Common tests & procedures
F84 is based on this code under the ICD-10-CM system.Upon reviewing the patient’s medical record, a physician, psychologist or an equivalent diagnosis (typically used by payers) for the underlying mental illness (autistic disorder) can be deemed. What Are The 5 Autism Spectrum Disorders?
What is the ICD 10 code for autism spectrum disorder?
Autism Spectrum Disorder DSM-5 299.00 (F84.0) DSM-5 Category: Autism Spectrum Disorder
What is the DSM-5 category for autism spectrum disorder?
The DSM-V is now the standard reference that healthcare providers use to diagnose mental and behavioral conditions, including autism. You can read the full text of the new diagnostic criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and the related diagnosis of Social (Pragmatic) Communication Disorder (SCD) below.
What is the new DSM-V for autism?
Autism Spectrum Disorder 299.00 (F84.0) A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by the following, currently or by history (examples are illustrative, not exhaustive; see text):
What is autistic spectrum disorder (ASD)?
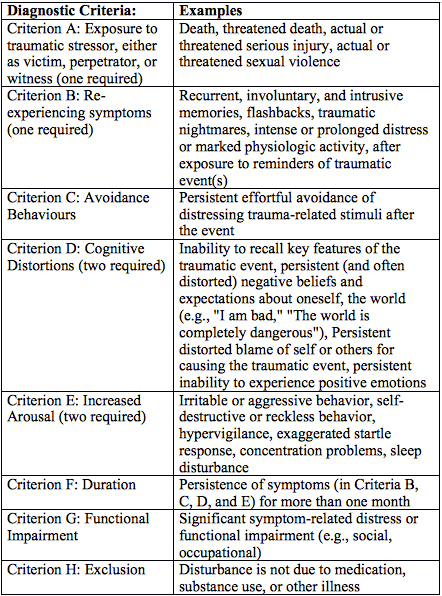
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for autism?
The ICD-10-CM code for ASD—F84. 0 (autistic disorder)—should be the physician's or psychologist's diagnosis (typically required by payers) of the underlying medical condition, documented in the patient's medical record.
What is the DSM-5 code for autism spectrum disorder?
0)
What is the difference between DSM-5 and ICD-10 with autism?
A single diagnosis: Autism spectrum disorder. In ICD-10, the 'spectrum' is divided into three subtypes. DSM-5 has relinquished subtypes such as Asperger in favour of a single continuous spectrum, reflecting the variability of symptoms and how they are expressed.
What is the ICD-11 code for autism?
6A02 Autism spectrum disorder - ICD-11 MMS.
How do you code autism?
Autism is assigned to ICD-9-CM code 299.0. A fifth digit subclassification is required as follows: 299.00, Current or active state; or 299.01, Residual state.
What is the CPT code for autism spectrum disorder?
The CPT code for both general developmental screening and for autism screening is 96110. Therefore, when deriving quality metrics from claims or from a practice EHR, it has not been possible to distinguish which screen has been used.
Why did the DSM change autism?
The rationale for this change is that these disorders have the same essential symptoms, but at varying degrees of severity. According to the APA, they are best thought of as a single disorder on a wide spectrum.
How is autism spectrum disorder diagnosed?
Diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can be difficult because there is no medical test, like a blood test, to diagnose the disorder. Doctors look at the child's developmental history and behavior to make a diagnosis. ASD can sometimes be detected at 18 months of age or younger.
What is the difference between ICD-11 and DSM-5?
Results. Both systems take an anosological approach and base the classification of mental disorders on psychopathology, which takes centerstage in the clinical evaluation for classification purposes. A major difference is the role of functional impairments, which are mandatory in DSM-5, but not ICD-11.
What does ICD-11 stand for?
18 June 2018 ¦ Geneva: The World Health Organization (WHO) is today releasing its new International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). The ICD is the foundation for identifying health trends and statistics worldwide, and contains around 55 000 unique codes for injuries, diseases and causes of death.
What is the difference between ICD-10 and ICD-11?
Coding Structure In terms of general improvements, the ICD-11 has a more sophisticated structure than the ICD-10. With around 55,000 codes that can be used to classify diseases, disorders, injuries, and causes of death, the ICD-11 offers a fine level of detail in coding these illnesses.
What is the DSM-5?
The DSM-5 is now the standard reference that healthcare providers use to diagnose mental and behavioral conditions, including autism. By special permission of the American Psychiatric Association, ...
How to contact Autism Response Team?
There are no available agents at the moment. You can also reach the Autism Response Team by phone or email: 888-288-4762, en Espanol 888-772-7050, or [email protected].
What are nonverbal communication deficits?
Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction, ranging, for example, from poorly integrated verbal and nonverbal communication; to abnormalities in eye contact and body language or deficits in understanding and use of gestures; to a total lack of facial expressions and nonverbal communication.
What is autism spectrum disorder?
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a developmental disorder in which the person affected exhibits impaired development in communication, interaction with others, and in. behavior (Dryden-Edwards, 2014). People suffering from this class of disorders may show a wide range of symptoms, deficits in skills, and levels of impairment.
When should a child be diagnosed with autism?
A child with delayed or regressed language and/or social interaction prior to age 3 should be considered for the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder (Dryden-Edwards, 2014). A complete medical history and physical exam begin the process of diagnosis.
What are the most common issues with autism?
Respiratory problems are more likely to be experienced. Emotional issues such as anxiety, depression and attention problems are struggles for those diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. Working to understand, accept, and prepare for the difficulties of caring for and living with an Autism Spectrum Disorder.
What are the two areas of the DSM-5?
There are two general areas in which symptoms are found. These are social impairment, especially communication, and behavior. In this latter area, repetitive. behaviors are most often seen. The DSM-5 has specific symptoms listed in both of these areas (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
Can autism be diagnosed?
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a complex disorder that may not be accurately diagnosed until the child has exhibited some of the symptoms of the disorder for quite. some time. Parents often see the symptoms in their children but believe the child will catch up developmentally to peers.
Can a pediatrician use the CHAT to predict autism?
However, adaptations that overcome this bias have been developed. In any case, pediatricians can use items on the CHAT that predict development of autism in their well-baby checkups. Cultural differences can have an impact on the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, also (Brasic, 2014).
Can autism be treated with medication?
Treatment. At this time, there are no medications that either cure autism spectrum disorder or effectively treat the core symptoms (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014). However, some medications are effective for helping these patients function better in some life areas.
What is autism in childhood?
Developmental delays in social interaction and language surface prior to age 3 years. Autism is a disorder that is usually diagnosed in early childhood.
What are the symptoms of autism?
The main signs and symptoms of autism involve communication, social interactions and repetitive behaviors. Children with autism might have problems talking with you, or they might not look you in the eye when you talk to them.
Is autism a spectrum disorder?
They often seem to be in their "own world."because people with autism can have very different features or symptoms, health care providers think of autism as a "spectrum" disorder. asperger syndrome is a milder version of the disorder.the cause of autism is not known. Autism lasts throughout a person's lifetime.
What is autism spectrum disorder?
Autism spectrum disorder and autism are terms used to refer to complication in the development of the brain, beginning in childhood. The disorders are normally characterized by the difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication. Autism symptoms include the presence of markedly abnormal or impaired development in social ...
What are the manifestations of autism?
The Autistic spectrum disorder is associated with difficulties in motor coordination, as well as physical health issues associated with sleep and gastrointestinal disturbance.
What is atypical autism?
Atypical autism arises most often in profoundly retarded individuals and in individuals with a severe specific developmental disorder of receptive language.
Why do autistic children increase?
The exact cause of autism is not known but the main reason for this common type of mental condition is gene mutation, as well as environmental factors that influence early brain development.
Can autistic children talk?
Children with autism might have problems talking with you, or they might not look you in the eye when you talk to them. They may spend a lot of time putting things in order before they can pay attention, or they may say the same sentence, again and again, to calm themselves down.

Introduction
Symptoms
Onset
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- There are two general areas in which symptoms are found. These are social impairment, especially communication, and behavior. In this latter area, repetitive behaviors are most often seen. The DSM-5 has specific symptoms listed in both of these areas (American Psychiatric Association, 2013). Social communication and interaction must occur across several aspects o…
Living with Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Autism Spectrum Disorder is a complex disorder that may not be accurately diagnosed until the child has exhibited some of the symptoms of the disorder for quite some time. Parents often see the symptoms in their children but believe the child will catch up developmentally to peers. Many times, parents will see normal development in the first year of life, then begin seeing less norma…
Help Us Improve This Article
- Early diagnosis is critical to the efforts to lessen the impact of Autism Spectrum Disorder. A child with delayed or regressed language and/or social interaction prior to age 3 should be considered for the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder (Dryden-Edwards, 2014). A complete medical history and physical exam begin the process of diagnosis. Formal hearing evaluation is recomm…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for knee hyperextension newborn
- 2. icd 10 code for l posterior hip pain
- 3. icd 10 code for valvular heart disease unspecified
- 4. icd code for tobacco use
- 5. icd 10 code for left lower dvt
- 6. icd 10 code for cholecystitis with gangrenous
- 7. icd 9 code for defibrillator
- 8. icd 10 code for m24621
- 9. icd 10 cm code for intertrigo candidal
- 10. icd 10 code for vaginal sling