILIZATION/D&C WITH MCC
- DRG 806 - VAGINAL DELIVERY WITHOUT STERILIZATION/D&C WITH CC
- DRG 807 - VAGINAL DELIVERY WITHOUT STERILIZATION/D&C WITHOUT CC/MCC
How would you treat a bacterial infection?
- Eat 2 cups of plain yogurt containing live cultures a day.
- Or, you can consult your doctor for taking probiotic supplements.
- Also, add other probiotic-rich foods to your daily diet to treat the bacterial infections.
What is the ICD 10 code for intra abdominal infection?
- NON-BILLABLE CODE - S36.892 for Contusion of other intra-abdominal organs
- BILLABLE CODE - Use S36.892A for initial encounter
- BILLABLE CODE - Use S36.892D for subsequent encounter
- BILLABLE CODE - Use S36.892S for sequela
- NON-BILLABLE CODE - S36.893 for Laceration of other intra-abdominal organs
- BILLABLE CODE - Use S36.893A for initial encounter
What is the ICD 10 code for Pseudomonas infection?
The ICD-10-CM code J15.1 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like bronchopneumonia due to pseudomonas or pneumonia due to pseudomonas. Index to Diseases and Injuries The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code(s).
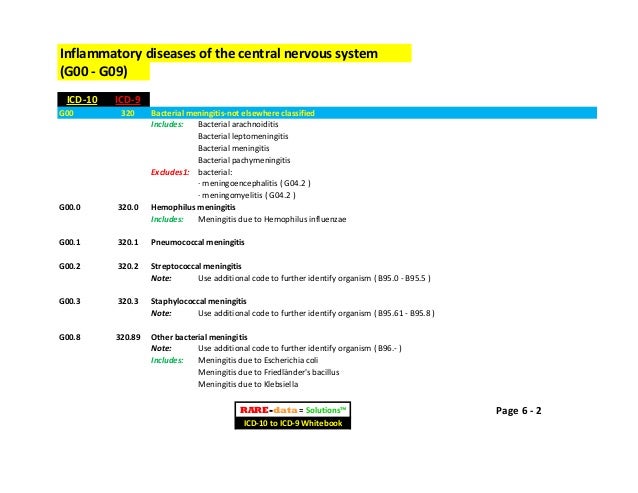
How do you code bacterial infections?
A49. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified infection?
A49. 9 - Bacterial infection, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What are 3 types of bacterial infections?
Bacteria can infect any area of the body. Pneumonia, meningitis, and food poisoning are just a few illnesses that may be caused by harmful bacteria. Bacteria come in three basic shapes: rod-shaped (bacilli), spherical (cocci), or helical (spirilla). Bacteria may also be classified as gram-positive or gram-negative.
What are 4 examples of bacterial infections?
Examples of bacterial infections include whooping cough, strep throat, ear infection and urinary tract infection (UTI).
What is the code for infected?
0016-0134-9061.
How do you code an infectious disease?
Common ICD-10 Codes for Infectious DiseaseB97.0. Adenovirus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere.B97.10. Unspecified enterovirus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere.B97.11. Coxsackievirus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere.B97.12. ... B97.19. ... B97.21. ... B97.29. ... B97.30.More items...
What are the names of bacterial infections?
Most Deadly Bacterial InfectionsTuberculosis.Anthrax.Tetanus.Leptospirosis.Pneumonia.Cholera.Botulism.Pseudomonas Infection.More items...
What is the most common bacterial infection?
Bacterial respiratory infections (and pneumonia) The most common cause is a pneumococcal infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae, although Staphylococcus aureus and Haemophilus influenzae can also cause it.
What is the most serious bacterial infection?
1. TuberculosisTuberculosis (TB) is one of the most Dangerous Bacteria on Earth. ... Additionally, it is due to the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). ... In addition to affecting other parts of the body.Most infections do not have symptoms, such as latent tuberculosis.More items...
What are 5 diseases caused by bacteria?
Other serious bacterial diseases include cholera, diphtheria, bacterial meningitis, tetanus, Lyme disease, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
What are the 2 classifications of bacteria?
There are broadly speaking two different types of cell wall in bacteria, that classify bacteria into Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. The names originate from the reaction of cells to the Gram stain, a long-standing test for the classification of bacterial species.
What is the difference between a bacterial infection and a viral infection?
Answer From Pritish K. Tosh, M.D. As you might think, bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, and viral infections are caused by viruses. Perhaps the most important distinction between bacteria and viruses is that antibiotic drugs usually kill bacteria, but they aren't effective against viruses.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for pseudogout right wrist
- 2. icd 10 code for achilles tendonitis bilateral
- 3. icd 10 code for abdomen fluid wet pocket
- 4. icd 10 code for etn
- 5. icd 10 code for benign neoplasm of hepatic flexure
- 6. icd 10 code for post surgical hypoparathyroidism
- 7. icd 10 code for animal bite
- 8. icd 10 code for diet controlled hyperlipidemia
- 9. icd 10 code for anxiety with agoraphobia
- 10. icd 10 code for nodule in right upper lobe