What is the ICD 10 code for gallbladder and bile duct?
Calculus of gallbladder and bile duct with acute and chronic cholecystitis without obstruction. K80.66 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for gallbladder calcification?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K80.66 K80.66 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Calculus of GB and bile duct w ac and chr cholecyst w/o obst
What is the ICD 10 code for CHR cholecyst?
K80.66 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Calculus of GB and bile duct w ac and chr cholecyst w/o obst The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM K80.66 became effective on October 1, 2019.
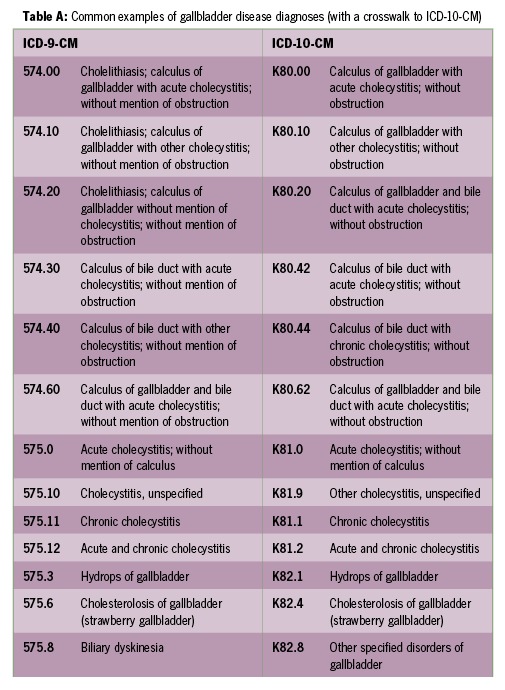
What is Calculus of gallbladder and bile duct?
From there, bile moves down the common bile duct and enters your small intestine. Sometimes this process is inhibited and bile builds up inside your gallbladder, causing it to become larger and inflamed. This buildup can lead to the creation of gallstones, or gallbladder calculi.
What is the ICD-10 code for Cholecystolithiasis?
ICD-10 code K80 for Cholelithiasis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD-10 code for Calculus of gallbladder with cholecystitis?
ICD-10 Code for Calculus of gallbladder with acute cholecystitis without obstruction- K80. 00- Codify by AAPC.
What is Calculous cholecystitis?
Calculous cholecystitis is the most common, and usually less serious, type of acute cholecystitis. It accounts for around 95% of all cases. Calculous cholecystitis develops when the main opening to the gallbladder, the cystic duct, gets blocked by a gallstone or a substance known as biliary sludge.
What is Calculus of gallbladder without cholecystitis without obstruction ICD-10?
ICD-10-CM Code for Calculus of gallbladder without cholecystitis without obstruction K80. 20.
What is the correct code for Calculus of the bile duct with chronic cholangitis with obstruction?
K8035K8000Calculus of gallbladder with acute cholecystitis without obstructionK8034Calculus of bile duct with chronic cholangitis without obstructionK8035Calculus of bile duct with chronic cholangitis with obstructionK8036Calculus of bile duct with acute and chronic cholangitis without obstruction68 more rows
What are ICD-10 combination codes?
What are ICD-10 Combination Codes? ICD-10 combination codes allow payers to report a single code which includes multiple characteristics of the diagnosis. In 2019, there were 279 new codes, 143 revised codes, and 51 deleted codes released by CMS and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS).
What K80 20?
ICD-10 code: K80. 20 Calculus of gallbladder without cholecystitis Without mention of obstruction of biliary tract.
Is K80 10 a dual code?
Cholelithiasis with chronic cholecystitis without obstruction (K80. 10) is an example of a dual code.
What is the difference between calculous and acalculous cholecystitis?
Acalculous cholecystitis has a slight male predominance, unlike calculous cholecystitis, which has a female predominance. The condition can occur in persons of any age, although a higher frequency is reported in persons in their fourth and eighth decades of life.
Is cholelithiasis the same as cholecystitis?
Cholelithiasis and cholecystitis both affect your gallbladder. Cholelithiasis occurs when gallstones develop. If these gallstones block the bile duct from the gallbladder to the small intestine, bile can build up in the gallbladder and cause inflammation. This inflammation is called cholecystitis.
What is cholecystitis without calculus?
Definition. Inflammation of the gallbladder in the absence of gallstones. [
How is calculous cholecystitis treated?
TreatmentFasting. You may not be allowed to eat or drink at first in order to take stress off your inflamed gallbladder.Fluids through a vein in your arm. This treatment helps prevent dehydration.Antibiotics to fight infection. ... Pain medications. ... Procedure to remove stones.
What causes chronic calculous cholecystitis?
Most of the time, chronic cholecystitis is caused by repeated attacks of acute (sudden) cholecystitis. Most of these attacks are caused by gallstones in the gallbladder. These attacks cause the walls of the gallbladder to thicken. The gallbladder begins to shrink.
Can cholecystitis be treated without surgery?
In some recent studies, nonsurgical treatments such as PC can be a lifesaving alternative in patients with comorbidities. In the present study, 48 (53.9%) patients underwent cholecystectomy while 41 (46.1%) patients were treated with non-surgical methods including PC or antibiotics only.
What is the main cause of cholecystitis?
Most often, cholecystitis is the result of hard particles that develop in your gallbladder (gallstones). Gallstones can block the tube (cystic duct) through which bile flows when it leaves the gallbladder. Bile builds up, causing inflammation. Tumor.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for fracture of right thumb
- 2. icd 9 code for transmetatarsal amputation
- 3. icd 10 code for divarication of recti
- 4. icd 10 code for 5th metatarsal fracture
- 5. icd 10 cm code for basal cell carcinoma forehead
- 6. what is icd 10 code for chlamydial inflammation of the testis
- 7. icd 9 code for parethesia of skin
- 8. icd 10 code for right midshaft fx ulna
- 9. icd 10 code for hereditary progressive muscular dystrophy:
- 10. icd 10 code for right middle cerebral artery stenosis