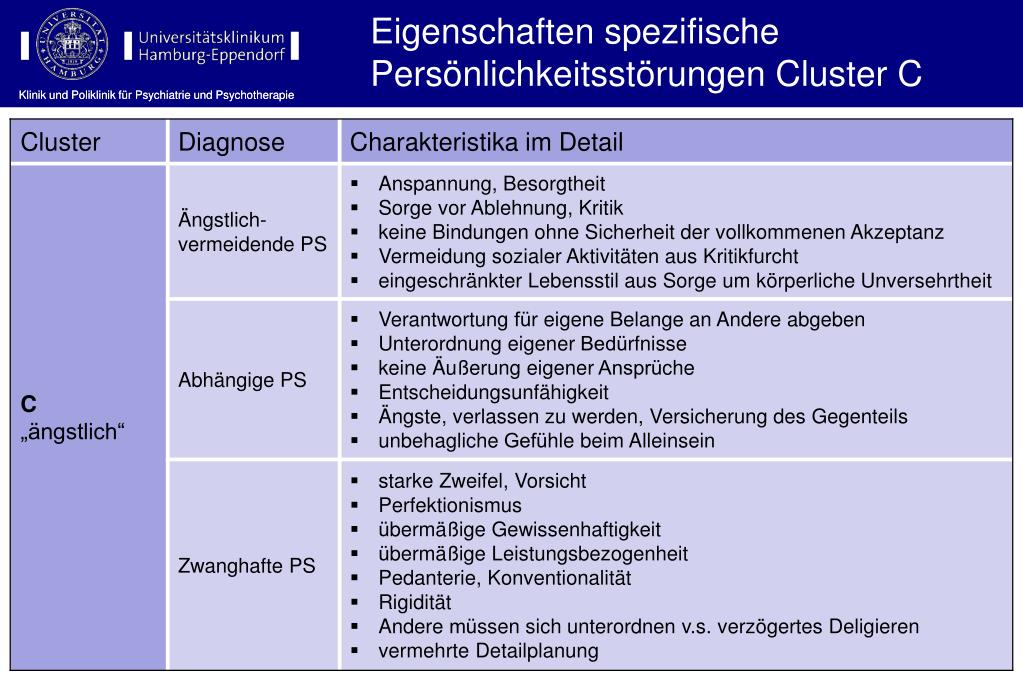
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic pulmonary coccidioidomycosis?
Chronic pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. B38.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for meningitis?
Coccidioidomycosis meningitis. B38.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is a fungal infection caused by Coccidioides immitis?
A fungal infection caused by coccidioides immitis. Affected individuals usually have mild flu-like symptoms. However, pneumonia and systemic involvement with the formation of abscesses may develop as complications of the disease. Infection with a fungus of the genus coccidioides, endemic to the southwestern United States.
What is chronic coccidioidomycosis?
Pulmonary coccidioidomycosis is an infection in the lungs caused by the fungus Coccidioides. Coccidioidomycosis is commonly called valley fever. You can get valley fever by inhaling spores from Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii fungi. The spores are so small that you cannot see them.
Is coccidioidomycosis the same as Valley fever?
Valley fever (also called coccidioidomycosis or “cocci”) is a disease caused by a fungus that grows in the soil and dirt in some areas of California and the southwestern United States.
What is coccidioidomycosis diagnosis?
The most common way that healthcare providers test for Valley fever is by taking a blood sample and sending it to a laboratory to look for Coccidioides antibodies or antigens. Healthcare providers may do imaging tests such as chest x-rays or CT scans of your lungs to look for Valley fever pneumonia.
Is coccidioidomycosis the same as Coccidioides?
Valley fever, also called coccidioidomycosis, is an infection caused by the fungus Coccidioides. The fungus is known to live in the soil in the southwestern United States and parts of Mexico and Central and South America.
What is the ICD 10 code for Valley fever?
Acute pulmonary coccidioidomycosis B38. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B38. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What's another name for Valley fever?
The scientific name for Valley fever is “coccidioidomycosis,” and it's also sometimes called “San Joaquin Valley fever” or “desert rheumatism.” The term “Valley fever” usually refers to Coccidioides infection in the lungs, but the infection can spread to other parts of the body in severe cases (this is called “ ...
What is coccidioidomycosis meningitis?
One of the most severe is coccidioidal meningitis, a form of disseminated infection. As with other forms of extrathoracic disseminated coccidioidal infection, Coccidioides appear to spread hematogenously after an initial pulmonary infection and establish a tissue-destructive lesion in the meninges.
Why is coccidioidomycosis called Valley fever?
Valley fever is caused by a person inhaling spores of certain fungi. The fungi that cause valley fever — Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii — live in the soil in parts of Arizona, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico, California, Texas and Washington. It's named after the San Joaquin Valley in California.
Is coccidioidomycosis an infection?
Coccidioidomycosis is not contagious, meaning it cannot be passed from person to person. Most people who get coccidioidomycosis have minimal symptoms and do not require treatment. Symptoms appear between one to three weeks after exposure and last a few weeks to a few months.
How is coccidioidomycosis transmitted?
Coccidioidomycosis is typically transmitted by inhalation of airborne spores of C immitis or C posadasii (see Etiology). Infection occurs in endemic areas and is most commonly acquired in the summer or the late fall during outdoor activities.
How do you get coccidioidomycosis?
Coccidioidomycosis is acquired by inhaling spores. Spores are present in soil and can become airborne in dust that can travel downwind. Thus, certain occupations (eg, farming, construction) and outdoor recreational activities increase risk.
How do you say coccidioidomycosis?
0:021:19How to Pronounce "Coccidioidomycosis" - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipCoccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosisMoreCoccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis coccidioidomycosis
Why is coccidioidomycosis called Valley fever?
Valley fever is caused by a person inhaling spores of certain fungi. The fungi that cause valley fever — Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii — live in the soil in parts of Arizona, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico, California, Texas and Washington. It's named after the San Joaquin Valley in California.
How is coccidioidomycosis transmitted?
Coccidioidomycosis is typically transmitted by inhalation of airborne spores of C immitis or C posadasii (see Etiology). Infection occurs in endemic areas and is most commonly acquired in the summer or the late fall during outdoor activities.
How do you get coccidioidomycosis?
Coccidioidomycosis is acquired by inhaling spores. Spores are present in soil and can become airborne in dust that can travel downwind. Thus, certain occupations (eg, farming, construction) and outdoor recreational activities increase risk.
Can Valley fever be cured?
Most people who have Valley fever will make a full recovery. A small percent of people develop long-term lung infections that can take several years to get better. In very severe cases of Valley fever, the nervous system can be affected and there may be long-term damage, but this is very rare.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for bee sting to forearm
- 2. icd 10 code for brca1 mutation
- 3. icd 10 code for pain right shoulder
- 4. icd code 10 for aki
- 5. icd 10 code for acute l-s strain
- 6. 2017 icd 10 code for microdiscectomy
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for nasal congestion
- 8. icd 10 code for diabetic ulcer lt 5th digit
- 9. icd 9 code for left total hip replacement
- 10. icd 10 code for mva during pregnancy