What does steatohepatitis mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (non-AL-kuh-HAW-lik STEE-uh-toh-HEH-puh-TY-tis) A type of liver disease in which fat builds up in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol. This causes inflammation of the liver and damage to the cells in the liver, which may lead to cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) and liver failure ...
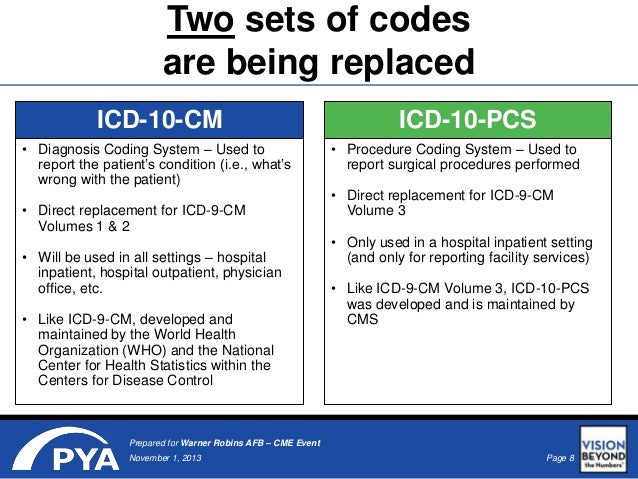
What is the ICD 9 code for fatty liver?
[18] NAFLD is traditionally billed using ICD-9 codes 571.8, 'other chronic nonalcoholic liver disease' or 571.9, 'unspecified chronic liver disease without alcohol'.
What causes non alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver?
NAFLD and NASH are both linked to the following: Overweight or obesity. Insulin resistance, in which your cells don't take up sugar in response to the hormone insulin. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia), indicating prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
What is ICD-10 code for fatty liver?
ICD-10 code K76. 0 for Fatty (change of) liver, not elsewhere classified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic liver disease?
ICD-10-CM Code for Liver disease, unspecified K76. 9.
What is the ICD-10 code for liver failure?
Hepatic failure, unspecified without coma K72. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K72. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How long can you live with nonalcoholic cirrhosis of the liver?
Survival and mortality The median survival was 24.2 (range 0.2-26.1) years in the NAFLD group and 19.5 (range 0.2-24.2) years in the AFLD group (p = 0.0007). Median follow-up time for the non-alcoholic group was 9.9 years (range 0.2-26 years) and 9.2 years (0.2-25 years) for the alcoholic group.
Where do you itch with liver problems?
Itching associated with liver disease tends to be worse in the late evening and during the night. Some people may itch in one area, such as a limb, the soles of their feet, or the palms of their hands, while others experience an all-over itch.
How long do you have to live with cirrhosis of the liver?
A liver biopsy may be the only way to confirm a diagnosis of cirrhosis. Median survival in patients with compensated cirrhosis is approximately nine to 12 years.
What causes fatty liver?
Eating excess calories causes fat to build up in the liver. When the liver does not process and break down fats as it normally should, too much fat will accumulate. People tend to develop fatty liver if they have certain other conditions, such as obesity, diabetes or high triglycerides.
What is the ICD 10 code for obesity?
ICD-Code E66* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Overweight and Obesity. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 278.
What is the CPT code for fatty liver?
402205: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Advanced Fibrosis Rule-Out Cascade | Labcorp. For hours, walk-ins and appointments.
ICD-10 Equivalent of 571.8
As of October 2015, ICD-9 codes are no longer used for medical coding. Instead, use the following two equivalent ICD-10-CM codes, which are an approximate match to ICD-9 code 571.8:
Historical Information for ICD-9 Code 571.8
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
Not Valid for Submission
571.8 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other chronic nonalcoholic liver disease. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Convert 571.8 to ICD-10
The following crosswalk between ICD-9 to ICD-10 is based based on the General Equivalence Mappings (GEMS) information:
Information for Patients
Your liver is the largest organ inside your body. It helps your body digest food, store energy, and remove poisons.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
ICD-10 Equivalent of 571
As of October 2015, ICD-9 codes are no longer used for medical coding. Instead, use this equivalent ICD-10-CM code, which is an exact match to ICD-9 code 571:
Historical Information for ICD-9 Code 571
Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for std screen
- 2. icd 10 code for amyloid cardiomyopathy
- 3. when coding two codes for icd diagnosis which code goes first
- 4. icd 10 code for easy bruising
- 5. icd 10 code for benign prostatic hypertrophy with urinary obstruction
- 6. icd 10 code for rectal erythema
- 7. icd 10 code for enchinococcus grandulosus infection, other sites
- 8. icd 10 code for post-tonsillectomy pain
- 9. icd 10 code for chronic obstructive lung disease
- 10. icd 10 code for scoliosis cervical spine