What ICD-10 code covers vitamin D deficiency?
E55. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What diagnosis will cover a vitamin D level?
The measurement of 25(OH) Vitamin D levels will be considered medically reasonable and necessary for patients with any of the following conditions: Chronic kidney disease stage III or greater. Hypercalcemia. Hypocalcemia.
What is the diagnosis code for Vitamin D 25 Hydroxy?
This test is appropriate for assessment of vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxy (CPT code 82652) is primarily indicated during patient evaluations for hypercalcemia and renal failure.
What is the deficiency disorder of vitamin D?
Rickets is a rare disease that causes the bones to become soft and bend. African American infants and children are at higher risk of getting rickets. In adults, severe vitamin D deficiency leads to osteomalacia. Osteomalacia causes weak bones, bone pain, and muscle weakness.
Why is vitamin D not covered by insurance?
Vitamin D testing is unproven and not medically necessary for routine preventive screening due to insufficient evidence of efficacy. Vitamin D testing is proven and medically necessary for conditions or medical diagnoses associated with Vitamin D deficiency or risk of hypercalcemia.
What is the difference between vitamin D and vitamin D3?
There are two possible forms of vitamin D in the human body: vitamin D2 and vitamin D3. Both D2 and D3 are simply called “vitamin D,” so there's no meaningful difference between vitamin D3 and just vitamin D.
Does Medicare pay for vitamin D level?
Medicare considers vitamin assay panels (more than one vitamin assay) a screening procedure and therefore, non-covered. Similarly, assays for micronutrient testing for nutritional deficiencies that include multiple tests for vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and various metabolic functions are never necessary.
Is vitamin D level covered by Medicare?
Do Medicare prescription drug plans cover vitamin D3? No. In general, Medicare prescription drug plans (Part D) do not cover this drug.
How often will Medicare pay for a vitamin D blood test?
Only one 1,25-OH vitamin D level will be reimbursed in a 24 hour period if medically necessary. Assays of vitamin D levels for conditions other than for Rickets, vitamin D deficiency, osteomalacia, and aluminum bone disease will be limited to once a year.
What are the 14 signs of vitamin D deficiency?
These include:Aching Muscles. Aching muscles can be a sign of vitamin D deficiency because this nutrient is essential for keeping your muscles healthy. ... Painful Bones. ... Fatigue. ... Reduced Endurance. ... Low Moods. ... Problems Sleeping Well. ... Sweaty Head. ... Losing Hair.More items...•
Does a vitamin D deficiency cause hair loss?
“Both vitamin D deficiency, as well as vitamin D excess, may cause hair loss,” Chacon explains. A 2020 study in the International Journal of Dermatology found that vitamin D deficiency may also play a role in the development and severity of androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness.
What causes vitamin D deficiency in older adults?
Risk factors contributing to vitamin D deficiency in older adults include reduced nutritional intake of vitamin D, increasing adiposity, decreased cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D, and less time spent outdoors (Table 1) [22, 21].
Does Medicare cover a vitamin D blood test?
For Medicare beneficiaries, screening tests are governed by statute. Vitamin D testing may not be used for routine screening. Once a beneficiary has been shown to be vitamin D deficient, further testing is medically necessary only to ensure adequate replacement has been accomplished.
What DX covers CPT 82306?
This notification is to inform you that for dates of service beginning June 1, 2016, for all commercial plans SelectHealth® will only cover CPT 82306 Vitamin D; 25 hydroxy, and CPT 82652 Vitamin D; 1, 25 dihydroxy consistent with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) guidelines, which provide coverage when ...
Can low vitamin D cause neurological symptoms?
Vitamin D is an important vitamin that plays a role in many different functions in the body. Vitamin D deficiency can cause a number of neurological problems, including fatigue, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating.
Does insurance cover vitamin D?
On average, a vitamin D deficiency test can cost $50, typically covered by health insurance.
What is the most infamous vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency may lead to a variety of disorders, the most infamous of which is rickets. Evaluating patients’ vitamin D levels is accomplished by measuring the level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Measurement of other metabolites is generally not medically necessary.
