What are the early signs of pulmonary fibrosis?
- Symptoms: Discussing symptoms with your doctor is key to determining the severity of your PF. ...
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) or Lung Function Tests give your doctor important information about the amount of air the lungs can hold and how forcefully you can empty air from ...
- A six-minute walk test may be done to measure your exercise capacity.
How to diagnose pulmonary fibrosis?
a CT scan of your lungs, which uses X-rays to produce detailed images of your lungs. breathing and lung function tests to measure how well your lungs are working. blood tests. For some types of pulmonary fibrosis, the results from a CT scan can be very clear and allow a diagnosis to be made. On a CT scan, IPF often shows up as a distinctive ...
What is the ICD 10 code for fibrosis?
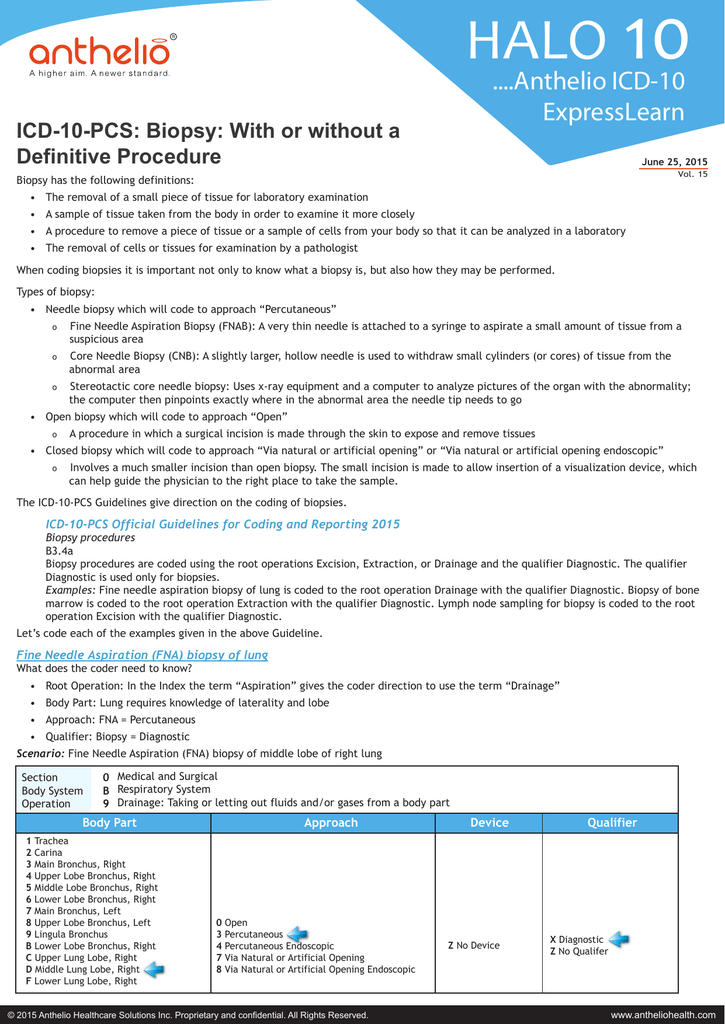
ICD-10-CM Code J84. 112. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Similarly, what is pulmonary fibrosis? Pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic and progressive lung disease where the air sacs in the lungs, called the alveoli, become scarred and stiff, making it difficult to breathe and get enough oxygen into the bloodstream.
What is diagnosis code 10?
What is an ICD-10 diagnosis code? The ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) is a system used by physicians and other healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
Is pulmonary fibrosis and COPD the same thing?
No, pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are not the same. However, they are similar in some ways. Pulmonary fibrosis and COPD are both lung diseases that get worse over time. Both conditions can make breathing difficult.
What is the CPT code for pulmonary fibrosis?
J84. 10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J84. 10 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the difference between lung fibrosis and pulmonary fibrosis?
To break it down phonetically: pulmonary means lung and fibrosis means scar tissue, so basically the name pulmonary fibrosis translates to 'scarring in the lungs. ' Beyond the problem scars present, pulmonary fibrosis impacts how you breathe and get oxygen into the blood.
What is the ICD-10 code for lung scarring?
Mayo Clinic defines Pulmonary Fibrosis as lung disease that occurs when lung tissue becomes damaged and scarred. If the scarring is an imaging finding then that will be integral to the actual condition of fibrosis, so only code J84. 10 will be needed.
What is pulmonary fibrosis unspecified?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that occurs when lung tissue becomes damaged and scarred. This thickened, stiff tissue makes it more difficult for your lungs to work properly. As pulmonary fibrosis worsens, you become progressively more short of breath.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
9 – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Unspecified.
What are the two types of pulmonary fibrosis?
There are two categories of NSIP: cellular and fibrotic. Fibrotic NSIP is the type that is associated with pulmonary fibrosis and occurs when the inflammation of the alveoli walls is accompanied by tissue thickening and scarring. Prognosis for both types of NSIP is usually very positive.
Is all lung scarring pulmonary fibrosis?
Some interstitial lung diseases don't include scar tissue. When an interstitial lung disease does include scar tissue in the lung, we call it pulmonary fibrosis.
What is the life expectancy of a person with pulmonary fibrosis?
A diagnosis of PF can be very scary. When you do your research, you may see average survival is between three to five years. This number is an average. There are patients who live less than three years after diagnosis, and others who live much longer.
Is pulmonary fibrosis an interstitial lung disease?
Interstitial lung disease refers to a group of about 100 chronic lung disorders characterized by inflammation and scarring that make it hard for the lungs to get enough oxygen. The scarring is called pulmonary fibrosis. The symptoms and course of these diseases may vary from person to person.
What causes pulmonary fibrosis?
Causes of pulmonary fibrosis include environmental pollutants, some medicines, some connective tissue diseases, and interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease is the name for a large group of diseases that inflame or scar the lungs. In most cases, the cause cannot be found.
What is the treatment for pulmonary fibrosis?
There are 2 medicines that can help slow down the progression of IPF in some people: pirfenidone and nintedanib. Some people also take a medicine called N-acetylcysteine, although its benefits are uncertain.
What is the code for emphysema?
Per Coding Clinic, a diagnosis of emphysema with acute exacerbation of COPD should be coded as J43.9. Categories J44 Other chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and J43 Emphysema include mutual Excludes1 notes; and emphysema without mention of chronic bronchitis falls into category J43. COPD is not synonymous with chronic bronchitis; therefore, COPD exacerbation with emphysema is reported J43.9, rather than a code from category J44.
What is the term for the loss of elastic lung recoil?
Emphysema is defined by Brunner and Suddarth’s Medical-Surgical Nursing (12 th edition) as excessive loss of elastic lung recoil. It’s a pathologic term that describes an abnormal distention of the air spaces beyond the terminal bronchioles and destruction of the walls of the alveoli.
Is J45.909 a type of asthma?
According to Coding Clinic, if COPD and asthma are unspecified in the documentation, J44.9 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, unspecified is sufficient: J45.909 Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated should not be added. “Unspecified” is not a type of asthma — as opposed to “mild intermittent,” “mild persistent,” “moderate persistent,” “severe persistent,” etc.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for fall due to rain
- 2. icd 10 code for dry needling
- 3. icd 10 code for ovarian cancer screening
- 4. icd 10 code for knee replacement status
- 5. icd 10 code meaning for adverse effect of correct penicillin properly administered
- 6. icd 9 code for paresthesia of arm
- 7. icd 10 code for burniing to feet
- 8. icd 10 code for recent tlif
- 9. what is icd-10 code for ocd
- 10. icd code for cholesterol