Why is vitamin D called a vitamin?
Vitamin D is called a “vitamin” because of its exogenous source, predominately from oily fish in the form of vitamin D2 and vitamin D3.
What is the Task Force on Vitamin D?
The Endocrine Society Task Force for Evaluation, Treatment and Prevention of Vitamin D deficiency (2011) recommended screening for vitamin D deficiency in individuals at risk for deficiency. The Task Force did not recommend population screening for vitamin D deficiency in individuals who are not at risk (high quality evidence).
How long does vitamin D last in the body?
A major source of vitamin D for most humans comes from exposure of the skin to sunlight typically between 1000 hours and 1500 hours in the spring, summer, and fall. Vitamin D produced in the skin may last at least twice as long in the blood compared with ingested vitamin D.
How much vitamin D3 should I take daily?
The USPSTF recommends against daily supplementation with 400 IU or less of vitamin D3 and 1,000 mg or less of calcium for the primary prevention of fractures in non-institutionalized postmenopausal women. (Grade: D Recommendation).
What happens if you don't take vitamin D?
Vitamin D deficiency results in abnormalities in calcium, phosphorus, and bone metabolism. Specifically, vitamin D deficiency causes a decrease in the efficiency of intestinal calcium and phosphorus absorption of dietary calcium and phosphorus, resulting in an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels.
What is the optimal clinical indicator of vitamin D metabolism?
II. Serum concentration of 25 hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) is the optimal clinical indicator of vitamin D metabolism due to the rapid conversion of vitamin D to 25 OHD with only a small fraction converted to 1,25 hydroxyvitamin D (1, 25 OHD).
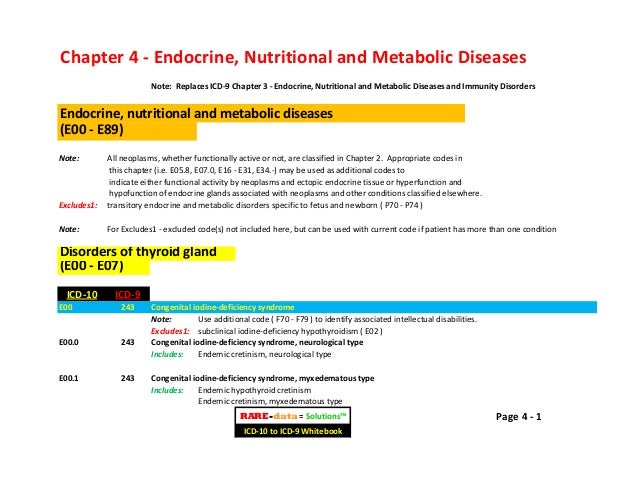
What is the ICD code for vitamin D deficiency?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code E55 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the two child codes of E55 that describes the diagnosis 'vitamin d deficiency' in more detail.
What is the cause of hypovitaminosis D?
It can result from inadequate nutritional intake of vitamin D and/or inadequate sunlight exposure (in particular sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays), disorders limiting vitamin D absorption, and conditions impairing vitamin D conversion into active metabolites —including certain liver, kidney, and hereditary disorders. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, leading to bone softening diseases as rickets in children and osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults. Emerging evidence suggests vitamin D plays a role in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Does vitamin D affect bone mineralization?
Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, leading to bone softening diseases as rickets in children and osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults. Emerging evidence suggests vitamin D plays a role in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Specialty: Endocrinology. MeSH Code:
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for postmenopausal hot flashes
- 2. what is icd 10 code for left uvj stone
- 3. icd 10 code for transgerder men routine gyn exam
- 4. icd 10 code for penile curvature
- 5. icd 10 code for squamous cell carcinoma of right tonsil
- 6. icd 10 code for intrauterine pregnancy 2nd trimester
- 7. what icd 10 code for compulsively talking
- 8. icd 10 code for postpartum visit
- 9. icd 10 code for aftercare following neoplasm
- 10. icd 10 cm code for cystitis with proteus